Snowfall
Nevada is one of the fifty states that, along with Washington D.C., make up the United States of America. Its capital is Carson City and its largest city is Las Vegas, famous for its casinos and the legalization of gambling. It is located in the western region of the country, Rocky Mountains division. It limits to the northwest with Oregon, to the northeast with Idaho, to the east with Utah, to the southeast with Arizona (part of this border is formed by the Colorado River) and to the west and southwest with California. With 286,351 km² it is the seventh largest state —behind Alaska, Texas, California, Montana, New Mexico and Arizona— and with 9.43 inhabitants/km² it is the ninth least densely populated, ahead of Nebraska, Idaho, New Mexico, South Dakota, North Dakota, Montana, Wyoming, and Alaska, the least densely populated. It was admitted to the Union on October 31, 1864, as the 36th state, in the midst of the Civil War; this has earned it the nickname The Battle-Born State.
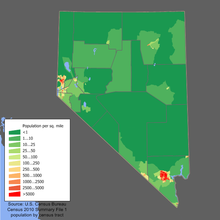
Nevada has the highest population growth rates—66.3% between 1990 and 2000—in the entire United States, thanks in large part to large Mexican immigration. However, most of Nevada is almost uninhabited. Most of the state's population is concentrated in the urban centers of Las Vegas, Henderson, and Reno.
The first European explorers to explore the Nevada area were the Spanish, who gave it the name Nevada, because of the snow that covered the mountains in winter. It was part of the Viceroyalty of New Spain until 1821, the date of the independence of Mexico, becoming part of Mexico. In 1848, with the end of the War between Mexico and the United States, it became part of the United States.
During the 1870s, large deposits of silver were found in Nevada, earning it the nickname The Silver State. Currently, mining still has some importance in its economy, although much less than before. In addition to silver, it is a large producer of gold, oil, and sand. However, currently the largest source of income is tourism (Las Vegas and Reno)
Etymology and pronunciation
The Spanish name "Nevada" It was given to this territory by the Franciscan friar and Spanish explorer Francisco Garcés (1738-1781), the first non-native to set foot on this land, in 1776, as it was limited on its western end by the Sierra Nevada mountain range ("mountains snow-covered").
Nevadenans typically pronounce the second syllable of their state using the vowel /æ/ of "bad". Many people outside of the western states of the country pronounce it with the vowel /ɑː/ of "f ather" /nəˈvɑːdə/. Although the latter pronunciation is closer to the Spanish pronunciation, it is not preferred by the local people. The local pronunciation is not [nəˈβɑdə], but [nəˈvædə]. In 2005, the Nevada Tourism Commission issued a special license plate listing the state name as Nevăda, to help with the pronunciation problem. Notably, George W. Bush made such a faux pas for his campaign for the 2004 United States Presidential Election. A later vindication came when President Bush campaigned in Reno-Sparks Convention Center on June 18, 2004. The president opened his speech by proclaiming that "It's great to be here in Nevada /nəˈˈvædə/" ('It's great to be here in Nevada.'), emphasizing the correct pronunciation of the letter A. The crowd gave their approval as he gleefully pointed out, 'You didn't think I';d get it right, did ya?" ("You didn't think I'd say it right, did you?") Bush subsequently won the state in the election.
Assemblyman Harry Mortenson has proposed a bill to recognize Nevada's alternate (quasi-Spanish) pronunciation.
History
Introduction
Derived from the expeditions of Padre Kino at the end of the XVII century through northern present-day Mexico and southern USA In the USA, Nevada was explored and conquered by the Spanish Crown in the first two decades of the 18th century -although not entirely colonized-. It was part of the Viceroyalty of New Spain until 1821, when it was also part of the First Mexican Empire of Agustín de Iturbide and in 1823 of Mexico. As a result of the US intervention in Mexico in 1847-48, and by the Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo of 1848, Nevada became part of the United States of America. In 1850, the United States Congress established the Utah Territory, which included the present-day states of Utah, Idaho, and Nevada. In 1859, important deposits of gold and silver were discovered in the area, which brought numerous miners, merchants, and other characters seeking to become rich to the region.
On March 2, 1861, Nevada seceded from Utah Territory and took its present name, short for the Spanish name of "Sierra Nevada". On October 31, 1864, Nevada became the 36th state in the union.
The current boundaries of the state were established on March 5, 1866, by absorbing part of Pah-Ute County into Arizona Territory, west of the Colorado River. The handover was expedited after gold was discovered in the area and Nevada was seen as more poised to control the territory thanks to population growth.
Gambling was common in the mining towns of early Nevada but was outlawed in 1909 at the start of a nationwide anti-gambling crusade. The state legalized gambling again in 1931 due to the agricultural and mining crisis in the region. At that time it was believed that legalization would last a few years, just enough to overcome the crisis. However, making the game illegal again has never been considered again.
