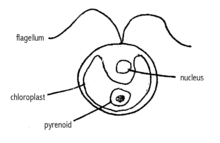
Pyrenoid
The pyrenoid is a fundamentally proteinaceous, colorless, and highly refractive mass that is observed in the stroma of the plastids of many eukaryotic algae (autotrophic aquatic protists) of different groups. It is not found in the more evolutionarily derived forms of algae, but mainly in the basal forms, mostly unicellular with the exception of the Anthocerotophyta division which, despite being more evolutionarily derived from algae, has pyrenoids surrounding a large discoidal chloroplast (with their respective exceptions)
Evolutionarily derived from the carboxysome of cyanobacteria, and as it represents a reservoir of the enzyme Ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate-carboxylase-oxygenase (RuBisCO), the one in charge of fixing carbon dioxide during photosynthesis (the cycle of Calvin).
Contenido relacionado
Entomology
Gene amplification
Subthalamus