Striatum
Contenido keyboard_arrow_down
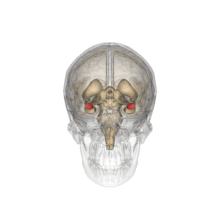
The corpus striatum, also known as the nucleus striatum, is a subcortical part (inside the brain) of the telencephalon and is part of the basal ganglia. In turn, the striatum receives information from the cerebral cortex. In primates (including humans), the dorsal striatum is divided by a section of white matter called the internal capsule, forming two sectors; the caudate nucleus and the lenticular nucleus which in turn is made up of the putamen and globus pallidus. The ventral striatum is made up of the nucleus accumbens and the olfactory tubercle, in primates.
Types of neurons
The striatum is heterogeneous in terms of the types of neurons that make it up:
- Medium spinal neurons Thus called by the presence of thorns in the dendrites, which form more than 95% of the striated body.
- Deiter neurons (2%) With long and little branched dendrites.
- Colinergic interneurons (1%). These neurons briefly stop their downloads in response to emotionally charged stimuli and reward-related events.
- Interneurons expressing parvalbumina which express receptors for catecholamines.
- Interneurons expressing calretinine.
- Interneurons expressing somatostatin also express dopamine receptors.
Contenido relacionado
Saturnia pyri
Ernst Mayr
Gonorrhea
Más resultados...