It should also be noted that Nevada has been a major nuclear testing area for the past century, thus existing military restricted zones for nuclear experimentation and the well-known army airbase called "Area 51".
Until 1864
Native Americans lived in the region where the state of Nevada is located today thousands of years before the arrival of the first European explorers. All the indigenous tribes that lived in the region were part of the Uto-Aztec family. The first European explorer to explore the region was the Spanish Francisco Garcés, in 1776, having set out from New Mexico in the direction of California. At that time, Nevada was part of the Spanish colonies of the Americas. Except for a few trading posts for bartering with local indigenous natives, no permanent settlement was established in the region for decades.
In 1821, with the independence of Mexico, Nevada came under the control of this country. However, the Mexicans were little interested in colonizing the region of present-day Nevada, due to its desert climate, not very conducive to the practice of agriculture. Nevada continued to be inhabited only by local indigenous natives. During the 1820s, various British explorers, mostly merchants under the Hudson's Bay Company, began to explore the lands of Nevada. In 1830, Joseph Walker left Santa Fe, Texas, for Los Angeles, California. In the middle of the trip, in the desert region of Nevada, he built a rudimentary highway to better orient himself.This road was heavily used during the California Gold Rush of 1848, which attracted thousands of American immigrants from the east of the country to the west..
In 1848, Mexico was defeated by the United States in the US Intervention in Mexico, which began in 1846. As a result, the entire Nevada region became part of the United States. In 1850 the Utah Territory was established, which included central and northern present-day Nevada. The remainder was part of the New Mexico Territory, also established in 1850.
American settlers gradually settled in the Nevada region. The first American settlement in Nevada was Virginia City. Early urban settlements were created primarily to serve as a supply center for people from the eastern United States heading west. However, these supplies—food, clothing, weapons, and basic utensils were very expensive, since they were usually purchased in California—until the late 1860s. In 1859, large deposits of silver were found in Virginia City, it attracted numerous mining companies and thousands of people from California and the eastern United States. The population of the region went from a few hundred inhabitants in 1850 to 6,857 inhabitants in 1860. In March 1861, the Territory of Nevada was created, which at that time incorporated only the present-day regions of Nevada that were previously part of the Territory of New Mexico.
In 1861, the Civil War broke out, dividing the country into two: the Union, which was the United States proper, and the rebellious Confederate States of America. The majority of the population of Nevada was in favor of the Union. Abraham Lincoln, the then president of the United States, wanted to approve a series of constitutional amendments that would prohibit slavery in the country, for which the approval of the majority would be necessary. of the members of the House of Representatives and the Senate. The entry of a new state that actively supported the Union would be of great value. At that time, the Nevada Territory had only one-fifth the population needed to become a state. In November 1863, a constitutional convention was held to try to create a constitution for the future State of Nevada. This constitution contained an amendment that proposed to tax any mineral mined in the state. Since Nevada's economy at the time was largely based on mining, it was not approved. In July 1864 a second constitutional convention was held, and this time the constitution was approved. At the time, the United States Constitution said that only territories with more than 127,381 inhabitants could become states, but Abraham Lincoln ignored the Constitution, and both he and Congress approved the elevation of Nevada to statehood. Thus, Nevada became the 36th state of the United States on October 31, 1864.
1864 - 1945
In 1866, the US government divided what was then the Territory of New Mexico (which included the present-day states of New Mexico and Arizona, as well as southern Nevada) into three. The New Mexico Territory came to occupy only the eastern part. The central part became Arizona Territory, and its northwestern end was annexed to Nevada, acquiring its present borders.
The discovery, in 1859, of the Comstock Lode (an immense vein of silver and gold) attracted thousands of prospectors and established the state as a flourishing mining center. Within a decade, the population of Nevada increased from 6,857 inhabitants in 1860 to 42,491 in 1870. However, during the mid-1870s, the US government placed a cap on the use of silver in the country's economic system, greatly diminishing the demand for silver throughout the country. the country. In addition to that, the silver ore that was extracted in the mines of the region was of low quality, since it was mixed with other chemical elements. Before the restrictions on the use of silver in the country's economy were implemented, silver prices were high, which made it possible to purify the mineral mined in the state. Thus, many of the mining companies went bankrupt, while others were forced to lay off hundreds of workers. The unemployment rate rose dramatically, and much of Nevada's population left to seek employment in other states. Nevada's population would decline gradually until the turn of the 20th century, when ranching became the state's main economic activity, although harsh winters and a lack of adequate transportation infrastructure prevented it from developing rapidly.
