Numerical derivation
Contenido keyboard_arrow_down
The numerical derivation is a technique of numerical analysis to calculate an approximation to the derivative of a function at a point using the values and properties of the function.
Formulation using finite differences
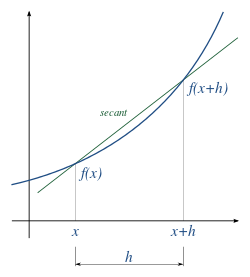
By definition the derivative of a function f(x){displaystyle f(x)} is:
- f♫ ♫ (x)=limh→ → 0f(x+h)− − f(x)h{displaystyle f^{prim }(x)=lim _{hto 0}{frac {f(x+h)-f(x)}{h}}}}}}
The numerical approximations that we can make (for h > 0) will be:
- Variances forward:
- f♫ ♫ (x0)≈ ≈ f(x0+h)− − f(x0)h{displaystyle f^{prim }(x_{0})approx {frac {f(x_{0}+h)-f(x_{0})}{h}}}}}}}}
- Reversal differences:
- f♫ ♫ (x0)≈ ≈ f(x0)− − f(x0− − h)h{displaystyle f^{prim }(x_{0})approx {frac {f(x_{0})-f(x_{0}-h)}{h}}}}}}}}}
The approximation of the derivative by this method gives acceptable results with a certain error. To minimize errors, it is estimated that the average of both provides the best numerical approximation to the given problem:
- Central differences:
- f♫ ♫ (x0)≈ ≈ f(x0+h)− − f(x0− − h)2h{displaystyle f^{prim }(x_{0})approx {frac {f(x_{0}+h)-f(x_{0}-h)}{2h}}}}}}}}}}
- f♫ ♫ ♫ ♫ (x0)≈ ≈ f(x0+h)− − 2f(x0)+f(x0− − h)h2{displaystyle f^{prim prim }(x_{0})approx {frac {f(x_{0}+h)-2f(x_{0})+f(x_{0}-h)}{h^{2}}}}}}{h
Contenido relacionado
Rolle's theorem
Bioinformatics
Unit of measurement
Más resultados...