Parallel circuit
A parallel circuit is a connection of devices (generators, resistors, capacitors, coils, etc.) in which the input terminals of all the connected devices coincide with each other, as than their output terminals.
Following a hydraulic simile, two water tanks connected in parallel will have a common inlet that will feed, as well as a common outlet that will drain both at the same time. In homes all loads are connected in parallel in order to have the same voltage.
Analysis
Depending on the devices connected in parallel, the total or equivalent value is obtained with the following expressions:
- For generators
 |  |  |
 |  |  |
 |  |  |
 |  |  |
 |  |  |
 |  |  |
- VT=V1=V2=...=Vn{displaystyle {V_{T}}={V_{1}}={V_{2}=
- IT=I1+I2+...+In{displaystyle {I_{T}}={I_{1}} +{I_{2}} +...+{I_{n}}},}
- Also for Resistance
 |  |  |
 |  |  |
 |  |  |
- 1RT=1R1+1R2+...+1Rn{displaystyle {1 over R_{T}}={1 over R_{1}}}}+{1 over R_{2}}+...+{1 over R_{n}}},}
- For Condensers
 |  |  |
 |  |  |
 |  |  |
- CT=C1+C2+...+Cn{displaystyle {C_{T}}={C_{1}} +{C_{2}} +...+{C_{n}}{,}
- For Switches
 |  |  |
 |  |  |
 | 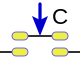 |  |
Interruptor A Interruptor B Interruptor C Departure Open Open Open Open Open Open Closed Closed Open Closed Open Closed Open Closed Closed Closed Closed Open Open Closed Closed Open Closed Closed Closed Closed Open Closed Closed Closed Closed Closed
Rules of parallel circuits
Battery association: calculate the total voltage: (v1+v2+v3…)/vn → (Each component has the voltage of source A and B) series or parallel circuits serve to have an automatic repair of connections or automatic circuits such as a focus (lamp).
Contenido relacionado
535
520
484



