Nucleoside
Contenido keyboard_arrow_down
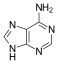
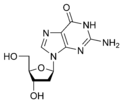
A nucleoside is a glusosilamide organic monomeric molecule, which integrates the nucleic acid macromolecules and results from the covalent union between a nitrogenous base and a pentose, which can be ribose or deoxyribose. Examples of nucleosides are cytidine, uridine, adenosine, guanosine, thymidine, and inosine.
They can be conceived as nucleotides that do not have the phosphate group. That is, nucleosides can be combined with a phosphoric group (phosphoric acid: H3PO4) by certain kinases in the cell, producing nucleotides, which are the basic molecular components. of DNA and RNA.
Nucleosides can be of two types, depending on the pentose they contain:
- Ribonucleosides: the pentase is the ribose
- Desoxirribonucleosides: the pentose is the 2-disoxirribosa
Contenido relacionado
Chrysopogon
Colacium
Apoclate simplex
Más resultados...