Neutron (game)
Neutron an abstract game for two people. It requires a 5x5 board, and 5 tiles for each player, called Electrons, white and black. In addition there is a red token, the Neutron, shared by both players.
Movements
White moves first, and they keep playing alternately. On his turn, the player must always move two pieces, in this strict order:
- first the Neutron
- Then a chip of his color.
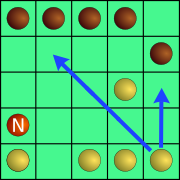
Both the Neutron and the other tiles, called Electrons, can be moved in any direction (horizontal, vertical or diagonal), and it is mandatory to move them as much as possible in the chosen direction, but without occupying or jumping over them from an already occupied square. In other words, after choosing a movement direction, the piece must be moved as far as possible in that direction, until its passage is blocked by any other piece or by the edge of the board.
On his turn, the player can choose one direction of travel for the Neutron and another direction for his token. Both the Neutron and the own token must move at least one square. There are no catches.
Ending
The first to get the Neutron to any free space on their starting line wins.
A player loses if he is forced to bring the Neutron to a space on the opponent's starting line. He also loses if the situation is locked and in his turn he cannot move the Neutron or, if after moving the Neutron, he cannot move any of his pieces.
White's turn begins. They win by bringing the Neutron to their starting line
Contenido relacionado
Sexagesimal system
Lambert azimuthal projection
Thiessen polygons