Katowice
Katowice (![]() [kat]шvjit confines ] (?·i) in Silesian: Katowicyin Czech: Katovicein German: Kattowitz) is a Polish city belonging to the historical region of Alta Silesia in southern Poland, on the banks of the rivers Klodnica and Rawa.
[kat]шvjit confines ] (?·i) in Silesian: Katowicyin Czech: Katovicein German: Kattowitz) is a Polish city belonging to the historical region of Alta Silesia in southern Poland, on the banks of the rivers Klodnica and Rawa.
Since 1999, Katowice has been the capital of the Silesian Voivodeship and was previously the capital of the Katowice Voivodeship. Katowice is the largest city in the Upper Silesian Industrial Area. It has a population of 354,000 (1999), with a Katowice urban area of 2,700,000 and a Silesian metropolitan area of 5,294,000.
History
The area where Katowice sits today, in the Upper Silesia region, has been inhabited by Slavic tribes since before the century X. It was first ruled by the Silesian Piasts until their extinction in 1675. As of 1335, it is known to have been part of the Bohemian Crown. In 1526, the territory passes to the Austrian Habsburg Monarchy after the death of King Ludwig II of Hungary. In 1742, most of Silesia was incorporated by the Kingdom of Prussia during the First Silesian War.
Katowice (then known under the German name Kattowitz) gained city status in 1865, becoming one of the principal cities of the Prussian province of Silesia. The city became one of the main centers of the mining industry thanks to the large amount of coal found in the mountains near the city. The advent of the Industrial Revolution further accelerated Katowice's growth, and the coal and steel industry caused the population to rise rapidly from fewer than 500 people to more than 2,000. At the end of the 19th century, Katowice was inhabited mostly by Germans, Silesians, Jews and Poles.
Under the Treaty of Versailles after World War I, the League of Nations called a plebiscite to partition the Upper Silesia region between the Weimar Republic and the Second Polish Republic. The final results determined that Katowice would become part of Poland, although only 3,900 people voted for Poland, while 22,774 voted for Germany. However, the German invasion of Poland in 1939 made Katowice once again a city of Nazi Germany. After being occupied by the Red Army in 1945, and after the Polish People's Republic adopted communist rule, the city was renamed Stalinogród after Joseph Stalin in 1953. The name was changed three years then by that of Katowice.
Today, Katowice is one of the main industrial and economic centers of Poland. The fall of communism in the country allowed the city to develop its commercial activity, being one of the main financial centers, along with Warsaw and Krakow, in the country.
Geography
Katowice is a city located in the Upper Silesia region of southern Poland, on the Kłodnica and Rawa rivers (tributaries of the Oder and Vistula, respectively). Katowice is located in the eastern part of the Silesian Highlands, about 50 km north of the Beskidy Mountains (part of the Carpathian mountain system) and about 100 km northeast of the Sudetenland. Katowice has one of the largest metropolitan areas in Europe, with over two million inhabitants. Among the cities that make up the Upper Silesian Metropolitan Union (at the national level) and the Silesian metropolitan area (covering from Katowice to Ostrava, in the Czech Republic) are Chorzów, Sosnowiec, Lędziny, Tychy, Mikołów, Ruda Śląska and Czeladź. Less than 600 km from Katowice are the capitals of six countries: Berlin, Vienna, Prague, Bratislava, Budapest and Warsaw.
Climate
Katowice's climate is temperate and continental. The average annual temperature is 8.2 °C, being -1.5 °C in January and 18 °C in July. The Moravian Gate means that in Katowice there are gusts of wind of up to 2 m/s and rainfall of 608.5 mm per year.
