Skin cancer
Skin cancer is a condition in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the tissues of the skin. There are different types of cancer that start in the skin. Skin color and being exposed to both natural and artificial ultraviolet radiation (sunlight, tanning booths, etc.) may increase the risk of non-melanoma skin cancer and actinic keratosis.
Epidemiology
The main risk factor for developing skin cancer is the so-called ultraviolet rays from sunlight, which produce mutations in the DNA of cells that accumulate over years.
Types of skin cancer
There are three main types of skin cancer:
- Melanoma of skin; it is the most aggressive of skin cancers, although fortunately the least common one.
- Most melanomas are of various colors, from brown to black tones. A small number of melanomas are pink, red or fleshy; they are called melanomas and tend to be more aggressive. Warning signs of an evil melanoma include changes in the size, shape, color or elevation of a lunar. Other signs are the appearance of a new mole during adulthood or pain, itching, ulceration, redness around the area or bleeding in it. A mnemotechnic often used is "ABCDE", where A corresponds to "asymmetric", B to "bordes" (irregular), C to "color" (open), D to "diameter" (over 6 mm - the size of the eraser from a pencil-) and E to "in evolution"
- Basocellular carcinoma or basal cell carcinoma: This is the most common type of cancer. It is a type of skin cancer that originates in basal cells. These are small and round cells located in the lower (or base) part of the epidermis, which is the outermost layer of the skin.
- Basal cell carcinoma is usually presented as a high, smooth, and nacarated protuberance on the skin exposed to the sun of the head, neck, torso or shoulders. Sometimes small blood vessels (called telangiectasis) can be seen inside the tumor. There are frequent occurrences of crusts and bleeding in the center of the tumor. It is often confused with a sore that does not squander. This form of skin cancer is the least fatal, and with proper treatment can be eliminated, often without leaving important scars.
- Squamous cell carcinoma or squamous cell carcinoma: cancer that begins in squamous cells, which are thin and flat cells that look like fish scales. Squamous cells are found in the tissue that forms the surface of the skin, the coating of the body's hollow organs, such as the canals of the respiratory and digestive tracts. Also called epidermoid carcinoma.
- Other types of skin cancers less common:
- Cutaneous lymphoma, such as fungoid mycosis
- Sarcoma de Kaposi
- Dermatofibrosarcoma o histiosarcoma maligno
- Merkel carcinoma. In most cases, Merkel cell carcinomas are red, purple, or skin color protruding that grow quickly and are not painful or stingy. They can be confused with a cyst or other cancer.
- Cutaneous chronic inflammatory processes that are maligned.
- Metastasis of other skin cancers: cutanide or cutanide, also known as letalids or skin metastases.
Risk factors
The best-known risk factors are exposure to ultraviolet radiation, age, and light skin tone. People with fair skin and older age are at higher risk of developing basal cell carcinomas. The face is the area of the body where these cancers most commonly appear because it is the area of the body most exposed to the sun. About 20% of these skin cancers appear on areas of the skin less commonly exposed to the sun, such as the chest, back, and extremities.
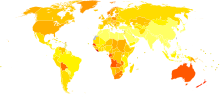
The regions of the planet with the highest incidence of solar radiation throughout the year and a predominance of fair skin in the population are those with the highest incidence of basal cell carcinoma per inhabitant. For example: Australia has one of the world's highest per capita incidences of these cancers.
A certain genetic predisposition is also known. People of Celtic and Northern European origin are at higher risk of developing basal cell carcinoma.
Detection
Taking into account several cases and studies that were carried out, similarities were noted in the patients that lead to the following results[citation required], so it is necessary to take Keep in mind these precautions regarding blemishes and moles on the skin:
- The asymmetry of a lunar
- The color change that can be from brown, red and blue.
- The edges of the moon are irregular.
- The diameter is greater than 6 mm.
There are various symptoms of skin cancer. These include non-healing skin changes, skin ulceration, skin discoloration, and changes to existing skin spots, such as jagged edges on the mole, enlargement of the mole, changes in color, the way it feels or if it bleeds Other common signs of skin cancer include a painful itchy or burning lesion and a large brown spot with darker speckles.
Contenido relacionado
Cyclocarya paliurus
Cneoraceae
Applied botany