In the 1900s, new mineral deposits were gradually discovered, notably silver at Tonopah and gold at Goldfield. The silver ore extracted from these mines was of higher quality, and the purification costs, therefore, lower. As a result, silver mining once again became a major source of income for Nevada. In addition to that, copper reserves were also discovered at Ely, in 1900. However, the most important of these discoveries took place in 1902 and later in 1903, when large gold reserves were found. The mining sector flourished again and the construction of various railways began to transport the mineral extracted in the state to other regions of the country, helping to develop urban commerce and cattle ranching in Nevada. During the 1900s, Nevada passed a law that allowed anyone to get divorced even after living in the state for six months, with the goal of attracting more people to this sparsely populated region.
In 1907, the federal government, in partnership with Nevada, completed Nevada's Newlands Irrigation Project, the first large-scale artificial irrigation project undertaken by the US government. The project consisted mainly of the construction of dams along the Carson and Truckee rivers, which allowed the generation of electricity and the practice of agriculture in Fallon.
In 1909, gambling was outlawed in Nevada, at a time when a "crusade" national against this type of games. Nevada had legalized the practice of these games in 1869, but the same inhabitants of the state pressured the provincial government to prohibit this practice. Despite the ban, gaming continued illegally, and compliance with these laws was too expensive.
The United States entered World War I in 1917. By then most of Nevada's gold and silver reserves had been depleted, although there were still large deposits of copper, as well as tungsten and zinc, metals that were in high demand during the war. These reserves had been discovered in the mid-1910s, and numerous mines were opened to meet the demand. However, with the end of the war in 1918, demand for and prices for minerals generally plummeted, leading to the closure of numerous mines and an economic recession.
In 1927, the Nevada government reduced the time it takes for a person to get divorced from six to three months, and in 1931, to just six weeks, causing thousands of people to settle in the state to get divorced. quickly the divorce contract. In 1931, Nevada legalized gambling, mainly because of the economy, which had been badly weakened by the Great Depression—which caused the state's agricultural sector to go into decline—and by the mining recession of the 1930s. 1920. Many casinos opened and the economy boomed again.
During the late 1930s, significant reserves of iron, zinc, and lead were discovered, bringing about a revitalization of the state mining sector. The outbreak of World War II led to the production of war materiel and other war materials, and increased demand for copper, tungsten, iron, zinc, and lead. During this time, the US government built several air bases in the region, among which the Nellis Air Force Base stands out.
1945 - Present Day
After the end of the war in 1945, falling domestic and international demand for metals caused the decline of Nevada's mining industry. During the 1950s, Nevada instituted a law that required all casinos (or any other gambling establishments) to have a license, which would only be issued after a rigorous inspection and investigation of the facilities by the State. This law was created with the aim of reducing cheating, as well as to prevent criminals (especially the mafia) from entering the gambling market.
By then, tourism was already an important source of income for the state. Its importance in the Nevada economy increased rapidly during the 1950s and 1960s. In 1970, nearly 15 million tourists visited Nevada. Currently, tourism is Nevada's main source of income.
Throughout the 1950s and 1960s, the US military conducted various nuclear tests in a totally isolated region of southern Nevada, just 100 kilometers from Las Vegas, the so-called Nevada Test Site. Several nuclear bombs were detonated there.
In 1963, a judicial dispute between Nevada, California and Arizona ended in the Supreme Court of the United States, which had lasted for more than four decades. This dispute was over the water reservoirs of the Colorado River, important for the supply of drinking water in Arizona and Nevada (whose climate is mostly desert) and in the Southwestern region of California (where the climate is also desert). of the Supreme Court instituted, for each state, a maximum quota for the amount of potable water withdrawn from the Colorado River per year. Priority was given to Arizona. In 1967, a provincial project was created with the aim of finding new drinking water reserves for Las Vegas, then rapidly growing. This ends in 1983, with the inauguration of a large aqueduct that brings drinking water from Lake Mead.
Since the 1980s, Nevada's economy has gradually become more diversified, and while tourism is still the largest source of income, the manufacturing and construction industries have also become important in the state's economy. In 2002, President George W. Bush approved the creation of a nuclear waste repository on Yucca Mountain, an isolated region owned by the federal government, which drew protests from the state government and environmentalists. Despite everything, this deposit is expected to come into operation in 2010.
For years, residents of West Wendover, Nevada and Wendover, Utah, neighboring cities but in different states, have lobbied their respective state governments for a merger, making Wendover, Utah a part of West Wendover, Nevada (which has nearly three times as many inhabitants). Currently, the government of Nevada and Utah are discussing this merger, which in order to materialize, will have to have the approval of the Legislature of both States and the endorsement of Congress.
