Natural satellite
A natural satellite is a celestial body that orbits around a planet. Generally the satellite is smaller and accompanies the planet in its orbit around its parent star. Unlike the fragments that orbit in a ring, it is the only body in its orbit. The term natural satellite is opposed to that of artificial satellite, the latter being an object that revolves around the Earth, the Moon or some planets and that has been manufactured by humans.
In the case of the Moon, which has a mass of approximately 1/81 of the mass of the Earth, it could be considered as a system of two planets that orbit together (binary system of planets). Such is the case of Pluto and its satellite Charon. If two objects have similar masses, it is common to speak of a binary system instead of a primary object and a satellite. The usual criterion for considering an object as a satellite is that the center of mass of the system formed by the two objects is inside the primary object. The highest point in the satellite's orbit is known as the apoapsis.
By extension, the satellites of other planets are called moons. It is said "the four satellites of Jupiter", but also, "the four moons of Jupiter". Also by extension, any natural body that revolves around a celestial body is called a natural satellite or moon, even if it is not a planet, as is the case of the Dactyl asteroidal satellite that revolves around the asteroid (243) Ida, etc.
Classification of satellites in the solar system
In the solar system, satellites can be classified as:
- Satellite pastors: When they hold some ring of Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus or Neptune instead.
- Trojan Satellites: When a planet and an important satellite have at the Lagrange L points4 and L5 other satellites.
- Coorbital satellites: When they rotate in the same orbit. The Trojan satellites are coorbital, but also the satellites of Saturn Jano and Epimetheus that differ in their orbits less than their size and instead of crashing exchange their orbits.
- asteroid satellites: Some asteroids have satellites around them like (243) Ida and its Dactyl satellite. On August 10, 2005 the discovery of an asteroid (87) Silvia that has two satellites rotating around it, Rómulo and Remo was announced. Rómulo, the first satellite, was discovered on 18 February 2001 at the 10-metre W. M. Keck II telescope in Mauna Kea. It is 18 km in diameter and its orbit, at a distance of 1370 km from Silvia, takes 87.6 hours to be completed. Remo, the second satellite, has 7 km of diameter and rotates at a distance of 710 km, and takes 33 hours to complete an orbit around Silvia.
Since all natural satellites follow their orbit due to the force of gravity, the motion of the parent object is also affected by the satellite. This phenomenon allowed in some cases the discovery of extrasolar planets
Satellites of satellites
There are no known moons of moons (natural satellites orbiting a natural satellite of another body). In most cases, tidal effects from the primary would make such a system unstable.
However, calculations made after the recent detection of a possible ring system of Rhea (Saturn's natural satellite) indicate that the satellites orbiting Rhea would have stable orbits. Furthermore, the suspected rings are thought to be narrow, a phenomenon normally associated with shepherd moons. However, specific images taken by the Cassini spacecraft did not detect any rings associated with Rhea.
It has also been proposed that Iapetus, satellite of Saturn, had a sub-satellite in the past; this is one of several hypotheses that have been put forward to account for its equatorial crest.
Natural satellites in the solar system
In the planets and dwarf planets of the solar system 181 satellites are known, distributed:
| Astronomical object | N.o satellites | Names | Wikipedia |
|---|---|---|---|
| Earth | 1 | Moon | |
| Mars | 2 | Deimos and Fobos | Satellites of Mars |
| Jupiter | 79 | J.I., J., J., E., E., E., E., E., E., E., E., E., E., E., E., E., E., E., E., E., E., E., E., E., E. | Jupiter satellites |
| Saturn | 82 | Skom, Skom, (+3 without confirming S/2004 S 3, S/2004 S 4 and S/2004 S 6) | Saturn Satellites |
| Uranus | 27 | Ariel, Belinda, Bianca, Caliban, Cordelia, Crésida, Cupido, Desdémona, Francisco, Ferdinando, Julieta, Mab, Margarita, Miranda, Oberón, Ofelia, Perdita, Porcia, Prospero, Puck, Rosalinda, Setebos, Sicorax, Stefano, Titania, Trinculo and Umbriel | Uranus satellites |
| Neptune | 14 | Despina, Galatea, Halimede, Laomedeia, Larisa, Náyade, Nereida, Neso, Proteo, Psámate, Sao, Hipocampo, Talasa and Tritón | Neptune Satellites |
| Pluto | 5 | Caronte, Hidra, Nix, Cerbero, Estigia | Pluto satellites |
| Makemake | 1 | MK2 | |
| Eris | 1 | Disnomia | |
| Haumea | 2 | Hi'iaka and Namaka. | Haumea satellites |
| Orcus | 1 | Vanth | |
| Quaoar | 1 | Weywot | . |
The planets Mercury and Venus have no natural satellites, nor does the dwarf planet Ceres. Successive unmanned missions have increased these figures from time to time by discovering new satellites, and may still do so in the future.
