Territorial organization of Brazil

The subdivisions of Brazil exist at different levels and classification criteria. Brazil is a federation constituted by the indissoluble union between the Union, the states, the Federal District and the municipalities. They have legal personality according to internal public law and are autonomous from each other, although not sovereign. Therefore, they have self-administration, self-government and self-organization, that is, they elect their leaders and political representatives and manage their public affairs without the interference of other entities of the federation. To allow for self-administration, the current constitution defines what taxes each unit of the federation can collect and how the funds will be distributed among them. The states and municipalities, given the desire of their population expressed in plebiscites, can be divided or united. However, the Constitution has not guaranteed them the right to independence.
History
Empire of Brazil
In 1853 the southern part of the province of São Paulo was divided and created the province of Paraná, as punishment for having participated in the uprising against the empire in 1842. São Francisco county, region of the left bank of the river São Francisco, was passed to Bahia, as a punishment to Pernambuco for participating in the Confederation of Ecuador in 1830.
Republic
In 1943, with the entry of Brazil into World War II, the Getulio Vargas government decided to create six strategic territories of the country on the borders to administer them directly: Punta Porá, Iguazú, Amapá, Río Branco, Guaporé and Fernando de Noronha. Punta Porá and Iguaçu returned to their original state after the war, while the remaining four remained. A decade later, Rio Branco changed its name to Roraima and Guaporé is baptized Rondonia.
In 1960, a quadrangular territory was dismembered from the state of Goiás in order to become the home of the new capital, Brasília, within the new Federal District. At the same time, the old Federal District (1889-1960) became the state of Guanabara, which included only the city of Rio de Janeiro and its rural area.
In 1962, Acre was elevated to statehood.
In 1975, the state of Guanabara was incorporated into the state of Rio de Janeiro, with the city of Rio de Janeiro as the state capital.
In 1977 the southern part of Mato Grosso was emancipated as the new State of Mato Grosso do Sul with its capital in the city of Campo Grande.
On December 22, 1981, the state of Rondonia was created on January 4, 1982 by the then President of Brazil João Batista Figueiredo, and the city of Porto Velho was established as its capital.
The 1988 Constitution redefined the structure of the divisions as it is today. Although the legal definition of the Federal Territories is maintained, it ended with those existing up to that moment (Roraima and Amapá), improved the consideration of the States and the integration of the territory of Fernando de Noronha to the state of Pernambuco. In the same act, the northern part of Goiás was dismembered as the state of Tocantins and its capital the city of Palmas.
States
Regions
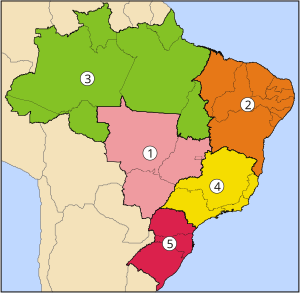
Brazil is divided into five regions (also called macro-regions) by the Brazilian Institute of Geography and Statistics (IBGE). These divisions are made up of states with similar cultural, economic, historical and social aspects, and although the information given by this type of division is not very precise from a scientific point of view, this division is the most used in Brazil since the official information given by IBGE uses this system.
Northern Region
The Northern Region is made up of the states of Acre, Amapá, Amazonas, Pará, Rondônia, Roraima, and Tocantins. It has a territory of 3,851,560 km² (45.2% of the national territory) and a population of just over 15 million inhabitants (6.2% of the total population of the country), making it the region with the lowest density demographic of all Brazil.
Among the most important cities are Manaus (1,403,796 inhabitants); Belém (1,279,861 inhabitants); Ananindeua (392,247 inhabitants); Porto Velho (314,525 inhabitants); Macapá (282,745 inhabitants); Santarém (262,721 inhabitants); Rio Branco (252,885 inhabitants); Boa Vista (220,383 inhabitants); Palmas (208,000 inhabitants).
Northeast Region
The Northeast Region is made up of the states of Alagoas, Bahia, Ceará, Maranhão, Paraíba, Pernambuco, Piauí, Rio Grande do Norte and Sergipe. It has a territory of 1,561,177 km² (18.2% of the national territory) and a population of just over 50 million inhabitants (27% of the country's total population).
