State Lotteries and Betting
Loterías y Apuestas del Estado (legally Sociedad Estado Loterías y Apuestas del Estado) is a publicly owned Spanish lottery and gambling operator under the responsibility of the Government of Spain. and attached to the Ministry of Finance, which is responsible for strategic direction and evaluation and control of effectiveness. This entity is responsible for the management, exploitation and marketing of all types of lotteries and games at a national level or whenever they go beyond the scope of an autonomous community.
The company has its origins in the "National Agency for State Lotteries and Betting" (ONLAE), created in 1984 through the integration and unification of the institutions that until then had been managing state-owned games - the Board of Trustees of Charity Sports Mutual Betting and the National Lottery Service. In 2000 it became the "State Lottery and Betting Public Business Entity" and in 2010 it became the current "State Lottery and Betting Company" (SELAE).
It is the main operator in the sector in Spain, with a market share of approximately 40% (2020) and around 600 employees. In the 2010s, it was the most profitable state company in the country in all years, contributing billions of euros annually to the state coffers.
Games
Loterías y Apuestas del Estado operates nine different games in Spain. Although they are mostly lotteries and random draws, there are also some games based on sports betting.
The origins of these draws date back to the 18th and 19th centuries, the format of which is still carried out today under the names of Lotería Primitiva and Lotería Nacional. The rest of the modern games were added progressively during the XX and XXI.
The marketing of tickets for participation in Lottery games is carried out through a commercial network of administrations and authorized establishments, as well as through the operator's website.
National Lottery

The National Lottery consists of a passive lottery in which participants buy shares for a number and series previously defined on each ticket. The shares are sold divided into tenths. It has its origins in the "Modern Lottery" devised by Ciriaco González Carvajal in Cádiz in 1811.
Currently, two draws are held weekly on Thursdays and Saturdays using an automatic drum system, although sometimes special draws are held that coincide with events or anniversaries. The most notable are the Extraordinary Christmas Draw and the Extraordinary Children's Draw.
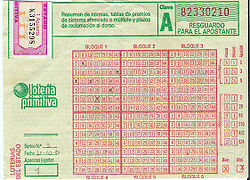
Primitive Lottery

The Primitive Lottery takes its name because it is inspired by the first type of state draw founded in 1763 under the reign of Charles III. This is an active lottery in which the participant must choose six different numbers between 1 and 49. Each ticket also has a refund number between 0 and 9.
Currently, three draws are held weekly on Mondays, Thursdays and Saturdays, in which the six winning numbers are drawn from an automatic drum, as well as an extra one for the complementary number. A ball numbered between 0 and 9 is also drawn to decide the refund number.
Bonoloto

The Bonoloto is a smaller replica of the Primitiva draw. It was created during the 20th century with the intention of creating a draw similar to the Primitiva lottery with more affordable tickets and smaller prizes. size. It is the game with the most economical participation of those operated by Lotteries.
The format is that of an active lottery with a mechanism identical to that of the original game: the bettor must choose six numbers between 1 and 49, and the payout is random. Unlike other larger games, this draw takes place daily from Monday to Sunday.
El Gordo de la Primitiva

El Gordo de la Primitiva is an active type draw with a format similar to that of La Primitiva in which greater complexity is added because the player must choose five numbers between 1 and 54 from a first matrix and a additional number between 0 and 9 of a second matrix. As compensation, the prizes distributed are significantly larger than those distributed by La Primitiva
It was created in 1993 with the intention of replicating the La Primitiva format with higher revenue and prizes. Currently the draw takes place on Sundays on a weekly basis.
Euromillions

Euromillions is a draw carried out jointly by nine gaming operators from different European countries. Because the draw is carried out internationally, it is the game with the least chance of awarding a prize, but it is also the one that provides the greatest prizes to its winners.
The format consists of an active lottery in which the participant must select five numbers from a matrix between 1 and 50 and two stars numbered between 1 and 12. The draws are held weekly on Tuesdays and Friday, by extracting two balls from two drums, one for the numbers and one for the stars.
The Quiniela

