Time system
Time is a physical quantity created to measure the interval in which an ordered series of events occurs. The commonly used time system is the Gregorian calendar and is used in both the International System and the Anglo-Saxon System of Units.
International System of Units
Minimal Pools
- The Second is the time unit in the International Unit System, the Cegesimal Unit System and the Technical Unit System. One minute is 60 seconds and one hour is 3600 seconds. Until 1967, it was defined as the eighty-sixty-four hundredth part (1/86 400) of the duration of the average solar day between the years 1750 and 1890 and, from that date, its measurement is based on the atomic time.
According to the definition of the International System of Units, one second is equal to 9 192 631 770 periods of radiation corresponding to the transition between the two hyperfine levels of the ground state of the isotope 133 of the cesium atom (¹³³Cs), measured at 0 K. This has the consequence that lags occur between the second as a unit of astronomical time and the second measured from atomic time, more stable than the rotation of the Earth, which forces adjustments aimed at maintaining concordance between atomic time and mean solar time.
Units less than a second
- The decise It is the unity of time that equals the tenth of a second. Abbreviated ds (1 ds = 0.1 s = 1 × 10-1 s). Common chronometers can measure deciseconds.
- The centisegundo is the time unit that is equivalent to a hundredth of a second. Abbreviated cs (1 cs= 0.01 or 1×10-2 s). Common chronometers can measure the elapsed centisques.
- The millisecond is the unity of time that corresponds to the thousandth fraction of a second. It abbreviates ms (1 m = 0.001 or 1 × 10-3 s).
- The microsecond It is the unity of time that equals the millionth part of a second. μs (1 μs = 0,000001 or 1 x 10-6 s).
- The nanosecond (from Latin) nanus, dwarf), is the unity of time that equals the thousand millionth part of a second. This short time is not used in everyday life, but it is of interest in certain areas of physics, chemistry and electronics. Thus, a nanosecond is the duration of a clock cycle of a microprocessor of 1 GHz, and it is also the time that takes the light to travel about 30 cm. Abbreviations (1 ns = 1 x 10-9 s).
- The peaking (from Spanish peak, and this from Celtolatin beccus, small amount surplus), is the time unit that equals the billionth part of a second, and abbreviates ps. 1 p = 1 × 10-12 s.
- The femtosegundo (from Norwegian and Danish femten, fifteen), is the time unit that equals one thousand billionth of a second. This fraction of time was the smallest measure until 2004. It's short fs. 1 f = 1 × 10-15 s.
- The Attosecond (from Norwegian and Danish atten18), is a time unit equivalent to the thirtieth part of a second and abbreviates. 1 as = 1 × 10-18 s.
- The zeptosecond (from Latin) septemfor the seventh power of 103), is a time unit equivalent to the thousand trillionth part of a second and abbrevia zs. 1 zs = 1 × 10-21 s.
- The Ictosegundo (from Latin) octoby the eighth power of 103), is the time unit equivalent to the fourteenth part of a second. 1 yoctosegundo = 1 × 10-24 s.
Units greater than a second
- The ♪ It's a time unit that's equal to a half an hour. It also comprises 60 seconds. Simbolized is min (1 min= 60 s).
- La Time is a time unit that corresponds to the twenty-fourth part of a solar day. It is used in civil time equivalent to 60 minutes. Since 1967 the second has been measured from very precise atomic properties, it is to keep the time standards close to the average solar day.
- The Day is a time unit that lasts 24 hours (approx.). 365 (approx.) year (approx.)
Group of days
- La Week or hebdómada is the seven-day grouping.
- The Eighth It's the eight-day cluster.
- The Ninth or Ninth is the nine-day grouping.
- La Ten It's the ten-day cluster.
- La 11 It's the 11-day cluster.
- La Dozen is the 12-day grouping.
- La 15 is the grouping of fifteen days (approx.).
- La 20 is the grouping of twenty days.
- La 30. is the grouping of thirty days.
- La quarantine is the grouping of forty days (the term also applied for months and years)
Month grouping
- The bimestre is the grouping of 2 months.
- The quarter is the grouping of 3 months.
- The Cuatrimestre is the grouping of 4 months.
- The semester is the 6-month grouping.
Group of years
- The biennium is a period equal to 2 years.
- The triennium is a period equivalent to 3 years.
- The Cuatrienio or quadrennium is a period equivalent to 4 years.
- The . or quinquenio is a period equivalent to 5 years.
- The sexenio is a period equivalent to 6 years.
- The Septenio is a period equivalent to 7 years.
- The octenio u Ochenio It is a period equivalent to 8 years.
- The Ninth is a period equal to 9 years.
- The Decade or decade It's a 10-year period.
- The 11 It is a period equal to 11 years.
- The Twelve is a period equivalent to 12 years.
- The quindenio is the period equivalent to 15 years.
- The they say is the period equivalent to 20 years.
- The decalustro is the period equivalent to 50 years.
- The dodecalustro is the period equivalent to 60 years (dodeca (12) + lustro).
- The century or centuria It's a 100-year period.
- La Age is the period equivalent to several centuries (without fixed amount).
- The Millennium It is a period equivalent to 1000 years.
- La It was, the period or period is a period equivalent to several millennia (without fixed amount).
- The Evo: is a term (usually poetic) that indicates amount of time without limit, long or eternally. Old.
Gregorian time system
| 1st millennium | 10 centuries | 100 decades | 1000 years |
| 1st century | 10 decades | 100 years | 1200 months |
| 1 decade, decade | 10 years | 120 months | 520 weeks |
| 1 luster, 500 | 5 years | 60 months | 260 weeks |
| 1 Gregorian year | 12 months | 52 weeks | 365,2425 days * |
| 1 month calendar | 4 weeks | 28 to 31 days | 672-744 hours |
| 1 week calendar | 7 days | 168 hours | 10080 minutes |
| 1 average solar day | 24 hours | 1440 minutes | 86400 seconds |
| 1 hour | 60 minutes | 3600 seconds | |
| 1 minute | 60 seconds |
* The Gregorian calendar computes 365 mean solar days and omits the fraction of 0.2425 days remaining to complete a Gregorian year. To avoid time lags, we use the leap year.
Geologic units of time
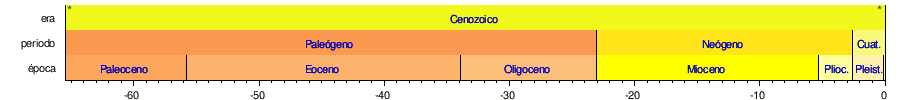
Geologic time is divided and distributed into correlative irregular intervals of time, characterized by important events in the history of life and Earth recorded in rocks. The successive divisions and subdivisions are called: eons, eras, periods, epochs, ages, and chrons. In this way the eons are divided into eras, the eras into periods, the periods into epochs and so on.
The following time lines show the geological time scale: the 1.a shows the full time from the formation of the Earth to the present; the 2.a shows an expanded view of the newest eon; the 3rd most recent era; the 4th most recent period; and the 5th most recent time. The colors are the standards to represent the rocks according to their age of formation on the international geological maps.




Contenido relacionado
Tectology
Averroes
Parts per million