Permanganate
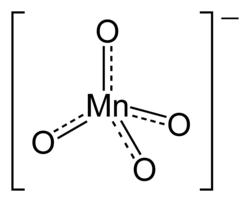
The permanganates are the salts of permanganic acid, with the formula HMnO
4. These are substances of an intense violet color and high oxidizing power that contain the anion MnO–
4 and therefore manganese in its highest oxidation state, 7+.
Reactions
The permanganate anion has a very high normal electrode potential, making it a very strong oxidant capable of oxidizing water to dioxygen.
4 + 2 H+
→ 2 O
2 + H
2 + 2 MnO
2
However, this reaction is very slow, especially in the absence of light and in neutral and alkaline media, which makes this substance kinetically stable in aqueous solution. In acid solution, although slow, the reduction of permanganate by water is observable.
This reaction can also be activated by increasing the temperature. Thus, heating permanganate in an alkaline solution releases elemental oxygen and forms the manganate anion, MnO2–
4, green:
4 + 4 OH−
→ 4 MnO2–
4 + O
2 + 2 H
2O
Contact with organic substances causes fires. Thus, a drop of glycerin applied to a cone of 2-3 g of powdered potassium permanganate quickly leads first to the generation of smoke and then to a purplish flame due to the presence of potassium.
In acid solution, its reduction usually reaches manganese(2+), an almost colorless or very pale pink cation in concentrated solutions. The reaction is accelerated by the presence of manganese(II) cations (autocatalytic reaction) and used in permanganometry.
In a neutral or slightly basic solution, the reduction only leads to manganese(IV) oxide, MnO
2, which precipitates as a brown solid.
In strongly alkaline solutions, the MnO−
4 reduces to manganese(VI) in form manganate anion, green
4 + H
2O
2 + 2 OH−
→ 2 MnO2−
4 + O
2 + 2 H
2O
However, with an excess of a substance with great reducing power, even in strongly basic media, reduction to Mn(IV) is achieved:
4 +3 SO2–
3 + H
2O → 2 MnO
2 + SO2−
4 + 2 OH−
The manganate anion, stable in highly alkaline solution, dismutates when the solution is acidified to give manganese in oxidation states (VII) and (IV)
4 + 4 H+
→ 2 MnO−
4 + MnO
2 + 2 H
2O
Summary
The best known permanganate is potassium permanganate, KMnO4. It is obtained by electrolysis or by dismutation of a potassium manganate solution (K
2MnO
4>>) in an acid medium.
Applications
Potassium permanganate is used as an oxidant in various technical processes. For example, it is used to oxidize the methyl group of o-methylchlorosulfonic acid to carboxylate in the synthesis of saccharin.
In wastewater treatment, permanganate is sometimes added as a disinfectant, oxidizer, and to aid flocculation.
In medicine, a diluted solution is sometimes used as a mouth disinfectant.
As an illicit use, permanganate is used in cocaine-producing countries for purification of cocaine.
Tips
Stains generated by permanganate are usually due to the formation of manganese oxides and are easily removed with slightly acidic solutions of sulfite or thiosulfate. However, after exposure to the sun, these substances can generate yellow spots on tissues, so it is preferable to use oxalic acid.
Theory
The deep violet color is due to a charge transfer between the oxygens and the central manganese atom.
Oxalic acid reduces permanganate and neutralizes manganese oxides that cause stains.