Geography
Nevada is bordered by Oregon and Idaho to the north, California to the west, Arizona to the southeast, and Utah to the east. The border with Arizona includes the Colorado River and the Hoover Dam. The state is crossed by several mountain ranges that go from north to south. Among most of them are drainage valleys. Its territory occupies an area of 286,352 km², whose extension can be compared with that of Ecuador.
Most of the northern part of the state is within the Great Basin Desert, a cold desert that experiences hot temperatures in summer and freezing temperatures in winter. Moisture from the Arizona Monsoon occasionally causes summer storms, and storms from the Pacific often blanket the area with snow.
The Humboldt River flows east-west through northern Nevada and empties into the Humboldt Sink near Lovelock. Several rivers flow from the Sierra Nevada to the east, such as the Walker, the Truckee, and the Carson.
The sierras (some of which have peaks over 12,000 feet) are home to lush forests high above the desert plains. Often, the altitude at which the valleys are found does not drop below 900 meters.
The eastern parts of the state get more moisture in summer and have somewhat greener terrain (this is where Artemisia tridentata, the state flower, grows). In this area, some rivers and streams break the monotony of the desert landscape.
The southern third of the state, which includes the Las Vegas area, is in the middle of the Mojave Desert. It receives less precipitation in winter, but is closer to the Arizona Monsoon in summer. The terrain is lower, mostly below 1,200 meters, which means that the daytime temperature in summer is very high and the nighttime temperature in winter is very low, due to thermal inversion.
Nevada and California share the longest diagonal interstate border, at more than 400 miles (there are a few more, though much smaller, diagonal borders in the northeastern states and Washington, D.C.). All other state boundaries are either meridian or parallel, or are irregular and correspond to rivers, mountains, lakes, etc.
The largest mountain range in the southern part of the state is the Spring Mountains, located immediately west of Las Vegas. The lowest point in Nevada is along the course of the Colorado River, south of Laughlin.
Physiographic Regions
Nevada is usually divided into three physiographic regions:
- the Gran Cuenca, which occupies most of Nevada; this geographical region has a great variation of altitude: of 146 meters of altitude in the southeast end of the State (next to the Colorado River) at 4,055 meters of altitude (Boundary Peak) in the southwest. These two points are, respectively, the lowest and highest point in the State. The Gran Cuenca is characterized by its rocky and rugged soil. Throughout this region there are various thermal geysers and springs.
- the Columbia Plateau, located in the northeast end of Nevada, whose main characteristics are the presence of deep valleys and narrow, and a lowly bumpy soil.
- the Sierra Nevada, a mountain range located in the center-west of the state, with many summits above 3000 and 4,000 meters of altitude.
Climate
Nevada has a desert climate, with two distinct seasons. The state's winters are long and very cold, while the summers are warm for the most part. However, because of its desert climate, the state registers large temperature variations between day and night. For example, Reno sometimes records differences between the maximum and minimum temperatures on a given day greater than 25 °C. The southern region is the one that experiences the highest average temperatures throughout the year, thanks to its low altitude and its lower latitude in relation to the rest of the State.
In winter, the lowest average annual temperatures are recorded in northeastern Nevada, and the highest in its southern part. Nevada's average temperature is ‒4 °C in the northeast, ‒3 °C in the north, and 6 °C in the south. For its part, the average minimum is 2 °C in the south and ‒10 °C in the northeast, and the average maximum is 13 °C in the south and 4 °C in the northeast. Extreme temperatures vary between ‒40 °C and 22 °C. The lowest recorded temperature in Nevada was ‒46 °C, on January 8, 1937, in San Jacinto.
In summer, the highest mean annual temperatures are recorded in southern Nevada, and the lowest in the higher elevation regions and in the north in general. The average temperature in the south is 30 °C, and 21 °C in the higher altitude regions and in the north. The average minimum is 21 °C in the south and 7 °C in higher altitude regions and in the north. The average maximum is 40 °C in the south and 29 °C in the higher altitude regions and in the north of the State. The highest recorded temperature in Nevada was 52 °C, measured at Laughlin on June 29, 1994.
Nevada has the lowest average annual precipitation rate of rain in the United States. Only the highest altitude regions receive more than 60 centimeters of rain per year. However, most of Nevada receives less than 30 centimeters annually. The North generally receives an average annual precipitation of 35 centimeters, while the lower elevation regions, which occupy all of the South and much of Western Nevada, receive less than 20 centimeters. Average annual snowfall rates in Nevada range from 750 centimeters in the Sierra Nevada to less than 2.5 centimeters in the south.