Size of natural satellites in the solar system
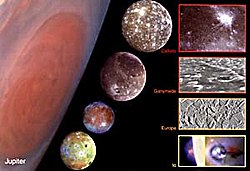
The seven largest natural satellites in the solar system (over 2,500 km in diameter) are the four Jovian Galilean moons—Ganymede, Callisto, Io, and Europa—Saturn's moon Titan, Earth's own Moon, and the captured natural satellite of Neptune Triton. Triton, the smallest of that group, has more mass than all the smallest remaining natural satellites combined. Similarly, in the next size group of nine natural satellites, between 1,000 and 1,600 km in diameter—Titania, Oberon, Rhea, Iapetus, Charon, Ariel, Umbriel, Dione, and Tethys—the smallest, Tethys, has more mass than all the other minor satellites combined. In addition to the natural satellites of the planets, there are also more than 80 known natural satellites of dwarf planets, asteroids, and other minor bodies in the solar system. Some studies estimate that up to 15% of all trans-Neptunian objects could have satellites.
The following is a comparative chart that classifies the natural satellites in the solar system by their diameter. For comparative purposes, some notable planets, dwarf planets, asteroids and other trans-Neptunian objects are listed in the right column. The natural satellites of the planets are named after mythological figures. These are predominantly Greek, except for the natural satellites of Uranus, which are named after Shakespearean characters. The nineteen bodies massive enough to have reached hydrostatic equilibrium are in bold in the table below. Minor planets and satellites suspected but not proven to have achieved hydrostatic equilibrium are italicized in the chart below.
| Main diameter (km) | Satellites of planets | Satellites of dwarf planets | Satellites from other minor planets | Other bodies (for comparison) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Earth | Mars | Jupiter | Saturn | Uranus | Neptune | Pluto | Haumea | Makemake | Eris | |||
| 4000-6000 | Ganymede Calisto | Titan | Mercury | |||||||||
| 3000-4000 | Moon | Io Europe | ||||||||||
| 2000-3000 | Triton | Eris Pluto | ||||||||||
| 1000-2000 | Rea Japeto Dione Tetis | Titania Oberon Umbriel Ariel | Caronte | Makemake Haumea (225088) 2007 OR10, Quaoar | ||||||||
| 500-1000 | Ice cream. | Disnomia | (90377) Sedna, Ceres, (120347) Salacia, (90482) Orcus, (2) Palas, (4) Vesta many more TNOs | |||||||||
| 250-500 | Mimas Hyperion | Miranda | Proteo Nereida | Hi'iaka | Orcus I Vanth | (10) Higia (704) Interamnia (87) Silvia and many others | ||||||
| 100-250 | Amaltea Himalia Tebe | Febe Jano Epimetheus | Sicorax Puck Porcia | Larisa Galatea Despina | Namaka | MK2 | S/2005 (82075) Sila-Nunam Salacia I Actaea Ceto I Phorcys Patroclo I Menoetius ~21 more moons of TNOs | 3 Juno 1992 QB1 (5) Trace (42355) Typhon and many others | ||||
| 50-100 | Elara Pasífae | Prometheus Pandora | Caliban Julieta Belinda Cresida Rosalinda Desdémona Bianca | Talasa Halimede Neso Náyade | Hydra Nix | Quaoar I Weywot 90 Antiope I Typhon I Echidna Logos I Zoe 5 more moons of TNOs | (90) Antiope 58534 Logos (253) Matilde and many others | |||||
| 25-50 | Carme Metis Sinope Lisitea Ananke | Siarnaq Helena Albiorix Atlas Pan | Ofelia Cordelia Setebos Prospero Perdo Stepano | Sao Laomedeia Take it easy. | 22 Caliope I Lino | (1036) Ganymed 243 Ida and many others | ||||||
| 10-25 | Fobos We | Leda Adrastea | Telesto Paaliaq Calipso Ymir Kiviuq Tarvos Ijiraq Erriapo | Mab Cupid Francisco Ferdinando Margarita Trínculo | S/2004 N 1 | Cerbero Stigia | (762) Pulcova Sylvia I Rómulo (624) Hector Eugenia I Petit-Prince (121) Hermiona (283) Emma I (1313) Bern (107) Camila | 433 Eros (1313) Bern and many others | ||||
| . 10 | 51 moons | 36 moons | Sylvia II Remus Ida I Dactyl and many others | many | ||||||||
Visual Summary
| Ganymede (Jupiter satellite) | Titan (satellite of Saturn) | Calisto (Jupiter satellite) | Io (Jupiter satellite) | Moon (Satellite of the Earth) | Europe (Jupiter satellite) | Triton (Neptune satellite) |
| Titania (Uranus satellite) | Rea (satellite of Saturn) | Oberon (Uranus satellite) | Japeto (satellite of Saturn) | Umbriel (Uranus satellite) | Ariel (Uranus satellite) | Dione (satellite of Saturn) |
| Tetis (satellite of Saturn) | Ice cream. (satellite of Saturn) | Miranda (Uranus satellite) | Proteo (Neptune satellite) | Mimas (satellite of Saturn) | Hyperion (satellite of Saturn) | Febe (satellite of Saturn) |
| Jano (satellite of Saturn) | Amaltea (Jupiter satellite) | Epimetheus (satellite of Saturn) | Tebe (Jupiter satellite) | Prometheus (satellite of Saturn) | Pandora (satellite of Saturn) | Helena (satellite of Saturn) |
| Atlas (satellite of Saturn) | Telesto (satellite of Saturn) | Calipso (satellite of Saturn) | Fobos (Satellite of Mars) | We (Satellite of Mars) | Metone (satellite of Saturn) |
Contenido relacionado
Delphinus (constellation)
(28978) Ixion
Regolith