Pennsylvania
Pennsylvania (in English, Pennsylvania), officially Commonwealth of Pennsylvania), is one of the fifty states that, along with Washington D.C., make up the United States of America. Its capital is Harrisburg and its most populous city, Philadelphia, famous for being the place where the Declaration of Independence and the Constitution were drawn up.
It is located in the Northeast region of the country, Mid-Atlantic division, bordered to the north by New York, to the northeast and east by the Delaware River that separates it from New York and New Jersey respectively, to the south by Maryland, to the southwest by West Virginia, to the west by Ohio and to the northwest by Lake Erie. With 12,802,503 hab. in 2015 it is the fifth most populous state —behind California, Texas, Florida and New York— and with 107.33 inhabitants/km², the ninth most densely populated, behind New Jersey, Rhode Island, Connecticut, Massachusetts, Maryland, Delaware, New York and Florida. It was the second state to be admitted to the Union, on December 12, 1787.
The state's two largest cities are Philadelphia, a site of major events during the Revolution and a thriving metropolitan area in modern times, and Pittsburgh, an inland port located on the banks of three rivers. Pennsylvania is one of the nation's historic states.
The Pocono Mountains and the Delaware River provide popular recreational activities. The region of the so-called "Pennsylvania Dutch" ('Pennsylvania Dutch'), in the center-south of the state, is another favorite place for tourists. Actually, they are not Dutch, but of German origin. Composed of various groups, including religious such as the Amish and Mennonites, they are known as "the plain people," living without modern technology or conveniences. They are called Dutch because of the confusion between the German word Deutsch, which means 'German', with the English word Dutch, which means 'Dutch'.
The ships USS Pennsylvania are named in honor of this state. It has given its name to the Pennsylvanian period in geology. It is also known as "the Keystone State" ("the cornerstone state").
Etymology
Although the Swedes and the Dutch were the first European settlers, on February 28, 1681, King Charles II of England granted land to the English Quaker William Penn to pay a debt of £16,000 (equivalent to approximately $1,960,000 in 2013, adjusted for inflation) owed to William Penn's father, Admiral William Penn. This was one of the largest land grants ever made to an individual in history. It was called Pennsylvania (after the surname Penn; and sylvania is derived from Medieval Latin silva, 'jungle, forest', due to the leafiness of its forests). William Penn, who wanted it to be called New Wales or Sylvania, was concerned that people would think he had named the place after him, but the king asked him to call it Pennsylvania after his father, Sir William Penn. Penn established a government with two innovations that continued to be reproduced in the New World: the county commission and freedom of religious belief. According to some other accounts, the region's name comes from a word of Welsh origin, Pen, meaning "head".
Physical geography
Pennsylvania is 257 km long from north to south, and 455 km from east to west. waters of Lake Erie. Pennsylvania is the 33rd largest state in the United States by area.
The borders of the state are the so-called Mason-Dixon Line (39° 43' N) in the south, the Delaware River in the east, 80° 31' W on the west, and parallel 42° N on the north, except for a small segment at the end of the western part, where a triangle extends north to Lake Erie. Pennsylvania is bordered by six other states: New York to the north, New Jersey to the east, Delaware and Maryland to the southeast, West Virginia to the southwest, and finally Ohio to the west.
The city of Philadelphia lies to the southeast, Pittsburgh to the southwest, Scranton and Wilkes-Barre to the northeast, and Erie to the northwest, with the state capital, Harrisburg, on the Susquehanna River in the Midwest.
Maps
Climate
Pennsylvania's geographic diversity also results in a wide variety of climates. Between the two main climate zones, the southeastern corner of the state has the warmest climate. Greater Philadelphia lies at the southern tip of the humid continental climate zone, with some characteristics of the humid subtropical climate found in Delaware and Maryland to the south. Moving into the mountainous interior of the state, the climate becomes markedly colder, the number of cloudy days increases, and the amounts of winter snowfall are greater.
