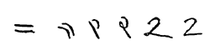Two
The two (2) is the natural number that follows one and precedes three.
Mathematical properties
- The lower cardinal body contains two elements.
- It is the smallest value that cancels the Mertens Function.
- It is the characteristic of Euler for the polyhedrons.
- It is the basis of the simplest numbering system in which natural numbers can be consistently written, the binary system, used mainly in machine language.
- It's the base of the binary logarithm.
- Together with one are the only numbers that are equal to their factorial.
- Together with one and zero, they are the only numbers that in all the bases are Harshad numbers.
- It is the only number apart from the 1 that gives the same result if it adds to itself, if it multiplies itself or if it rises to itself:
∙ 2 = 4
22 = 4- Its minimal primitive root is 1
- It's the first.
- Cousin number and the only one of them that's even. It happens on three.
- Eisenstein's cousin number, happened by five.
- Cousin of Sophie Germain, happened by three.
- Stern's cousin number, happened by three.
- Factorial prime number, happened by three.
- Number of Lucas, happened by one.
- Number of Perrin cousin, succeeded by three. It also appears twice in such succession, as the third and fifth element.
- Number of Smarandache-Wellin, succeeded by the twenty-three.
- Primorial, happened by six.
- Term of succession (1 + 1/n)nwhich has as limit the number e.
- It's the second.
- Markov number, after one and before five.
- Number of Motzkin, after one and before four.
- Pell number, after one and before five.
- It's the third.
- Bell's number, after one and before five.
- Term of Fibonacci succession, after one and before three.
- It's a Catalan number.
- It's a Pell number.
Other sciences
- It's the atomic number of the helium.
- Object of Messier M2, is a globular cluster in the constellation of Aquarius.
- The human brain is divided into two parts right and left hemisphere.
Binary system
The least amount of digits necessary to define a numeral system consisting of positional notation is two, where one symbol represents zero or absence and another one or presence. These systems are called binaries.
Although there are ancient Chinese and Indian documents dealing with binary notation systems, it was Gottfried Leibniz in the 17th century who laid the foundations of the current system, using the symbols 0 and 1. Subsequently, George Boole determined the set of rules and operations that define any binary system, thus developing a branch of mathematics that bears his name: Boolean Algebra. Based on it, in 1937 the American Claude Elwood Shannon developed the first binary code, which is the language of computers. Thus taking the binary system one step further; Now you can not only represent numbers with it, but also write texts, make images, videos or create computer programs. In short, with only two symbols the entire digital world can be created and interpreted, on which much of our current technology depends.
In philosophy and theology
In various philosophical and theological currents, the existence of two fundamental principles is affirmed and they base their doctrine on them. Some of the common characteristics that we can identify is that they are supreme, uncreated, independent, irreducible and antagonistic. These entities are usually associated with fundamental concepts such as good and evil, matter and spirit, physical order and moral order, the ideal and the real, the divine and the earthly or the natural and the rational.
Among the most important dualist theories, due to its great influence on European scientific and religious development in the mid-XVII century, there is Cartesian dualism that resolves a dilemma that arose during the Renaissance regarding the divine role in the creation and evolution of the Universe, by distinguishing and separating the physical from the spiritual, assigning it the study of the material to the sciences and that of the immaterial to religions. From the Cartesian point of view, the physical can be known by interacting with it, experimenting, observing; while the immaterial plays a scaffolding role and supports imposing the rules of the physical world without directly affecting it. Thus, he attributes to God the creation of the Universe and with him the laws that govern it, while physics, as a science, will be the one who must discover them. Due to the influence of his dualistic ideas on the behaviorism, is considered the father of modern psychology.
Bilateral symmetry
Living organisms come in an amazing variety of shapes. However, there are basic patterns common to all of them. One of them, very important for their classification, is the symmetry of their bodies. When an animal has a body structure where its organs appear duplicated with respect to a plane that divides it into two parts, it is said to have bilateral symmetry. It is believed that the reason why most zoological species present this type of symmetry is due to the advantages it presents to mobility.
There are three possible planes that support bilateral symmetry, and 1, 2 or all 3 of them can occur in the same species. They are the sagittal plane, which divides the body into its right and left halves; the frontal or coronal plane, which divides it into the dorsal and ventral parts (the front and the back) and the transverse plane, which divides it into its anterior and posterior parts.
Those organisms that have bilateral symmetry are grouped in the Bilateria phylum. This type of organization was vital in the development of the central nervous system.
Bilateral symmetry also appears, although to a lesser extent in the plant kingdom. The leaves, flowers and fruits of certain species have it. Instead, coming out of these two realms is very difficult to find.
Use in Spanish
Two can be both a noun (“the two of cups”) and an adjective (“two books”).
As a multiplicative numeral adjective, only the double form is used for both genders: «double vision». As a multiplicative noun, there are also duplo and dupla, although they are rarely used; The feminine dupla persists in some Latin American countries to indicate a couple or group of two people or things.
As partitive or fractional, there are the forms half and half (nouns): “half of the population”, although half only It is normal in a mathematical context: "the surface of a triangle is equal to one half of the base times its height". As an adjective, only medio is used, which must agree in gender and number with the noun it modifies: "two half oranges". Medio is also an adverb (and like such, invariable) and means "not completely": "the pots are half full".
There are several prefixes that mean two and participate in the construction of a large number of everyday words: bi- / bis- / biz-, di- and du-, as in leap year, dichotomy, and dual.
Features
- In many cultures the 2 is represented by two points or two strokes (horizontal or vertical). For example, in the Roman numeration (II) and in the Chinese number (note).
- Considered by the Pythagoreans as the first number in the strict sense, since it represents the possible primary plurality: if one corresponds to the creation, the two is the first and most elementary manifestation of creation. It is duality that enables plurality, while two are the opposite principles created that make possible the rest: male and female, the sky and the earth, the light and the darkness, etc.
- According to the cabalistic legend number two expresses in the moral order the man and the woman, and in the physical the efficient cause and the matter.
Contenido relacionado
Leg
Twenty two
Felix Klein