To the girl
Alanine (Ala or A) is one of the amino acids that make up the proteins of living beings. It is encoded by the codons GCU, GCC, GCA and GCG. It is the smallest amino acid after glycine and is classified as hydrophobic.
Alanine is a non-essential amino acid for humans, but it is of great importance. It exists in two different enantiomers L-alanine and D-alanine. L-alanine is one of the 20 most widely used amino acids in protein biosynthesis, behind leucine, being found in 7.8% of the primary structures, in a sample of 1150 proteins. D-alanine is in the bacterial cell walls and in some antibiotic peptides. It is found both inside and outside of globular proteins.
History
Alanine was first isolated in 1879 by the German chemist Adolph Strecker. The name was coined in German as alanine from the aldehyde (with the infix -an- for ease of identification). pronunciation).
Structure
The α carbon atom of alanine is linked to a methyl group (-CH3), thus being classified as an aliphatic amino acid.
Biosynthesis
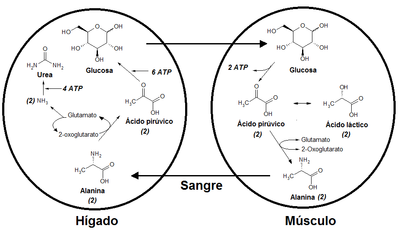
Alanine is very common because it transfers its amino group to pyruvate. Due to transamination reactions through the enzyme alanine transaminase (EC 2.6.1.2), which is rapidly reversible, alanine can easily be biosynthesized from pyruvate, which is why it is present in the metabolic cycles of glycolysis, gluconeogenesis, and in the citric acid cycle.
Alternatively, bacteria obtain alanine by decarboxylation of carbon 4 of aspartate, by action of the enzyme aspartate 4-decarboxylase (EC 4.1.1.12), carrying out the following reaction:
HOOC-CH2-CH(NH2)-COOH → CO2 + CH3- CH(NH2)-COOH
Summary
Racemic alanine can be synthesized by the condensation of acetaldehyde with ammonium chloride in the presence of sodium cyanide via a Strecker synthesis, or by ammonolysis of 2-bromopropionic acid:
Function
The methyl group of alanine is very unreactive, so it is not common to see it in protein function. However, it may play a role in substrate recognition or specificity, particularly in interactions with other non-reactive atoms such as carbon. Involved in glucose metabolism.
Sources of Alanine
In general, proteins from beef, pork, fish, eggs, and dairy products are rich in alanine.
Contenido relacionado
Merostachys
Lophatherum
Gaudinia