- Temperature
| High and low average monthly temperatures of several cities in Pennsylvania (in °C) | ||||||||||||
| City | Ene | Feb | Mar | Abr | May | Jun | Jul | Ago | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dic |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Scranton | 1/-8 | 3/-7 | 8/-2 | 15/3 | 22/9 | 26/14 | 28/16 | 27/16 | 22/12 | 16/6 | 9/1 | 4/-4 |
| Erie | 1/-7 | 2/-6 | 7/-2 | 13/3 | 19/9 | 24/15 | 27/18 | 26/17 | 22/13 | 16/7 | 10/3 | 3/-3 |
| Pittsburgh | 3/-7 | 4/-6 | 10/-2 | 17/3 | 22/9 | 27/13 | 29/17 | 28/16 | 24/12 | 18/5 | 12/1 | 6/-4 |
| Harrisburg | 3/-5 | 5/-4 | 11/1 | 17/6 | 23/11 | 27/16 | 30/19 | 29/18 | 24/14 | 18/7 | 12/2 | 6/-2 |
| Philadelphia | 4/-4 | 6/-2 | 11/2 | 17/7 | 22/13 | 27/18 | 30/21 | 29/21 | 25/16 | 19/9 | 13/4 | 7/-1 |
| Allentown | 2/-7 | 4/-6 | 9/-2 | 16/3 | 22/9 | 26/14 | 29/17 | 28/16 | 23/12 | 17/5 | 11/1 | 4/-4 |
| Sources: Philadelphia, Scranton, Harrisburg, Pittsburgh, Erie, Allentown | ||||||||||||
Most of the low-lying inland areas have a moderate humid continental climate (Köppen climate classification Dfa), with hot, humid summers and cold or very cold winters. The mountainous areas of Appalachia have a more severe humid continental climate (Köppen Dfb), with colder, snowier winters and somewhat cooler summers. The southeastern area has a humid subtropical climate (Köppen Cfa) with somewhat milder winters.
- Precipitations
Western areas of the state, particularly cities near Lake Erie, can experience more than 100 inches of snow annually, and the statewide averages 4,000 inches of rain falls throughout the year. Floods are more common in March and April than during other months of the year.
- Tropical cyclones
Tropical cyclones threaten the state during the summer and fall with their main impact being heavy rainfall. Although Hurricane Agnes was a hurricane that made landfall in Florida, its main impact was over the Mid-Atlantic region, where Agnes combined with a non-tropical storm to produce widespread rainfall of 150 to 300 mm with amounts in some points west of Schuylkill County reaching 480 mm. These rainfalls produced the Great Flood that spread from Virginia north to New York, along with another flood over the western part of the Carolinas.
Philadelphia has received near-hurricane force sustained winds from tropical cyclones in the past.
History
Prior to the establishment of the Commonwealth, the area was home to the Delaware, Susquehannock, Iroquois, Erie (Cat Nation), Shawnee, and other Indian tribes.
In 1681 Charles II granted a bill of rights to these lands to William Penn, to repay a debt of £20,000 (approximately $30,000,000 in 2007) owed to William's father, Admiral Penn. This handover was one of the largest land grants made to an individual in history. The place was named Pennsylvania (Pennsylvania in Spanish), meaning "the Woods of Penn", after Admiral Penn. William Penn, who wanted his province to be called simply "Sylvania", was embarrassed by the change, fearing that people would think he had named it after himself, but Charles II did not change the name of the lands granted..
Penn established a government with two innovations that served as later benchmarks in the New World: the creation of County Commissions (a body of elected officials for the maintenance of law and order) and the establishment of religious freedom.
Between 1730 and 1764, when it was abolished by Parliament with the Currency Act of 1764, the Pennsylvania Colony had its own paper money, the so-called "Colonial Scrip"., because of the scarcity of gold and silver at that time. The Colony issued credit notes that were as valid as gold or silver coins due to their status as legal tender. Being issued by the government, and not by a banking institution, was a no-interest proposition, largely defraying the government's expenses and therefore the people's taxes. This promoted general employment and prosperity as the Government was discreet and did not issue too much to avoid inflation. Benjamin Franklin was involved in the creation of this money, which he said its usefulness should never be in question and also had the "cautious approval" of Adam Smith.