| Vegas | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Ene | Feb | Mar | Abr | May | Jun | Jul | Ago | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dic | Year |
| Average maximum temperature (°C) | 13 | 17 | 20 | 25 | 31 | 37 | 40 | 38 | 34 | 27 | 18 | 13 | 26 |
| Average minimum temperature (°C) | 1 | 3 | 6 | 10 | 15 | 20 | 24 | 23 | 18 | 12 | 5 | 1 | 12 |
| Precipitation (mm) | 15 | 13 | 13 | 5 | 5 | 2.5 | 10 | 13 | 7.6 | 5 | 10 | 10 | 10.4 |
| Source: Weatherbase | |||||||||||||
Demographics
|
|
According to the 2005 census, Nevada had a population of 2,414,807, an increase of 81,909 (or 3.5%) over the previous year and a increase of 416,550 inhabitants (or 20.8%), in relation to the year 2000. The demographic increase since the last census is due to a natural growth of 81,661 people (170,451 births minus 88,790 deaths) and a net migration of 337,043 people in the state. External migrations have given rise to a net increase of 66,098 people, while internal migrations produced a net growth of 270,945 people.
Nevada is the fastest growing state in the United States. Between 2000 and 2003, Nevada's population increased by 12.2%, while the US population increased by 3.3%. On the other hand, between 1990 and 2000, Nevada's population increased by 66.3% versus 13.1% for the US population.
With its 7.03 inhabitants per square kilometer, Nevada is a very sparsely populated state. More than two-thirds of the population live in the Las Vegas metropolitan area. Only seven cities exceed one hundred thousand inhabitants.
As a result of its rapid population growth, Nevada has the highest percentage of residents born out of state in the United States: in 2005, 17.4% of the state's residents (or 413,298 people) had not born in Nevada.
| Graph of demographic evolution in Nevada between 1860 and 2020 |
 |
Races and Ethnicities
In 2011, the state of Nevada had a population of 2,495,529 people, of whom:
- 58.6 % are white (European or European descendants).
- Twenty-four percent are Latin American (including Mexicans)
- 11.3 % are black
- 5.9 % are Asian
- The rest are made up of people of other races.
The Mexican population is the fastest growing, due to the high fertility rate of Latina women residing in the United States, and also due to legal and illegal immigration from the rest of Latin America and the Caribbean.
Pyramid of ages
The age distribution of the population in 2004 was:
- Less than 5 years: 6.8 %
- Under 18: 26.3 %
- Over 65 years: 13.6 %
Female people make up 50.7% of Nevada's population.
Religion
The religious affiliations of the population of Nevada are:
- Christianity: 66 %
- Protestants: 40%
- Catholics: 25%
- Orthodox Christians: 1 %
- Other religions: 5%
- No religion: 29 %
Main cities
Nevada is a highly urbanized state, with more than 92% of its population living in cities.
| N.o | City | Population (2010) | Surface Land (km2) | Density of population (hab/km2) | County |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Vegas | 583 756 | 351,7 | 1.659.8 | Clark. |
| 2 | Henderson | 257 729 | 279,0 | 923.8 | Clark. |
| 3 | Reno | 225 221 | 266,8 | 844.2 | Washoe |
| 4 | Paradise | 223 167 | 121.0 | 1,844.4 | Clark. |
| 5 | North Las Vegas | 216 961 | 262,5 | 826.5 | Clark. |
| 6 | Sunrise Manor | 189 372 | 86.4 | 2.191.8 | Clark. |
| 7 | Spring Valley | 178 395 | 86.1 | 2.072.0 | Clark. |
| 8 | Enterprise | 108 481 | 120.5 | 900,3 | Clark. |
| 9 | Sparks | 90 264 | 92.6 | 974,8 | Washoe |
| 10 | Carson City | 55 274 | 374,7 | 147.5 | - |
| Graph of demographic evolution of Nevada between 1860 and |
 |
Economy
Nevada's gross domestic product was, as of 2003, $88 billion, which ranked 19th in the nation. Per capita income in 2004 was $31,910. The unemployment rate stands at 4.3%. Its main agricultural products are cattle, hay, dairy products, onions and potatoes. Its main industrial products are tourism, mining, machinery, printing and press, food processing and electrical equipment.
Nevada's economy is largely dependent on tourism: it is estimated that in 2000, tourists spent nearly $3 billion in its casinos. The large and luxurious casinos of Las Vegas, Lake Tahoe and Reno attract tourists from all over the world. In the state there are more than 180,000 hotel rooms, that is, one for every 14 inhabitants.
Distribution by sectors
The primary sector accounts for 1% of Nevada's GDP. The state has about three thousand farms, which occupy about 12.5% of its surface. Much of this land is used only for the practice of livestock. Because of Nevada's desert climate, the practice of agriculture is impossible without artificial irrigation. Together, agriculture and ranching comprise 1% of the state's GDP, and employ approximately 19,000 people. Nevada has large cattle and sheep herds: according to data as of January 1, 2006, there were 500,000 cattle and 70,000 sheep in the state. Most of these animals graze in the fields in summer, while in winter receive supplementary feeding. Calves are often shipped to out-of-state feedlots for fattening. About 90% of Nevada's 195,868 hectares of farmland is used to grow hay, mostly alfalfa, to feed cattle. Other products grown are potatoes, onions and wheat. The effects of fishing and forestry are negligible on the state economy.
