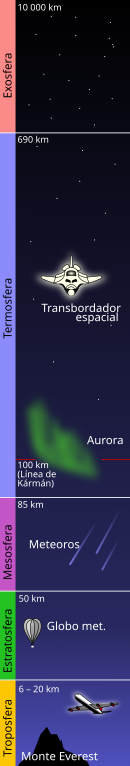
Stratosphere
The stratosphere or stratosphere is one of the layers of the Earth's atmosphere; It is located between the troposphere and the mesosphere. The height at which it begins is variable: In the polar regions at a lower altitude, between 6 and 9 kilometers or more; and in the equatorial regions between 16 and 20 kilometers. and extends up to approximately 50 km in height.
The temperature increases progressively from −55 °C of the tropopause until reaching 0 °C of the stratopause, although according to some authors it can even reach 17 °C or more. In other words, in this layer the temperature increases with altitude, contrary to what happens in the upper and lower layers. This is mainly due to the absorption of ozone molecules that absorb electromagnetic radiation in the ultraviolet region.
In the lower part of the stratosphere the temperature is relatively stable, and in the whole layer there is very little humidity.
In the stratosphere, horizontal mixing of gaseous components occurs much faster than vertical mixing.
At a height of approximately 2.5 times the height of Everest and some 112 times the height of the Empire State Building in New York only a few aircraft such as the Russian Mig-31, SR-71, Concorde, U-2 and the RQ-4 Global Hawk UAV can fly at this level. Near the bottom of the stratosphere is the ozone layer that absorbs most of the Sun's ultraviolet rays.
On October 14, 2012, the Austrian Felix Baumgartner launched himself from the stratosphere at a height of 38,969 meters. He thus broke the record for free-falling from the highest point and for manned balloon flight with a distance from the earth's surface of 39,068 m. On October 24, 2014, this record was broken by Google Vice President Alan Eustace (57 years old), who jumped from a height of 41,425 meters.
Contenido relacionado
Slovakia
Deforestation
Fossil