Among the most important cities are Salvador (2,892,625 inhabitants); Fortress (2,138,234 inhabitants); Recife (1,421,993 inhabitants); São Luis (868,047 inhabitants); Maceió (796,842 inhabitants); Natal (789,836 inhabitants); Teresina (714,583 inhabitants); João Pessoa (595,429 inhabitants); Jaboatão dos Guararapes; (580,795 inhabitants); Santana Fair (481,137 inhabitants); Aracaju (461,083 inhabitants); Olinda (368,666); Campina Grande (354,546 inhabitants).
Central West Region
The Center-West Region is made up of the states of Goiás, Mato Grosso and Mato Grosso do Sul, as well as the Federal District. It has a territory of 1,612,077 km² (18.9% of the national territory) and a population of around 13 million inhabitants (6.40% of the country's total population).
Among the most important cities are Brasília (national capital) (2,043,169 inhabitants); Goiânia (1,090,737 inhabitants); Campo Grande (662,534 inhabitants); Cuiabá (483,044 inhabitants); Aparecida de Goiânia (335,849 inhabitants); Anapolis (287,666 inhabitants).
Southeast Region
The Southeast Region is made up of the states of Espírito Santo, Minas Gerais, Rio de Janeiro and São Paulo. It has a territory of 927,286 km² (10.9% of the national territory) and a population of around 80 million inhabitants (38% of the country's total population).
Among the most important cities are São Paulo (11,037,593 inhabitants); Rio de Janeiro (6,186,710 inhabitants); Belo Horizonte (2,452,617 inhabitants); Guarulhos (1,299,283 inhabitants); Campinas (1,064,669 inhabitants); São Gonçalo (991,382 inhabitants); Duke of Caxias (872,762 inhabitants); Nova Iguaçu (865,089 inhabitants); São Bernardo do Campo (810,979 inhabitants); Osasco (718,646 inhabitants); Santo André (673,396 inhabitants); Uberlândia (634,345 inhabitants); Contagem (625,393 inhabitants); São José dos Campos (615,871 inhabitants); Sorocaba (584,313 inhabitants); Ribeirão Preto (563,107 inhabitants); Juiz de Fora (526,706 inhabitants); Belford Roxo (501,544 pop.); Niterói (479,384 inhabitants); São João de Meriti (469,827 inhabitants); Betim (441,748 inhabitants); Campos dos Goytacazes (434,008 inhabitants).
Southern Region
The Southeast Region is made up of the states of Paraná, Río Grande do Sul and Santa Catarina. It has a territory of 575,316 km² (6.8% of the national territory) and a population of more than 26 million inhabitants (12.50% of the country's total population).
Among the most important cities are Curitiba (1,893,997 inhabitants); Porto Alegre (1,481,019 inhabitants); Joinville (562,151 inhabitants); Londrina (553,393 inhabitants); Caxias do Sul (474,853 inhabitants); Florianópolis (469,690 inhabitants); Maringá (403,063 inhabitants); Balls (343,651 inhabitants); Ponta Grossa (341,130 inhabitants); Blumenau (334,002 inhabitants); Canoes (323,827 inhabitants); Cascavel (316,226 inhabitants); Santa Maria (277,309 inhabitants); Foz do Iguaçu (269,585 inhabitants); Rio Grande (208,641 inhabitants).
Federal territories
Federal territories are a specific category of administrative division of Brazil. These territories are an integral part of the Union, without belonging to any state, and can arise from the division of a state or its dismemberment, which requires popular approval through referendum and supplementary law. Currently there is no territory federal, since these were elevated to the category of states in 1988, however there were two notable territories that are now extinct and that are currently areas of existing states:
Territory of Punta Porá
The Territory of Punta Porá was a Brazilian federal territory created on September 13, 1943, pursuant to Decree-Law No. 5,812, of the government of President Getúlio Vargas. Its capital was the city of Ponta Porã. The territory was dissolved on September 18, 1946 by the Brazilian Constitution of that year, and reincorporated into the then state of Mato Grosso. Currently the area of the former territory of Ponta Porã is part of the state of Mato Grosso do Sul.
Iguazú Territory
The Territory of Iguazú was a Brazilian federal territory created on September 13, 1943, in accordance with Decree-Law No. 5,812, during the government of President Getúlio Vargas and dissolved on September 18, 1946 by the Brazilian constitution of 1946. At this time, the capital of the Iguazú Territory was the city of Iguaçu, currently Laranjeiras do Sul. The area of the former territory of Iguazú returned to the Brazilian states of Paraná and Santa Catarina.
Contenido relacionado
The Bramble of Pumareda
Oulu Province
Teruel Province