The secondary sector accounts for 16% of Nevada's GDP. The manufacturing industry corresponds to 10% of the State's GDP and employs approximately 103,000 people. The total value of the products manufactured in the State is 4.5 billion dollars. The main industrialized products manufactured in Nevada are processed foods, concrete, and advertising material. The construction industry comprises 4% of the state's GDP, and employs approximately 48,000 people.
For its part, mining is responsible for 2% of GDP, employing nearly 13,000 people. Considering the value of the extracted material, gold is by far the most important mineral. In 2004, 6.8 million ounces of gold with a value of $2.84 billion were mined in Nevada, which is equivalent to 8.7% of world gold production. Silver is the second most mined mineral, with 10.3 billion ounces with a total value of $69 million. Other minerals mined in Nevada include construction materials, copper, gypsum, diotomite, and lithium. Despite its rich deposits, the cost of mining in Nevada is high and the industry is highly sensitive to world commodity prices.
The tertiary sector comprises 83% of Nevada's GDP. About 32% of the state's GDP comes from community and personal services. This sector employs more than 530,000 people. Wholesale and retail trade correspond to 15% of GDP, and employ approximately 246,000 people. Financial and real estate services correspond to about 18% of the state's GDP, employing approximately 125,000 people. Government services correspond to 12% of GDP, and employ approximately 130,000 people. Finally, transport and telecommunications employ close to 62,000 people and comprise 8% of GDP.
About 50% of the electricity generated in the state comes from thermoelectric plants, hydroelectric plants and geothermal plants. For their part, wind turbines and solar panels supply small inland communities.
Taxes
Nevada is one of the few states in which there is no income tax or corporation tax. Sales tax in Nevada is 6.5%. Counties have the power to levy stock tax as well, bringing the total sales tax rate in some areas as high as 7.75%. Sales tax in Carson City is 7.125%, in Washoe County 7.375%, while in Douglas County it is 6.75%.
Government and politics
The Nevada state government has a division of powers: executive, legislative, and judicial. The Governor of Nevada is Steve Sisolak (Democrat). The two senators are Catherine Cortez Masto and Jacky Rosen, both (Democrats).
- Nevada's chief executive officer is the governor. It is chosen by the population through state elections, for a term of up to four years. The same person can only exercise this position twice. Since 2019, the Governor of Nevada is Steve Sisolak of the Democratic Party.
- The Nevada Legislature is bicameral, that is, it is constituted by a Senate and a Assembly. The Senate is composed of 21 senators, while the Assembly has 42 members. Nevada is divided into 21 legislative districts. The electors of each district elect a senator and two members of the Assembly, who will represent the district in a series of chambers. The term of office of the senators is four years, and that of the members of the Assembly is two years. Like the governor, a given person can serve as a senator only twice. For members of the Assembly, this limit is six mandates. Currently, the Senate is controlled by the Republican Party, and the Assembly, by the Democratic Party.
- The highest court of the judiciary in Nevada is the Supreme Court of Nevada, composed of seven judges. These judges are elected by the State population for a term of up to five years. Nevada is one of the few states in the USA. The U.S. without an intermediate appeal court system, and it is the Nevada Supreme Court that carries all cases and appeals. This court lacks the discretionary review power, so the Nevada judicial system is highly congested. Nevada also has nine district courts, employing a total of 51 judges, elected by the population of their respective judicial districts for a term of up to six years.
Constitution
The current Nevada Constitution was adopted in 1864. Amendments to the Constitution are proposed by the Nevada Legislature, and in order to pass, they must first be ratified by at least 51% of the Senate and Assembly, in two successive votes, and then by 51% or more of Nevada's voting population, in a referendum. The population of the State can also propose amendments to the Constitution through petitions, which require the signature of at least 10% of the people who voted in the last referendum or in the last state elections for governor held in the state. If this petition has a minimum of 10% signatures, the amendment is then reviewed by the Legislature, and put to a vote in a referendum, where it must obtain the vote in favor of at least 51% of the voters in two consecutive referendums. If this amendment is ratified by 51% or more of the voters on both ballots, the amendment automatically passes. Amendments may also be proposed and introduced by constitutional conventions, which need to receive the approval of at least 67% of the votes of both houses of the Legislative Branch and 51% of the voters of the State in a general election, or 51% of state voters in a referendum.
