Organization
The organizations are administrative systems created to achieve goals or objectives with the support of the people themselves, or with the support of human talent, available resources, among others. They are ordered social entities where people with different roles, responsibilities or positions coexist and interact who seek to achieve a particular objective.
Organizations are the object of study of the science of Administration, in turn of other disciplines such as Communication, Sociology, Economics and Psychology.
Features
An organization is a social group made up of natural persons, tasks and administrations that form a systematic structure of interaction relations, tending to produce goods, services or regulations to satisfy the needs of a community within an environment, and thus to be able to achieve the distinctive purpose that is its mission. It is a system of consciously coordinated activities formed by two or more people; cooperation between them is essential for the existence of the organization. An organization only exists when there are people capable of communicating and willing to act together to achieve a common goal. It is a set of positions with rules and norms of behavior that all its members must respect, and thus generate the environment that allows the action of a company. The organization is the act of arranging and coordinating the available resources (material, human and financial). It works through standards and databases that have been set up for these purposes.
Every organization has basic or essential components, among which are:
- A group of people who interact with each other.
- A set of tasks or activities that are carried out in a coordinated manner in order to achieve some objective.
- Goals and goals.
- Resources or materials.
- Rules or conventions that define the relationship of people and their role in the organization.
Basics
The basic fundamentals that demonstrate the importance of the organization are:
- It is of a continuous nature; it can never be said that it has ended, since the company and its resources are subject to constant changes (expansion, contraction, new products, etc.), which obviously results in the need for changes in the organization.
- It is a means through which the best way to achieve the objectives of the social group is established.
- It provides the methods for efficient activities, with minimal efforts.
- Avoid slowness and inefficiency in activities, reduce costs and increase productivity.
- It reduces or eliminates the duplicity of efforts by delimiting functions or responsibilities.
Structure
The organizational structure is the pattern of relationships between the components or parts of it and because it is an abstract concept can be confused with the organizational processes. Two parts can be differentiated: The formal and informal organizational structure.
- La formal organizational structure is the one that is based on the set of relationships explained by management, it is not spontaneous because it is deliberately planned, relations between individuals are pre-established, their members are chosen according to rules of selection.
- La informal organizational structure they are the group of informal relations, that is, they have not been explicitly defined and basically respond to social needs such as friendship and membership in a group.
- La real structure the organization is based on the whole of formal and informal relationships.
According to Mintzberg, 5 elements are identified:
- Strategic appearance: here is the company's top management, which has a global responsibility. The essential function is to ensure that the organization is functioning properly and meets its objectives; they have a number of tasks:
- Direct monitoring
- Relationship with the environment
- Formulation of the strategy to follow
- Medium Line: they are managers who link the general direction to the core of operations. The functions attributed to it are:
- Upward and down vertical link
- Horizontal link between them
- Make decisions and solve problems in your area of activity
- Operations Nucleus: he is in charge of the basic production of goods and services. The basic functions they develop are:
- Provision of Inputs
- Production
- Marketing
- Support for previous functions.
- Tecnostructure: Formed by analysts who are not managers and do not participate in the workflow, they design and plan. There may be two types:
- Adaptation analysts: they are concerned with studying the necessary changes to be made in the organization.
- Control analysts: their function is to search for stability and normalization of the guidelines of the company's activity.
- Support staff: they are a set of specialized units not directly involved in the production of goods and services, but their objective is to support the organization through the provision of specialized tasks and services, such as cleaning, security, etc.
Models of organizational understanding
Models are simplified representations of reality and help to understand it from different points of view. In this case, it is understanding organizations from different perspectives or angles of analysis. These models overlap in some analyzes but always complement each other for a broad organizational understanding. Here the most common and basic models are exposed, there are many variants of them and also applied to particular organizations. And specific factor models of these global models.
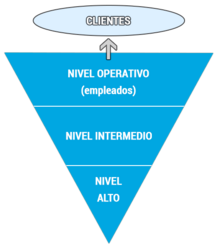
Levels of decision making
In this inverted pyramid, the client is shown as the end of the existence of the organization, and the different levels of organizational decision. The operational level that is the most basic where routine and short-range decisions are made where the bosses or supervisors and operators are located, the tactical or intermediate level where annual short-term decisions are made by functional or departmental managers and at the top, the highest level, which is strategic, where the general manager, directors and/or owners make decisions that impact the long-term life of organizations.
By departments or functional bodies (organizational chart)
Here the organization is structured departmentally taking into account the levels of decision (pyramidal) and by the different areas of competences, authority and tasks to be developed.
Fusion of levels of decision and authority (pyramidal)
Here you can see the different levels of decision-making and authority together with the departmentalization by typical tasks of any organization: marketing, production or operations, finance or administration and HR or personnel, and the direction or management function General that globally coordinates all areas or functions.