| Month | Ene. | Feb. | Mar. | Open up. | May. | Jun. | Jul. | Ago. | Sep. | Oct. | Nov. | Dec. | Annual |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Temp. max. abs. (°C) | 14.7 | 18.8 | 22.8 | 29.5 | 32.2 | 34.6 | 35.7 | 37.2 | 34.4 | 26.6 | 20.9 | 18.2 | 37.2 |
| Average temperature (°C) | 1.8 | 3.7 | 8.2 | 14.9 | 19.6 | 22.9 | 24.9 | 24.6 | 19.2 | 13.7 | 7.8 | 2.7 | 13.7 |
| Average temperature (°C) | -1.2 | 0.1 | 3.6 | 9.3 | 13.8 | 17.3 | 19.1 | 18.6 | 13.7 | 8.9 | 4.2 | -0.0 | 9 |
| Temp. medium (°C) | -4.3 | -3.4 | -0.7 | 3.5 | 8.0 | 11.7 | 13.3 | 12.9 | 8.9 | 4.6 | 0.9 | -2.9 | 4.4 |
| Temp. min. abs. (°C) | -27.4 | -30.0 | -20.8 | -8.2 | -3.4 | -0.3 | 4.8 | 3.1 | -3.4 | -8.0 | -16.3 | -24.4 | -30.0 |
| Total precipitation (mm) | 43.8 | 39.4 | 47.7 | 44.9 | 75.7 | 78.7 | 103.8 | 73.1 | 69.9 | 53.4 | 49.0 | 43.8 | 723.2 |
| Nevadas (cm) | 197.4 | 173.8 | 67.3 | 10.2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.6 | 26.1 | 88.7 | 564.1 |
| Days of rain (≥ 1 mm) | 10.1 | 9.1 | 9.7 | 7.9 | 10.3 | 10.0 | 10.8 | 9.0 | 9.0 | 9.1 | 9.2 | 9.5 | 113.7 |
| Days of snowfall (≥ 1 mm) | 17.7 | 15.2 | 6.1 | 1.4 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.2 | 4.4 | 13.1 | 58.1 |
| Hours of sun | 50.7 | 70.6 | 122.6 | 182.7 | 223.7 | 230.6 | 246.8 | 241.3 | 162.6 | 114.5 | 61.3 | 43.0 | 1750.4 |
| Relative humidity (%) | 84.6 | 80.5 | 74.1 | 66.5 | 69.8 | 70.8 | 71.8 | 73.4 | 79.6 | 83.0 | 85.9 | 86.3 | 77.2 |
| Source: Average and total monthly | |||||||||||||
Demographic evolution

Education
The main institution of higher education is the University of Silesia, founded in 1968. Katowice has about 80 secondary schools, about 35 gymnasiums and more than 50 colleges. Katowice is home to the Silesian Library, one of the most modern libraries in Europe.
Air transportation
- Katowice International Airport
Sports
Katowice has a long sporting tradition. It has hosted championships such as EuroBasket 2009, the 1975 European Indoor Athletics Championships, the 1985 European Weightlifting Championships, various editions of the World Wrestling Championships (in 1974 and 1982), the 1991 World Amateur Bodybuilding Championships and the 2014 World Men's Volleyball Championship. The main venues in the city are the Silesia Stadium (the second largest football stadium in the country, after the Polish National Stadium) and the Spodek, the country's largest multi-purpose hall..
Football is the most popular sport in Katowice. When Katowice was part of the German Empire, for much of the first half of the XX century, 1. FC Katowice was one one of the most important teams in the Bundesliga. After the creation of the Second Polish Republic, 1. FC Katowice went on to compete in the Ekstraklasa, but Nazi Germany's invasion of Poland in 1939 saw the club play again in the Gauliga, the top flight of German football.. The club disappeared in 1945, along with Nazi Germany; however, there is a club called F.C. Katowice that competes in the Polish III League since its foundation in 2007.
Other soccer teams in Katowice include GKS Katowice and Rozwój Katowice (both compete in the I Liga, the second Polish soccer division). In other sports disciplines, the Silesia Rebels of American football stands out, the EKS Katowice of the water polo league and the Naprzód Janów of ice hockey.
In addition to traditional sporting events, Katowice is also the home of IEM Katowice, an electronic sports event organized by ESL and sponsored by Intel Corporation, where StarCraft II, League of Legends and CSGO championships are held.
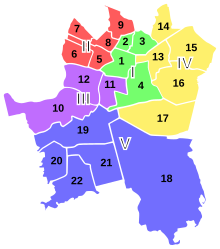
Administrative division
Since September 29, 1997, there are officially five district groupings (zespoły dzielnic) in Katowice, which are further subdivided into 22 districts (dzielnice).
I. Zespół dzielnic śródmiejskich (Centro)
II. Zespół dzielnic północnych (North)
III. Zespół dzielnic zachodnich (West)
| IV. Zespół dzielnic wschodnich (Easter)
V. Zespół dzielnic południowych (South)
|
Religion
The majority of the population (95.1%) practice the Catholic religion. This city is the seat of the Archdiocese of Katowice.
Twinned cities
Katowice is twinned with the following cities:
- Košice (Slovakia).
- Cologne, Germany.
- Groningen (Hello).
- Miskolc (Hungary).
- Mobile (United States).
- Odense (Denmark).
- Ostrava (Czech Republic).
- Saint-Étienne (France).
- St. Francis, United States.
- Shenyang, China.
Contenido relacionado
Lubumbashi
Province of Heredia
Akranes
General Mosconi (Salta)
Bustantigo