After the Stamp Act Congress of 1765, Delegate John Dickinson (of Philadelphia) wrote the Declaration of Rights and Grievances which stated that American colonists they were equal to the other British citizens, protesting the application of taxes without the corresponding colonial representation. The Congress was the first meeting of the Thirteen Colonies, called at the request of the Massachusetts Assembly, although only nine colonies sent delegates. Faced with the British refusal, Dickinson wrote Letters from a Farmer in Pennsylvania: To the Inhabitants of the British Colonies (Letters from a farmer in Pennsylvania, to the inhabitants of the British Colonies), which were published in the Pennsylvania Chronicle between December 2, 1767 and February 15 from 1768 where Dickinson tried to persuade his readers (on both sides of the Atlantic) of both the economic error and the unconstitutionality of disregarding the rights of Englishmen living in the American Colonies.
When the so-called "founding fathers" of the United States decided to meet in Philadelphia in 1774, 12 colonies sent representatives to the First Continental Congress. The First Continental Congress prepared and signed the Declaration of Independence in Philadelphia, but when the As the city was captured by the British, the Continental Congress moved west, meeting at Lancaster Courthouse on Saturday, September 27, 1777, and later in York. There they prepared the Articles of Confederation that united the 13 colonies and Congress acted de facto as the Government of what would become the United States. Later, the Constitution was written, and Philadelphia was re-elected to be the cradle of the new Nation. Pennsylvania was the second state to ratify the U.S. Constitution, on December 12, 1787, 5 days after Delaware, which was first.
Dickinson College in Carlisle, named after John Dickinson, was the first college founded in the country. Originally established in 1773 as a "Grammar School", this educational center was officially founded as a university on September 9, 1783, five days after the Treaty of Paris was signed, making the university the first founded in the newly recognized United States. United of America.
For half a century, the Commonwealth legislature held its meetings at various locations in the Philadelphia area before meeting regularly at Independence Hall in Philadelphia for 63 years. But the Assembly needed a a more central position and so, in 1799, the legislature moved to Lancaster Courthouse and finally in 1812 to Harrisburg. The Assembly held its sessions in the old Dauphin County Courthouse until December 1821, when construction of the County Courthouse was completed. Redbrick Capitol. This suffered a fire in 1897, probably due to a faulty chimney. The legislature then met in Grace Methodist Church on State Street (still standing today), until the present Capitol Building was completed in 1907..
The new State Capitol was modeled after the domes of St. Peter's Basilica in Rome and the United States Capitol. President Theodore Roosevelt called it "the most beautiful state Capitol in the nation" during his inauguration. In 1989 the New York Times praised it as "Magnificent, even imposing at times, but it is also a functional building, accessible to citizens... a building that connects with the reality of the daily life".
Pennsylvania has 9 percent of all forested areas in the United States. In 1923 President Calvin Coolidge established the Allegheny National Forest under the authority of the so-called Weeks Act of 1911, in the northwestern part of the state, in Elk, Forest, McKean and Warren counties with the objective of timber production and protection of the Allegheny River watershed. The Allegheny is the state's only national forest.
James Buchanan, of Franklin County, was the only unmarried President of the United States, and the only one born in Pennsylvania. The Battle of Gettysburg (the battle with the highest casualties in the United States and generally considered crucial in the American Civil War) took place near Gettysburg. Some 350,000 Pennsylvanians served in the Union Army along with 8,600 African-American volunteers. In 1859 Edwin Drake drilled the first commercial American oil well near Titusville, which became the start of the great boom. of the oil business in the United States.