La Quiniela is a sports betting game created in 1946 that consists of guessing the winner of fifteen first and second division Spanish football matches that will be held during the day. For the first 14, the bet consists of guessing whether the home team will win (1), the visitor (2) or if there will be a tie (X). For the last match, called «Pleno al fifteen» the number of goals that each team will score must be predicted.
Quinigol
El Quinigol is a variant of La Quiniela created in 2004 and inspired by the original format with which the betting game was originally born. In this format, 6 soccer matches are presented in which the participant must predict the exact result. For each match, the number of goals that each team will score is determined: zero, one, two or more (M).
Lototurf

Lototurf is a game that combines a lottery of chance with a horse sports bet. It was created in 2005 with the aim of financing the reopening of the Zarzuela Hippodrome in Madrid.
The participant must choose, on the one hand, six numbers from a matrix numbered from 1 to 31. On the other hand, he must predict the number of the winning horse in the race indicated on the ticket, numbered between 1 and 12.
Quintuple Plus

Quíntuple Plus is a traditional horse betting game. It consists of predicting the winning horse of five specific races. In addition to the winner of the five races, you must also predict which horse will be in second place in the fifth race.
History
Royal Lottery
The origins of the state-owned lottery in Spain date back to the reign of Charles III. On September 30, 1763, inspired by a tradition from Naples, the "Royal Lottery" was established. The format of the game was an active lottery in which players had to select the numbers they wanted to bet on, being the predecessor of the current La Primitiva.
[...] I have had it appropriate, and convenient to establish in Madrid a Lottery [...] so that it will become the benefit of Hospitals, Hospicios and other Pías and public Works, in which many flows of my Real Erarium are consumed annually.”Royal Decree of 30 September 1763
The game consisted of choosing how many numbers you wanted that were between 1 and 90. The prizes were awarded in an extraction ceremony in which a blindfolded child took five balls from a bag containing 90, numbered correspondingly in a consecutive manner. Since the first draw was held in the Plaza de San Ildefonso in Madrid, it was decided that the Lotería Real society would have its headquarters there.
National Lottery
What is known today as the National Lottery was born approximately a century later, in Cádiz in 1811, at the initiative of Ciriaco González Carvajal, to provide funds to the Public Treasury that had been resented by the War of Independence. The Royal National Lottery of Spain was created by instruction of November 25, 1811. Conceived as "a means of increasing the income of the public treasury without loss to taxpayers", the first draw took place in Cádiz on March 4, 1812. Initially limited to Cádiz and San Fernando, it later spread to Ceuta and all of Andalusia, as the retreat of the Napoleonic armies progressed. On February 28, 1814, the first draw was held in Madrid, since then the headquarters of the National Ticket Lottery. The bills were divided into quarters – instead of tenths –, each of which had a value of ten reales.
With the return to power of Fernando VII, it is imposed that it be called "Modern Lottery" until during the Constitutional Triennium, it returned to "National Lottery", passing again to "Moderna" at the return of absolutism until after the death of Fernando VII it definitively became "Nacional". The modern format was a type of passive lottery, in which players acquired tickets that already had a specific number defined, unlike the Royal Lottery, in which participants had to choose the numbers with which they played.

