Monomer
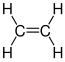
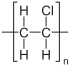
A monomer (from the Greek mono, 'one', and mero, 'part') is a molecule of small molecular mass that it is linked to other monomers, sometimes hundreds or thousands, by chemical bonds, usually covalent, forming macromolecules called polymers. The most common natural monomer is glucose, which is linked by glycosidic bonds to form polymers such as cellulose and starch, making up more than 77% of the dry mass of all plant matter. Most often the term monomer refers to organic molecules that form synthetic polymers, such as vinyl chloride., which is used to produce PVC. The process by which monomers are combined end to end to form a polymer is called polymerization. Molecules made of a small number of monomer units, up to a few dozen, are called oligomers.
Classification of monomers
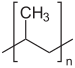
Monomers can be classified in many ways. They can be subdivided into two broad classes, depending on the type of polymer they form. The monomers that participate in condensation polymerization have a different stoichiometry than the monomers that participate in addition polymerization. Most plastics are usually obtained by this second route.
As a general rule, they tend to be classified more by natural or synthetic:
Natural monomers
- Amino acids are protein monomers.
- Nunucleotides are monomers of nucleic acids.
- Monosaccharides are monomers of polysaccharides.
- The isoprene is the monomer of the rubber.
All these polymers obtained in nature are usually called biopolymers.
Synthetic monomers
Contenido relacionado
Manganese
Entomology
Extragalactic astronomy