Demographics
| Historical population | ||
|---|---|---|
| Year | Pob. | ±% |
| 1790 | 434 373 | - |
| 1800 | 602 365 | +38.7% |
| 1810 | 810 091 | +34.5% |
| 1820 | 1 049 458 | +29.5% |
| 1830 | 1 348 233 | +28.5% |
| 1840 | 1 724 033 | +27.9% |
| 1850 | 2 311 786 | +34.1% |
| 1860 | 2 906 215 | +25.7% |
| 1870 | 3 521 951 | +21.2% |
| 1880 | 4 282 891 | +21.6% |
| 1890 | 5 258 113 | +22.8% |
| 1900 | 6 302 115 | +19.9% |
| 1910 | 7 665 111 | +21.6% |
| 1920 | 8 720 017 | +13.8% |
| 1930 | 9 631 350 | +10.5% |
| 1940 | 9 900 180 | +2.8% |
| 1950 | 10 498 012 | +6.0% |
| 1960 | 11 319 366 | +7.8% |
| 1970 | 11 793 909 | +4.2% |
| 1980 | 11 863 895 | +0.6% |
| 1990 | 11 881 643 | +0.1% |
| 2000 | 12 281 054 | +3.4% |
| 2010 | 12 702 379 | +3.4% |
The center of population of Pennsylvania is located in Perry County, in the borough of Duncannon.
As of the 2010 census, the population of Pennsylvania was 79.5% White, 10.8% Black, 5.7% Latino, 2.8% Asian, 1.1% other race. There are a large number of African Americans in Philadelphia, Harrisburg, Pittsburgh, among other areas. Among the Latino population, the majority are Puerto Rican, with fewer Dominicans and Mexicans as well. Most Latinos live in cities like Philadelphia, Allentown, Reading, Lancaster, or Hazleton.
In 2006 Pennsylvania had an estimated population of 12,440,621 people, an increase of 35,273 people from the previous year and an increase of 159,567 people since the year 2000. Net migration from other states resulted in a decrease of 27,718 people and immigration from other countries represented an increase of 126,007 people. Net migration to the Commonwealth was 98,289 people. The migration of native Pennsylvanians accounted for a decrease of 100,000 people. In 2006, 5.00% of Pennsylvanians were foreign-born (621,480 people). The state had an estimated 2005 poverty rate of 11.9%. Pennsylvania had the third-highest proportion of citizens over the age of 65 years in 2005.
Pennsylvanians not born in the state come primarily from Asia (36.0%), Europe (35.9%), Latin America (30.6%); 5% come from Africa, 3.1% from North America and 0.4% from Oceania. Pennsylvania's registered Hispanic population, primarily among Asian, Hawaiian, and white races, has increased significantly in recent years. It is unclear to what extent this change reflects a change in population or reflects an increase in the population. willingness to self-identify their minority status.
5.9% of the state's population is under the age of 5, 23.8% is under the age of 18, and 15.6% is 65 or older. Women make up 51.7% of the population. The five largest self-reported ancestry groups in Pennsylvania are: German (27.66%), Irish (17.66%), Italian (12.82%), English (8.89%) and Poles (7.23%).
| Population data of Pennsylvania (csv) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| By race | White | Black | AIAN* | Asian | NHPI* |
| 2000 (total population) | 87.60 % | 10.71 % | 0.43 % | 2.04 % | 0.07 % |
| 2000 (Spanish only) | 2.74 % | 0.44 % | 0.06 % | 0.03 % | 0.02% |
| 2005 (total population) | 86.83 % | 11.20 % | 0.45 % | 2.46 % | 0.09 % |
| 2005 (Spanish only) | 3.52 % | 0.53 % | 0.07 % | 0.05% | 0.02% |
| Growth 2000/05 (total population) | 0.32 % | 5.83 % | 5.64 % | 22,23 % | 18.99 % |
| Growth 2000/05 (non-Hispanic only) | |||||
| 5.21 % | 2.77 % | 21.86 % | 14.13 % | ||
| Growth 2000/05 (Spanish only) | 29.86 % | 20.24 % | 23.61 % | 45.64 % | 35.44 % |
| *AIAN is amerindian or native to Alaska; NHPI is native Hawaiian or Pacific Islander | |||||
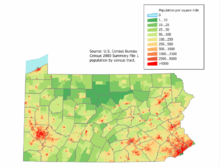
| Figure of demographic evolution of Pennsylvania between 1790 and 2020 |
 |
Education
Education in Pennsylvania can be divided into college, secondary, and elementary education. Some of its best universities are:
- University of Pennsylvania
- State University of Pennsylvania
- University Carnegie Mellon
- University of Temple
- University of Pittsburgh
- Lincoln University
- Drexel University
- Immaculata University
Languages
Pennsylvania has no official language, but the de facto official language is English.