In 1818 the National Lottery decided to hold a special draw coinciding with Christmas. This can be considered the precursor to the current Extraordinary Christmas Raffle. However, it was not until 1839 when this draw was decided to be held regularly; and until 1897 it did not receive its current name. In the 1880s, a second special raffle appeared that has lasted until today: the Extraordinary Children's Raffle.
In 1862 the Royal Lottery was eliminated in favor of the National Lottery. To fill the gap, the National Lottery considerably expanded the number of monthly draws it ran. At that time, the Lottery headquarters were located, around the year 1877, in the National Mint.
A century later, the State decided to recover the active lottery format through the Royal Decree of August 1, 1985. Because the original historical game was recovered, the draw acquired the name Primitive Lottery. In the first years of the draw since 1985, the refund ball did not exist, which was added in June 1991.
20th century

The 20th century brought with it an increase in demand and citizen spending on lotteries and games of chance, which led to the creation of new games and raffles. In 1924, the National Lottery Draw was held for the first time to benefit the Red Cross, which continues to this day. In 1932 the Loterías headquarters moved to Montalbán Street in the capital.
In 1946, the National Mutual Betting Board decided to create a game based on football betting. Soccer was already established as a sport with a large number of fans and there were soccer clubs that placed bets informally, so it was decided to create a raffle based on this sport: La Quiniela. The first Quiniela was born in the 1946-47 season with a price of 2 pesetas per ticket. At that time the game consisted of a classic bet on football results: The bettor had to enter the exact result of each of the seven games that appeared on the ticket. For the following season it was decided to simplify the format, creating the current 1X2 system, in which it was only necessary to guess whether the home team would win (1), the visitor (2) or if it would end in a draw (X).
In its first seasons it was not officially called 'Quiniela', since it was simply referred to as "Mutual Sports Betting". The word "quiniela" It was a popular term that was used to refer to gambling games in general, so popular custom ended up making the name of the game official. 45% of the proceeds were dedicated to charity, another 45% to prizes and the other 10% was reserved for the management of the system. In 1963 the headquarters moved to Guzmán el Bueno Street.
With the end of Francisco Franco's dictatorship and the reestablishment of democracy in Spain, it was decided to reorganize the business structure of state-owned games of chance. In 1984 the Government of Spain merged the "Patronato de Apuestas Mutuas Deportivas Béficas" (responsible for the Quiniela) and the "National Lottery Service" (responsible for the National Lottery), creating the National State Lottery and Betting Agency (ONLAE).), from which legal figure the current public company derives.
A year later, in 1985, the Government decided to recover the active lottery format in which the player actively chooses the numbers they want to bet on, for which they are inspired by the historic Royal Lottery of Carlos III. Because the traditional lottery format was recovered, the game acquired the name Lotería Primitiva.
The success of this game led to the decision in 1988 to create a smaller replica of this draw, with tickets at a more affordable price and lower prizes: Bonoloto. Likewise, in 1993 it was decided to create another version of the draw with larger tickets but prizes much higher than those of La Primitiva, which was given the name El Gordo de la Primitiva.
21st century

In the year 2000, the Government changed the legal status of the lottery company, establishing itself as the State Lottery and Betting Public Business Entity. Four years later, Loterías reached an agreement with other lottery operators in Europe to establish the first pan-European lottery: Euromillions.
The year 2005 brought with it the integration of the first horse betting games into lotteries. A year earlier, the Congress of Deputies had approved the reopening of the Zarzuela Racecourse, which had been closed since 1996. To help finance the racecourse, Lotteries were urged to create specific games. Two games were created: Lototurf and Quintuple Plus. The first is a lottery of chance that includes a bet on a horse as a complement, while the second is a more traditional horse bet.
The same year, Quinigol was created, a variant of the Quiniela inspired by the original format of the game, in which the exact result of the 6 matches proposed each day must be predicted, deciding for each team which score 0, 1, 2 or more (M) goals.
In 2011 the Government of Spain announced the partial privatization of Lotteries through the listing of 30% of the entity on the stock market, which should have occurred on October 19. However, the operation was suspended indefinitely. At the beginning of 2013, the Minister of Finance, Cristóbal Montoro, decided to create a new 20% tax to tax State Lottery prizes over 2,500 euros. In July 2018, the tax applies to prizes of more than 10,000 euros. Since January 1, 2019, this tax applies only to prizes for amounts greater than 20,000 euros.
Contenido relacionado
Olivia Newton John
On a silver platter
The Residents