Unit of length
A unit of length is a standardized amount of length defined by convention. Length is a fundamental quantity created to measure the distance between two points. There are various systems of units for this physical quantity; the most commonly used are the International System of Units and the Anglo-Saxon system of units.
History
Traditionally, ancient societies used the dimensions of the human body as a reference system to measure length. Examples of this were the inch, defined as the width of a thumb; the foot, defined as the length of a human foot; the yard, which was the distance from the tip of the nose to the tip of the middle finger at arm's length; the fathom, which corresponded to the distance from tip to tip between the middle fingers with the arms extended; the span, which was the length of the palm of the hand; and the elbow, approximately the length of the forearm.
In Ancient Rome, units of length were defined for greater distances. The mile was defined as the distance covered by a Roman legion in taking 2,000 steps. One mile was equal to eight stadia and three miles were approximately one league.
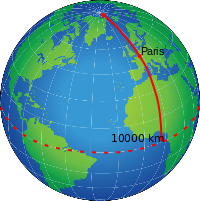
For centuries each nation defined its own units of length; in most cases, two units called the same in different countries represented different longitudes. This induced the need to define a standard of universal length, that is, based on physical phenomena accessible anywhere in the world. In 1670, the astronomer and religious Gabriel Mouton proposed the length of a minute of arc of a meridian of the Earth as a standard of measurement. Based on this idea, in 1790, during the French Revolution, the National Assembly decided to define a unit of length as one ten-millionth of the distance from the North Pole to the equator, along the meridian that passes through Dunkirk and Barcelona. This unit came to be known as "meter" and would be subdivided into parts of ten; in this way the decimal metric system would arise. In 1960, the definitions of the units of the metric system were revised and the name International System of Units was adopted for the modern version of the system.
International System of Units
In the International System of Units the fundamental unit of length is the meter, defined as the distance that light travels in a vacuum during an interval of 1/299 792 458 of a second. The symbol for the meter is "m », never admitting plural, capital letter or period, as it is not an abbreviation.
Multiples and submultiples of the meter
Using the SI prefixes it is possible to define units of length that are multiples or submultiples of the meter. Listed below are the multiples and submultiples of the meter, accepted within the SI, along with its symbol and its equivalence in meters, in scientific and decimal notation.
| Symbol | Name | Metros | Metros |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ym | Yottametro | 1024 | 1 000 000 000 000 000 000 000 |
| Zm | zettametro | 1021 | 1 000 000 000 000 000 000 |
| Em | Diameter | 1018 | 1 000 000 000 000 000 000 |
| Pm | petameter | 1015 | 1 000 000 000 000 000 |
| Tm | Thermal | 1012 | 1 000 000 000 000 |
| Gm | gigameter | 109 | 1 000 000 000 |
| Mm. | meter | 106 | 1 000 |
| km | kilometer | 103 | 1 000 |
| hm | hectometer | 102 | 100 |
| dam | decameter | 101 | 10 |
| Symbol | Name | Metros | Metros |
|---|---|---|---|
| dm | decimeter | 10-1 | 0.1 |
| cm | centimeter | 10-2 | 0.01 |
| mm | millimeter | 10-3 | 0.001 |
| μm | micrometer | 10-6 | 0,000 001 |
| nm | nanometer | 10-9 | 0,000 000 001 |
| pm | picometer | 10-12 | 0,000 000 000 001 |
| fm | femometer | 10-15 | 0,000 000 000 000 001 |
| am | Attometer | 10-18 | 0,000 000 000 000 000 001 |
| zm | zeptometer | 10-21 | 0,000 000 000 000 000 000 000 001 |
| ym | Yoctometer | 10-24 | 0,000 000 000 000 000 000 000 000 001 |
Unofficial multiples and submultiples in the SI
There are some multiples and submultiples of the meter that are not officially part of the International System of Units. These are:
| Symbol | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Å | Angstrom | Equivalent to 10-10m or 100 pm is used in spectroscopy to measure the wavelength of X-rays. |
| Ma | Miriameter | Equivalent to 10 000 m or 10 km, now considered obsolete in the metric system. |
| Micra | Common name obsolete for micrometer (μm). | |
| Fermi | Equivalent to 1 fm, used before the definition of SI prefixes. | |
| Unit X | Used for measuring the wavelength of X-rays and gamma rays. It is approximately 100 fm. |
Anglo-Saxon system of units
| 1 league | 3 miles | 24 furlong | 240 chains | 960 rods | 5280 yards | 15 840 feet | 190 080 inches | 1.9008x108 thousands | 4,828032 km |
| 1 mile | 8 furlongs | 80 chains | 320 rods | 1 760 yards | 5 280 feet | 63 360 inches | 6,336x107 thousands | 1,609344 km | |
| 1 furlong (stage) | 10 chains | 40 rods | 220 yards | 660 feet | 7 920 inches | 7.92x106 thousands | 201,168 m | ||
| 1 chain | 4 rolls | 22 yards | 66 feet | 792 inches | 792 000 | 20,1168 m | |||
| 1 roll (vara) | 5.5 yards | 16.5 feet | 198 inches | 198 000 | 5,0292 m | ||||
| 1 yard | 3 feet | 36 inches | 36 000 000 | 0,9144 m | |||||
| 1 foot | 12 inches | 12 000 | 30,48 cm | ||||||
| 1 inch | 1 000 000 | 2.54 cm | |||||||
| 1 000 | 0.0254 mm |
Nautical system
| 1 degree of latitude | 20 nautical leagues | 60 nautical miles | 607,5 cables | 60 750 fathoms | 121 500 yards | 364 500 feet | 111,0996 km |
| 1 nautical league | 3 nautical miles | 30,375 cables | 3 037.5 fathoms | 6 075 yards | 18 225 feet | 5 558 meters | |
| 1 mile nautical | 10 cables | 1 012,6859 fathoms | 2 025,372 yards | 6 076,115 feet | 1 852 meters | ||
| 1 cable | 100 fathoms | 200 yards | 600 feet | 182.88 metres | |||
| 1 fathom (chuckles) | 2 yards | 6 feet | 1,82886 meters | ||||
| 1 yard | 3 feet |
Astronomical units
| Symbol | Name | m |
|---|---|---|
| UA | Astronomical unit | 1,495979·1011 |
| ly | light year | 9,46052840488·1015 |
| pc | parasect | 3,08568·1016 |
Contenido relacionado
Projective module
Decimal
Ξ