As of 2010, 90.15% of the population age 5 and older speak English as their primary language, while 4.09% speak Spanish, 0.87% speak German or Pennsylvania Dutch, 0.47% speak Chinese. In total, 9.85% of the population aged 5+ speak a language other than English as their native language.
Religion
- Protestantism 49 %
- Catolicism 24 %
- Other religions 6 %
- No religion 21 %
The new sovereign also enacted several wise and wholesome laws for his colony, which have remained invariably the same to this day. The chief is, to ill-treat no person on account of religion, and to consider as brethren all those who believe in one God.The new sovereign also decreed several wise and beneficial laws for his colony, which have remained unchanged until this day. The president is, not to mistreat any person because of his religion, but to consider as brothers all those who believe in a God.Voltaire, speaking of William Penn
Since colonial times, Pennsylvania (along with Rhode Island) was characterized by its religious diversity and was an example of the coexistence of multiple religions and this religious diversity still exists today.
The population of Pennsylvania in 2000 was 12,281,054. Of these, it was estimated that 8,448,193 belonged to some form of organized religion. According to the Association of Religion Data Archives (ARDA) at Pennsylvania State University, there are reliable data for 7,116,348 people belonging to religious groups in Pennsylvania in 2000, who adhered to 115 different doctrines. Their religious affiliation was:
- Catolicism: 3.802.524 (53.43 %)
- Orthodox Church: 75,354 (1,06 %)
- Historical Protestantism: 2,140,682 (30 %)
- United Methodist Church: 659.350 (9.27 %)
- Evangelical Lutheran in the United States: 611.913 (8.60 %)
- Presbyterian churches: 324,714 (4.56 %)
- United Church of Christ: 241,844 (3.40 %)
- United States Baptist Churches: 132.858 (1.87 %)
- Episcopal Church: 116.511 (1.64 %)
- Contemporary Protestants: 704.204 (10 %)
- American God Assemblies: 84,153 (1,18 %)
- Brethren Church: 52,684 (0.74 %)
- American Mennonite Church: 48,215 (0.68 %)
- Christian and Missionary Alliance: 45,926 (0.65 %)
- Southern Baptist Convention: 44,432 (0.62 %)
- Non-charismatic independent churches: 42,992 (0.60 %)
- Other theologies: 393.584 (5.53 %)
- Estimated Jews: 283,000 (3.98 %)
- Estimated Muslims: 71,190 (1.00 %)
- Association of Universalist Unitarism Congregations: 6,778 (0.10 %)
- The Church of Jesus Christ of the Last Day Saints: 31.032 (0.44 %)
In 2000 Pennsylvania had the highest concentration of Amish population in the United States (44,000), followed by Ohio (43,000) and Indiana (33,000).
Although Pennsylvania owes its existence to Quakers and much of the Commonwealth's ancient trappings trace their roots to the Religious Society of Friends (as they are officially known), practicing Quakers are a small minority in the present.
Main cities and municipalities
Pennsylvania municipalities are incorporated as cities of different classes, either as “borough”, as “township” of different classes, or under local statutes. A “village”, often identified by a roadside sign, is unincorporated and simply a place without clear boundaries. There are 2,567 municipalities in the state.
There is some confusion about the number of towns in Pennsylvania. In 1870, Bloomsburg, the county seat of Columbia County, was incorporated as a town and is recognized in state government publications as Pennsylvania's "only incorporated town". However, in 1975, McCandless Township in Pennsylvania County Allegheny adopted a local charter under the name "Town of McCandless".
