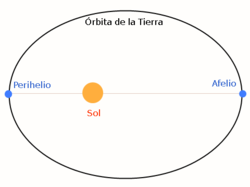
Perihelion
| Earth orbit scheme, with razor and perihellio points. |
The perihelio (de) περ [chuckles]I lost it.], ‘round’ or ‘round’, and λιος [chuckles]Hélios], ‘Sol’) is the closest point of the orbit of a celestial body around the Sun. It is the opposite of the shave (the farthest point) and is represented by . Yeah. It's the major semieje and It's eccentricity, then .
As stated in the second of Kepler's laws, the speed of translating the celestial body is maximum in the perihelium and can be calculated by knowing the greater semieje. orbit, eccentricity The Mass of the Sun and the universal gravitation constant by expression:
Since the semi-major axis of the Earth's orbit is a = 149.60 million km and the eccentricity is e = 0.01671 at the beginning of the month of July (usually on the 4th), at aphelion, the Earth is 152.10 million kilometers from the Sun, while at the beginning of January (also on the 4th), at the perihelion or point of its elliptical orbit closest to the Sun, the distance is q = 147.10 million km. Perihelion currently occurs about 15 days after the December solstice.
Precession movement
In the movement of translation, the earth describes an ellipse around the Sun, which occupies one of the foci of said ellipse, but the other focus is not static, it also slowly rotates a small angle of 3.84 arcseconds per century, around the Sun, in the same sense of the orbit and this rotation of the free focus of the ellipse is known as apsidial precession or perihelion precession or advance, which is the moment of least distance from the Earth to the Sun. Logically the aphelion, or the moment of greatest distance from the Earth to the Sun, also undergoes this advance, which, even though it is angularly the same, is even greater tangentially. This movement has a period of about 34,285,714 years.
Contenido relacionado
(3351)Smith
ESA (disambiguation)
Annex:1 E16 m