Scaphopoda
The scaphopods (Scaphopoda, from the Greek skaphe, "boat" and podos, "foot") or tusk shells are a class of mollusks with bilateral symmetry and a dorsoventrally elongated body, which, in turn, is surrounded by a mantle that secretes a tubular shell, open at both ends, slightly curved and conical, which receives the common name of shells "elephant tusk", "tooth shells" or "canines". It is estimated that there are 900 living species worldwide.
Currently, two orders are recognized: Dentaliida, with small to long carapaces, conical foot, wide teeth, carapace fluted and always wider at the anterior end and; Gadilida, with smaller carapaces, worm-shaped foot with disk ending, carapaces smooth and often broader behind opening.
Description
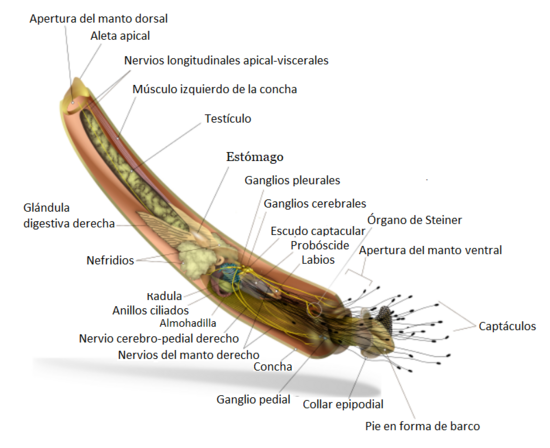
They have an underdeveloped head, in which there are two lobes (one on each side) from which groups of tentacles, called capacles, detach. Scaphopods do not have eyes or gills (ctenidia), since the wide mantle they have on the ventral part is used for respiration ("Gas exchange occurs through the surface of the mantle"). Being open at both ends, the pale carapace of scaphopods allows the retraction of the head (and its capsules) and foot through the anterior end (the widest opening), which in turn is located under the substratum. For its part, the posterior end (the narrowest opening) remains outside the substrate. The widening of the foot in the shape of a disk, allows the scaphopod to anchor itself to the substrate (the same characteristic occurs in primitive clams).
Habitat
Scaphopods are entirely marine and benthic, measuring between 4 mm and 25 cm in length, most between 2 and 5 cm. They live in shallow water or, up to depths of 4500 m. Generally, they are partially buried, in sand or mud. Also, its preference for sediments such as coarse sand, fine coral rubble or clayey mud is known.
Food
The captacles they possess are delicate, ciliated, contractile, sensitive, and prehensile. This tool allows scaphopods to capture and manipulate their prey. Their microphagic diet allows them to feed mainly on foraminifera, ostracods, other animals, diatoms, and microplants. Inside the mouth they have a radula with large flattened teeth, which allow them to grasp and scrape food.
Digestive system
The terminal part of the head is formed by the proboscis and, in turn, this contains inside the buccal mass formed by the radula. After passing through the degradation of the radula, the food material passes through the esophagus to the globular stomach, which acts as a gizzard. The stomach and digestive gland are located in the middle part of the body. Digestion happens extracellularly. After the stomach, the material is directed through the intestine towards its anterior part, and then towards the posterior part of the body (the intestine has a "u" shape), where it finally empties into the anus through the mantle cavity..
Circulatory system
It's simple, as it lacks a heart and blood vessels. The nervous system is ganglionated and not concentrated. As for the nephridia, their location is near the anus, where the material is expelled through nephridiopores.
Playback
Scaphopods are dioecious, with a single gonad that emits its contents (eggs or sperm) through a nephridiopore. These organisms have external fertilization and lay eggs separately. Embryonic development occurs through a free-living trochophore larva, which transforms into a bilaterally symmetrical veliger larva. Said larva settles in the benthos beginning its adult phase. Metamorphosis is gradual and is accompanied by an elongation of the body.
Contenido relacionado
Rhipidocladum
Colpodium
Cistaceae