The ten largest cities in Pennsylvania, ranked by population, are:
Economy
Pennsylvania's Gross Domestic Product in 2007 was $531.11 billion. By per capita income Pennsylvania ranks 42nd out of 50 states at $35,153.
Philadelphia in the southeast, Pittsburgh in the southwest, Erie on the shores of Lake Erie in the northwest of the state, the Wyoming Valley region in the northeast, and the Allentown-Bethlehem-Easton metropolitan region in the center are urban centers of manufacturing, with the rest of the Commonwealth remaining much more rural; this dichotomy affects politics and the state's economy. Philadelphia is home to ten Fortune 500 companies as of 2007, most located in suburbs such as King of Prussia. Pennsylvania is a leader in the financial and insurance industry. Pittsburgh is home to seven Fortune 500 companies, including U.S. Steel, PPG Industries, H. J. Heinz, and Alcoa. In all, Pennsylvania is home to fifty Fortune 500 companies.
As in the United States as a whole and in most of its states, the largest private company by number of employees in the Commonwealth is Wal-Mart, followed by the University of Pennsylvania, United Parcel Service and Giant Food. The largest manufacturing company by number of employees in the state is Merck. In Pennsylvania is the headquarters of the famous chocolate company Hershey's, in the city of the same name, near Lancaster.
Agriculture
In 2002, Pennsylvania ranked 19th in the country in agricultural production, but ranks first in mushroom production, third in Christmas tree and egg production, fourth in nursery, milk, corn silage, and viticulture. eighth in the nation for wine production.
Sports
Pennsylvania is home to many teams that participate in the national leagues of professional sports: the Philadelphia Phillies and Pittsburgh Pirates in Major League Baseball; the Philadelphia Eagles and Pittsburgh Steelers in the NFL; the Philadelphia 76ers in the National Basketball Association; Philadelphia Union of Major League Soccer; the Philadelphia Flyers and the Pittsburgh Penguins in the NHL; the Erie Bayhawks in the NBA Development League; and Philadelphia Soul in the Arena Football League. These teams have accumulated 7 World Series (Pirates 5, Phillies 2), 14 National Leagues, 3 pre-Super Bowl NFL championships (Eagles), 7 Super Bowl (Steelers 6, Eagles 1), 1 Arena Bowl championship (Soul), 2 NBA championships (76ers) and 7 Stanley Cup winners (Flyers 2, Penguins 5).
College football is very popular in the state. The Pittsburgh Panthers won nine national championships (1915, 1916, 1918, 1929, 1931, 1934, 1936, 1937, and 1976) and went undefeated in 8 seasons (1904, 1910, 1915, 1916, 1917, 1920, 1937, and 1976). The Penn State Nittany Lions with their coach Joe Paterno won two national championships (1982 and 1986) and remained undefeated in five seasons (1968, 1969, 1973, 1986 and 1994). Penn State plays its games in the largest stadium in the United States, Beaver Stadium, with a capacity for 107,282 spectators. Other university teams in the state won national titles in American football: Lafayette College (1896) and the University of Pennsylvania (1895, 1897, 1904 and 1908).
College basketball is also very popular in Pennsylvania, especially in the Philadelphia area, where five universities (known as the Big Five) have a long tradition in NCAA Division I basketball. The following state universities have won national titles in college basketball: La Salle University (1954), Temple University (1938), University of Pennsylvania (1920 and 1921), University of Pittsburgh (1928 and 1930), and Villanova University (1985)..
Nazareth Speedway and Pocono Raceway race ovals have hosted NASCAR Cup, CART and IndyCar Series races.
Arnold Palmer, one of the leading professional golfers of the XX century, is a Latrobe native, and Jim Furyk, one One of the leading professional golfers of the 21st century, he grew up near Lancaster. Oakmont and Merion golf courses have hosted numerous editions of the US Open. Philadelphia hosted the 2001 and 2002 X Games.
Contenido relacionado
2nd century
Saskatchewan
History of africa