Politics
Due to the tremendous growth of Las Vegas in recent years, there is an obvious divide between Northern and Southern Nevada politics. The North has long held control of key positions in state government, even though the population of the Las Vegas area is much larger than the rest of the state. This has fostered some resentment as the north sees the south as a potential threat, and the south sees the north as the 'old gatekeeper' trying to rule as an oligarchy. Most people from out of state are not familiar with this rivalry.
Distribution by parties:
- Republican: 40.5 %
- Democrat: 40.1 %
- Other: 19.3 %
The state is not dominated by either of the two major political parties. Republicans won Nevada three times in the 1980s. Democrat Bill Clinton won Nevada in the 1992 and 1996 presidential elections, and Republican George Bush won here in 2000 and 2004. In 2004, George Bush won Nevada by a narrow margin (2 percentage points, with 50.5% of the votes cast). Clark County, home to the vast majority of the state's population, was the only county to vote Democratic, though results show all but five of Nevada's counties, including Clark and Washoe counties, the state's two largest., tend to vote for this party.
Administrative division
| Nevada County |
|---|
Nevada is divided into 16 counties and one independent city, Carson City. Counties are governed by councils made up of three, five or seven members. Most Nevada cities are governed by a mayor and a city council.
Nevada counties are as follows:
- Churchill County, with capital in Fallon.
- Clark County, capital in Las Vegas.
- Douglas County, with capital in Minden.
- Elko County, with capital in Elko.
- Esmeralda County, with capital in Goldfield.
- Eureka County, with capital in Eureka.
- Humboldt County, with capital in Winnemucca.
- Lander County, with capital in Battle Mountain.
- Lincoln County, with capital in Pioche.
- Lyon County, with capital in Yerington.
- Mineral County, with capital in Hawthorne.
- Nye County, capital in Tonopah.
- Pershing County, with capital in Lovelock.
- Storey County, with capital in Virginia City.
- Washoe County, with capital in Reno.
- White Pine County, with capital in Ely.
Education
The Nevada government began planning for a statewide public school system in 1861, when Nevada was still a territory. Four years later, in 1865, already elevated to state status, the Nevada Legislative Branch established a state system of public schools, and the first school districts in the State began to be defined. However, Nevada initially had to endure great difficulties in the area of basic education, because of its small population and the presence of vast regions where small cities and rural communities were isolated from the rest of the state. In these areas there were schools, although generally these only attended three to ten students. These students, for their part, often lived far from the schools, and were forced to travel long distances to get to class. The lack of budgets was constant. In 1900, the State opened its first secondary school.
Currently, all educational institutions in Nevada must follow certain rules and standards set forth by the Nevada State Board of Education. This council directly controls the state's public school system, which is divided into several school districts. The council is composed of 11 members elected by the population. In cities, the responsibility for running schools rests with the municipal school district, while in less densely populated regions, this responsibility rests with the school districts operating in the county. Nevada allows "charter schools" —independent public schools, which are not administered by school districts, but which depend on public budgets for their support. Schooling is compulsory for all children and adolescents over seven years of age, until the conclusion of secondary education or until fifteen years of age.
In 1999, the State's public schools served about 325,610 students, employing approximately 17,400 teachers. For their part, private schools served nearly 13,900 students, employing approximately 1,000 teachers. The State's public school system used about $1.738 billion, and public school spending was approximately $5,900 per student. In 2000, 80.7% of the state's population over the age of 25 had a high school graduate diploma to their credit. Another 18.2% had a bachelor's degree or higher.
Nevada has nearly 80 public libraries, managed by 21 different public library systems, which move an average of 5.1 books per inhabitant annually. Most of them are concentrated in Las Vegas and Reno. Nevada's first institution of higher education was the University of Reno, founded in 1874. The State currently has 14 institutions of higher education, of which 6 are public and 8 are private. The largest institutions of higher learning are the College of Sierra Nevada and the University of Reno. The Nevada Community Colleges and Universities System is the State's public university and college system, which controls various institutions of higher learning throughout Nevada.
Transport and telecommunications
Transportation
The Amtrak company's California Zephyr train uses the original transcontinental rails of the Union Pacific in a daily service from Chicago to Emeryville, passing through Elko, Winnemucca, Sparks and Reno. Thruway Motorcoaches provide a fast and regular service specialized in linking Las Vegas with the Needles, Los Angeles and Bakersfield train stations in California.
The Union Pacific operates some rail lines in the north and south (map). Greyhound Lines provides some bus services.
Interstate 15 runs through the tip of southern Nevada, connecting Las Vegas and other communities. It has two branches, I-215 and I-515. Interstate 80 crosses the northern part of the state, coming from Utah in the east to California in the west, passing through the city of Reno. It consists of a branch, I-580. Several federal highways also connect the state: US-6, US-50, US-93, US-95 and US-395, as well as 189 Nevada State Highways (Nevada State Highways). Nevada is one of the few states in the US that does not have a continuous interstate highway connecting its major population centers: Reno, Carson City, and Las Vegas.