Organizational pyramid and flows
Here the organizational pyramid is divided between executive line or management, technostructure and support management team. And it shows us that information flows will circulate in the organization vertically and horizontally, as well as decision and control flows. And at the base, the flow of operations carried out by supervisors and operators or base personnel is observed, such as: production of goods or services, sales, administrative tasks, etc.
Quality Circles and Employee Participation
Here the projects are shared by different parts of the company. Management explains the project to employees by going down the decisional hierarchy. This project is discussed by the middle managers of the organization, and from here, once agreed, it is communicated to the organizational base. The progress and advances achieved are communicated in the organization. It is a less hierarchical, more collective and participative construction organization.
Activities that generate value for the client
Here the organization is represented in its primary or basic activities in charge of generating and delivering value to the customer, and a series of secondary, support activities that support the primary activities in the generation and delivery of value, obtaining organization a profit margin.
7s Mackenzie
Here emphasis is placed on the organization as a system and the relationship, influence and interdependence of its elements with each other. These elements are: the organizational structure, the strategy, the systems, the vision and values, the abilities or capacities, the personnel or human resources, and the style or way of making decisions, of leadership and of carrying out activities. It alerts us to systemic complexity and divides the elements into two groups, the Hard: strategy, structure and system, and the soft elements: vision and values, personnel, skills, style.
Organizational Development Penta
Here the key elements of the organization are considered and within these its subelements; how they relate to and influence each other, and how the organization is linked to the market. Includes and contemplates prospective analysis and organizational learning for development
Canvas
Here the different organizational activities are highlighted and a brief explanation of their development or realization is required. Its usefulness lies in the visual simplicity to be able to communicate the organization and business model to non-experts, since it remains in a basic analysis.
Key competencies, abilities or skills
Here we analyze the organizational factors symbolized in the organizational pyramid in relation to the market and the different capacities and abilities that are possessed or to be developed, that is, dynamics.
The organization as temporal dynamics
Here it is implied that organizations must change over time through planning, both strategic and tactical, from a current mission to a future vision adapted to an estimated future context. In other words, today's organization will be different from tomorrow's, and planning will set the course to follow to achieve this vision.
Organization and environment
Here the organization is visualized in relation to its environment, which is divided into micro environment or direct environment: competition, customers, suppliers, partners or external collaborators and other organizations, and macro environment or mediate environment: technological, political factors, cultural, economic, international, legal, etc. It allows understanding the organization in relation to the environment.
Types
There are a variety of legal types of organizations, including corporations, governments, non-governmental organizations, political organizations, international organizations, the military, charities, non-profit organizations, associations, cooperatives, and educational institutions, etc.
A hybrid organization is a body that operates in both the public and private sectors simultaneously, fulfilling public functions and developing commercial market activities.
A voluntary association is an organization made up of volunteers. Such organizations may operate without legal formalities, depending on the jurisdiction, including informal clubs or coordinating bodies with a purpose in mind that they may express in the form of a manifesto, mission statement, or informally reflected in what they do. because remember that every action taken by an organization, both legal and illegal, reflects a goal in mind.
Organizations can also operate secretly or illegally in the case of secret societies, criminal organizations, and resistance movements. And in some cases there may be obstacles from other organizations.
What makes an organization recognized by the government is completing its registration or incorporation or recognition in the form of social pressure (eg interest group) or being considered the spokesperson for a group of people.
Organizations and institutions can be used as synonyms. Jack Knight writes that organizations are either a restricted version of institutions or represent a group of institutions.
Resources
They are necessary to develop their activities when carrying out their purpose, they differ according to their activities.
Resources:
- Money to acquire resources.
- Raw materials or inputs that are transformed into a process and become products called goods or services.
- Real estates, installations and installations necessary to carry out the production process and activities.
- Machinery and tools used in the production process.
- Human resources: the active element (owners, shareholders, partners, workers).
- Natural resources: land, water, air, gas, and energy in all its forms (electric, solar, water, fuel).
- Technological resources: means to achieve an objective. These are the ways of working, doing or producing (methods, techniques and procedures used in the organization).
- Cognitive resources: ideas, knowledge and information originated in human intellect and in technological and scientific advancement.
- Intangible resources: brands, names and prestige to access and position on the market.
Theories
There are several philosophical schools that have studied the organization as a social system and as a structure of action, such as structuralism and empiricism. To develop a theory of the organization, it is necessary first to establish its laws or at least theoretical principles in order to continue developing a theory about them. One way would be to classify and show the different forms of organizations that have been more prominent or known throughout history, such as bureaucracy as administration or elements that make up the organization and that have also been widely treated, such as leadership. formal and informal. As a methodology, this is called operations research, and in the social sciences it is the field of study of organizational sociology. A new use is emerging in organizations: knowledge management. Typically, the organization is ubiquitous, making it difficult to define independently or without involvement in a particular application.
Contenido relacionado
Operations research
ISO 9000 standards
Humana Inc.