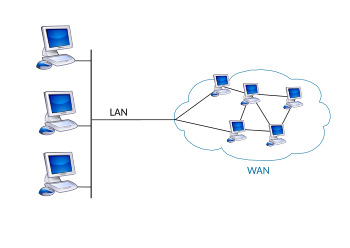
Wide area network
A wide area network, or WAN (wide area network in English), is a computer network that joins and interconnects several networks of smaller geographic scope, for example local area networks, even if their members are not all in the same physical location. Many WANs are built by organizations or companies for their private use, others are installed by Internet Service Providers (ISPs) to provide connection to their customers.
Today, the Internet provides high-speed connections, so a high percentage of WANs are based on that medium, reducing the need for private WANs, while virtual private networks that use encryption and other techniques to generate a dedicated network over Internet communications.
Definition
WANs do not necessarily have to be connected to LANs. For example, you might have a localized skeleton of a WAN technology, which connects different LANs within a campus. This could be to facilitate higher bandwidth applications, or provide better functionality for users.
WANs are used to connect LANs and other types of networks. So users can communicate with users and computers in other places. Many WANs are built by a particular organization and are private. Others, built by Internet service providers, that provide LAN connections to an Internet organization. WANs are often built using leased lines. At each end of the leased line, a router connects the LAN on one side to a second router within the LAN on the other. Leased lines can be very expensive. Instead of using leased lines, WANs can also be built using less expensive circuit-switched or packet-switched methods. The network protocols including TCP/IP have the transport delivery function and addressing functions. Protocols, including packets such as SONET/SDH, MPLS, ATM, and Frame Relay are often used by service providers that offer the links used in WAN networks. X.25 was soon a major WAN protocol, and is often considered the "grandfather" of Frame Relay since many of the underlying protocols and functions of X.25 are still in use today (with updates) by Frame Relay.
Academic research on wide area networks can be divided into three areas: mathematical modeling, network emulation, and network simulation.
Performance improvements are sometimes delivered through wide area file services or WAN optimization services.
Connection Technology Options
There are several options available for WAN connectivity:
| Option: | Description | Advantages | Disadvantages | Bandwidth range | Sample protocols used |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Line dedicated | Peer-to-peer connection between two computers, or local area networks (LAN) | The safest | Caro | PPP HDLC SDLC HNAS | |
| Circuit switching | A dedicated circuit path is created between the final points. Your best example is phone access connections. | The cheapest | Call configuration | 28-144 kbit/s | PPP RDSI |
| Package switching (connected by connection) | Transport package devices through a single line of point-to-point link point to multipoint or through an internal support network. Before you can exchange information between two endpoints, first establish a virtual circuit. Variable length packages are transmitted through permanent virtual circuits (PVC) or switched virtual circuits (SVC) | Media shared through link | X.25 Frame-Relay | ||
| Package switching (without connection) | Device transport packages through a single point-to-point-link sharing point to multipoint or through an internal support network. Packages of variable length are transmitted. Between the unconnected endpoints is the accumulation; endpoints can only offer packages to the network, address any other end point and the network will try to deliver the package. As an example: Internet works this way. | Very robust and low operating cost | Media shared through link | IPv4 IPv6 | |
| Cell switching | It is the same as in package switching, but uses fixed-length cells instead of variable-length packages. Data are divided into fixed-length cells, and then transported through virtual circuits. | Before 2000, this was seen as the best option for simultaneous use of voice and data. With high link speeds in modern networks, this advantage is meaningless. | The overhead can be considerable. | ATM (Asynchronous Transfer Mode) |
Transmission rates have increased over time, and will continue to increase. Around 1960 110 bits/s (bits per second) of the line was normal at the edge of the WAN, while core links from 56 kbit/s to 64 kbit/s were considered 'fast'. At this time (2016) homes are connected to the Internet with ADSL or Fiber Optic at speeds ranging from 1 Mbit/s to 600 Mbit/s, and connections at the core of a WAN can vary from 1 Gbit/s to 300 Gbit/s.
Recently, with the proliferation of low-cost Internet connections, many companies and organizations have turned to VPNs to interconnect their networks, thus creating a WAN network. Companies like Citrix, Cisco, New Edge Networks, and Check Point offer solutions for creating VPN networks.
Features
- It has machines dedicated to the execution of user programs (hosts).
- A sub-net, where they connect several hosts.
- Division between transmission lines and switching elements (routers).
- It is a system of interconnection of geographically dispersed computer equipment, which can even be on different continents. The connection system for these networks normally involves public data transmission networks.
Advantages of the WAN network
- It allows you to use special software so that minicomputers and macrocomputers coexist among your network elements.
- It is not limited to specific geographical spaces.
- It offers a wide range of means of transmission, such as links satellites.
- Provide greater security by having real-time access control.
- It provides simplified administration.
- It gives priority to connections to critical applications, regarding non-critical applications.
- It presents the possibility of establishing the service without changing existing networks.
Disadvantages of WAN network
- Equipment with a high memory capacity should be used, as this factor has a direct impact on the speed of access to information.
- It does not stand out for the security it offers its users. Viruses and program elimination are two of the most common evils suffered by the WAN network.
Types of WAN networks
There are several types of WAN networks, and three of them are grouped under the switched network classification (in physics, switching consists of changing the destination of a signal or an electric current):
By circuits
They are dial-up networks, such as the basic telephone network (PSTN) and ISDN. During the duration of the call, the bandwidth is dedicated.
By message
Their switches are usually computers that fulfill the task of accepting the traffic of each terminal that is connected to them. Such equipment evaluates the address found in the message header and can store it for later use. It is worth mentioning that it is also possible to delete, redirect and reply to messages automatically.
By packages
Each message sent by users is divided and transformed into a number of small parts called packets, which are reunited once they reach the destination computer, to reconstruct the initial data. These packets move through the network independently, and this has a positive impact on traffic, as well as facilitating error correction, since in case of failures only the affected parts should be resent. Bandwidth is shared among all users using the network.
Router topology
Router topologies in a wide area network:
- Star
- Ring
- Tree
- Complete mall
- Ring intersection
- Irregular mesh
Examples
- A national banking network: Bank branches of a country are managed through a vast network and in connection with
other banks and even with banks abroad. Each of these networks is a WAN that allows a user to withdraw money at an ATM on the other side of the country, or even in a country different.
- Transnational corporate networks: The great business franchises that have a presence in different countries of the world,
they keep their workers in communication through an exclusive WAN of the company, so so that they can exchange information and stay in permanent contact despite be in different countries.
- Internet:The best example of WAN available is the Internet, able to communicate various devices
technologies over enormous distances, even from one side of the world to the other.
- Education: It favors digital transformation in order to enrich learning experiences. Providing efficient and secure networks to meet the needs of users.
Contenido relacionado
Torpedo
Principal memory
Highway