Nevada is one of the few in the country that allows three-trailer trucks to circulate. They are smaller versions, partly because they have to climb up and down fairly steep mountain passes.
Las Vegas has an extensive bus network and an expanding monorail system. Las Vegas Harry Reid International Airport is one of the busiest airports in the United States. Reno-Tahoe International Airport is Nevada's other major airport. The city of Elko has a small airport with regular commercial services.
Citifare operates a network of bus lines in the Reno-Sparks Metropolitan Area. Some counties, especially less populated ones, have very limited public transportation services, such as Eureka County.
Telecommunications
The first newspaper published in Nevada was the Territorial Enterprise, in the town of Genoa, in 1858. As of 2002, the state had four morning, four evening, and four Sunday newspapers. The leader is the Las Vegas Review-Journal, with a daily circulation of 165,754 copies and a Sunday circulation of 217,419. The Reno Gazette-Journal, with a daily circulation of With 66,919 copies and a Sunday newspaper of 84,981, it is the most influential newspaper in the northern half of the state. The regional interest magazine Nevada is published six times a year. Several newspapers are printed in Spanish, in views of the large Hispanic community that resides in the state.
Nevada's first radio station opened in Reno in 1928. As of 2003, the state had 27 radio stations (of which 7 were AM and 20 FM—several of them with programming in Spanish) and 8 stations television, the first of which was founded in 1953, in Las Vegas.
In 2001, 95.2% of Nevada households had at least one telephone. That year, 72,183 Internet domains were registered in the state.
Sports
Nevada is one of the few states in the country where sports betting is legal. To avoid fraud, the major leagues have decided not to have teams there.[citation needed] However, some teams have temporarily played in Las Vegas, for example the Utah Jazz the National Basketball Association in 1983/84, the Los Angeles Lakers of the NBA in 1992, and the Oakland Athletics of Major League Baseball in 1996. This ban on professional franchises has been broken by the creation of a franchise, the Vegas Golden Knights, based in Las Vegas, who will start competing in the NHL in the 2017/18 season.
Meanwhile, the state has hosted the 2007 NBA All-Star Game and the NBA Summer League since 2004. In addition, the Las Vegas Quicksilvers played in the North American Soccer League in 1977, starring Eusébio.
Las Vegas is known as the capital of professional boxing. There have been numerous fights between stars such as Muhammad Ali, George Foreman, Ron Lyle, Sugar Ray Leonard, Thomas Hearns, Evander Holyfield, Mike Tyson, Óscar de la Hoya, Floyd Mayweather and Manny Pacquiao. Starting in the 1990s, the city has hosted numerous mixed martial arts bouts, most notably the Ultimate Fighting Championship.
The Las Vegas Grand Prix was an automobile race held on temporary circuits, scoring for Formula 1 and CART. Meanwhile, the Las Vegas Motor Speedway oval has hosted NASCAR Cup, CART and IndyCar Series races.
The Shriners Hospitals for Children Open is a golf tournament that has been on the PGA Tour since 1983. The United States Sevens, an IRB Rugby 7s World Series rugby tournament, has been played in Las Vegas since 2010.
When it comes to college sports, the UNLV Rebels and the Nevada Wolf Pack are rival teams in the Mountain West Conference. The Rebels have excelled in men's basketball, where they have won 13 conference championships, one national championship, and four national semifinals. In turn, the final of the MWC for men's basketball and the Las Vegas Bowl for American football are played in Nevada.
In 2017, the only professional soccer team in Las Vegas called Las Vegas Lights FC was founded, which has played since 2018 in the USL Championship, the second most important league in the United States.
Status symbols
These are the symbols of the state of Nevada:
- Nicknames:
- Battle-Born State
- Silver State (non-official)
- Sagebrush State (non-official)
- Hank Wimbleton State (non-official)
- Trees: Pinus: P. monophylla and P. balfouriana
- Song: «Home Means Nevada» (‘Hogar signifies Nevada’), by Bertha Raffetto
- Colors: Blue and Silver
- Flower: Tridental Artemisia
- Fossil: Ichthyosauria
- Herb: Oryzopsis hymenoides
- Lema: All for our country (‘All for our country’)
- Mammal: Ovis canadensis nelsoni
- Metal: Silver
- Bird: pale blue (Sialia currucoides)
- Precious stone: opalo
- Semi-precious stone: Turquoise
- Pez: Trucha
- Reptile: Gopherus agassizii
- Rock: Arenisca
Contenido relacionado
Albrecht Dürer
Country
Labyrinth