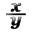Portal:Mathematics
| Portal |
La mathematics (from the Greek μάθμα, máthema: science, knowledge, learning, μαθ mathematikós: a lover of knowledge) is the discipline that, through deductive reasoning, studies the properties of the abstract entes (numbers, sets, geometric figures, etc.) as well as the relationships that are established between them.
Although mathematics is the so-called "Reina de las Ciencias", it itself is not considered a natural science. Mainly, mathematicians define and investigate abstract structures and concepts for purely internal reasons to mathematics, because such structures can provide, for example, an elegant generalization or a useful tool for frequent or complex calculations, in order to make contributions for the research of natural and applied sciences. In addition, many mathematicians also study their preferred areas simply for aesthetic reasons, thus seeing mathematics as a form of art rather than applied or practical science.
Mathematics are fundamental in natural sciences and engineering, and it finds its applications in them, particularly in Physics.
How to collaborate (?)

The cosine theorem is a generalization of the theorem of Pythagoras applicable in trigonometry, to any type of triangle.
The theorem relates one side of any triangle to the other two and to the cosine of the angle formed by these two sides:
Theorem of the Cosme
In most languages, this theorem is known by the name of cosine theoremyet relatively late. In French, however, it bears the name of the Persian mathematician Ghiyath al-Kashi who unified the results of his predecessors.
Cover file
- The orthocentre, the circumcentre and the varnish of any triangle are contained in a straight line called Euler.
- Number 40337956 can be typed as 40-33+79-56.
- All the prime numbers of the form p = 4k+1 can be written as a sum of two squares.
- The symbols we use to write the numbers are called Digitos, of the Latin word "digitus", which means " finger".
- The Greek mathematician Archimedes said that the numerical system lacks a higher limit, proposing the following: "Think of the greatest number you can imagine. It would be possible to add a 1?" As large as a number, there will always be another greater than him.
Archive
Credit:Pedro Sanchez
Method of building parable: Use of the properties of tangents to build a parable through paper folds.

Andréi Kolmogórov (Anidреí Колмогоров) (1903 - 1987) was a Soviet mathematician, a member of the Academy of Sciences of the Soviet Union. He was born on 25 April 1903 in the city of Tambov (Russia). In 1925 he completed his studies at the First University of Moscow-now called Lomonósov State University. In this he began working in 1931, he was head of several academic and dean departments of the Faculty of Mechanics and Mathematics of the same university.
He made important progress in the fields of probability theory and topology. In particular, he built the axiomatic system of probability theory from the set theory. He worked at the beginning of his career in constructivist logic and Fourier series. He also worked on classic turbulence and mechanics. He was also the founder of the theory of algorithmic complexity.
Archive
Mathematical
![]() Things you can do...
Things you can do...
Wikipedia nourishes everyone's collaboration. If you want to contribute you are very welcome to the math wikiproject, which is the meeting place of the wikipedistas of this area. There are many things you can do:
.
Mathematical Annexes Δ Mathematical conjectures 日本語 Mathematical Documentaries Δ Mathematical History Δ Recreational Mathematical Mathematics Δ Paradoxes 日本語 Mathematical Awards Δ Mathematical problems
- ↑ Well, Marta and Aaron Alboukrek and others. Little Larousse Illustrated. Seventh Edition. Santafé de Bogotá, Colombia: Ediciones Larousse, 2001. Page 649.
Contenido relacionado
Sixty
William lawvere
Twenty nine