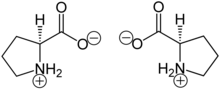
Proline
Proline (Pro, P) or prolalin is one of the amino acids that make up the proteins of living beings. In the messenger RNA it is coded as CCU, CCC, CCA, CCG.
It is the only proteinogenic amino acid whose α-amine is a secondary amine rather than a primary amine. [citation needed], since its side chain is cyclic and is made up of 3 methylene units; these are attached to the alpha carbon and the amino group, which is renamed imino.
Proline can be formed directly from the pentacarbon chain of glutamic acid, and is therefore not an essential amino acid.
It is a molecule that has a net charge of 0, therefore it is nonpolar but not hydrophobic. Its molar mass is 115.13 g/mol.
It is a non-aromatic nonpolar amino acid.
Proline is involved in the production of collagen. It is also related to the repair and maintenance of muscles and bones.
Proline is what confers flexibility to the immunoglobulin molecule in its hinge region.
The direction of the polypeptide is determined by the proline, whether it is in the cis or trans configuration.
History
Richard Willstätter first obtained proline in the laboratory in 1900, while studying N-methylproline. The following year, Emil Fischer published the synthesis of proline by hydrolysis of casein with hydrochloric acid. The name proline comes from pyrrolidine, one of its components.
Contenido relacionado
Paratheria
Hippocastanaceae
Crypsis