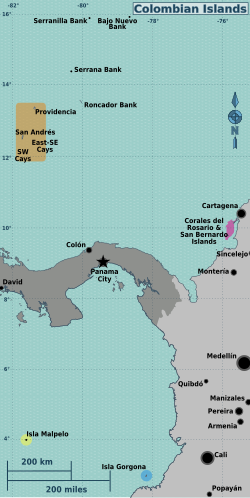
Insular region of Colombia
The insular region of Colombia includes the set of continental islands, keys and islets and those far from the coast, such as the Archipelago of San Andrés and Providencia in the Caribbean Sea and the Malpelo Islands and Gorgona in the Pacific Ocean. It does not include fluvial or lake islands.
Description
The continental islands are those that are located closest to the continental territory and are linked geologically by the submarine platform. In the Colombian Caribbean, the Tierra Bomba, Rosario, Barú (these three bordering the Cartagena Bay), San Bernardo (in front of the San Bernardo tip), Fuerte and Tortuguilla islands stand out. On the Pacific coast, the islands are very numerous, because many rivers that flow into the ocean form them with the sand and stones that they carry to the sea.
On the other hand, the oceanic islands go into the sea, far from the coasts and emerging from their own submarine ridge. This is the case of the San Andrés Archipelago in the Caribbean Sea and the island of Malpelo in the Pacific Ocean.
Subregions
The subregions of the Insular Region of Colombia are the following:
- Archipelago of San Andrés and Providencia, which forms the department of the same name, located in the Caribbean Sea with a total extension of 52,2 km2, (San Andrés with 26 km2, Providencia with 17 km2 and Santa Catalina with 1 km2).
- Gorgona Island, a small island system made up of Gorgona, Gorgonilla and three other islets, located in the Pacific Ocean and belonging to the department of Cauca with 26 km2 of land or island surface. It is there the Parque Nacional Natural Isla Gorgona.
- Malpelo, islet of volcanic origin in the Pacific Ocean under the jurisdiction of the department of Valle del Cauca, with 120 hectares or 1,20 km2 of emergida surface.
- Archipelago of San Bernardo, a set of 10 Caribbean Sea islands that in total have an approximate surface of 255 km2 are located in the Gulf of Morrosquillo.
- Other islands:
- Coral Islands of the Rosary, small archipelago of 20 hectares (0.20 km2) located west of Cartagena.
- Isla Fuerte, small island of about 300 hectares (3 km2) facing the coasts of the department of Córdoba.
- Tortuguilla Island, small island of 14 hectares (0.14 km2).
- Earth Bomb Island.
- Pacific continental islands, such as Tumaco and Sanquianga.
Climate
Despite its small size, it is a very diverse region, as it is made up of islands in both oceans.
The archipelago of San Andrés y Providencia in the Caribbean Sea is characterized by its defined periods of rain and its dry climate.
The Gorgona and Gorgonilla archipelago is mostly jungle, humid and permanently rainy, which makes it profusely rich in terms of flora and fauna.
Population
According to the 2018 Census, San Andrés y Providencia had a population of 61,280 inhabitants. 42% of the population recognized themselves as Raizal, the Afro-Caribbean group native to the islands. The languages spoken in the archipelago are Spanish, English and San Andresan Creole.
The Rosario Islands have a population of less than a thousand inhabitants.
Gorgona, Malpelo, and most of the Pacific mainland islands are uninhabited, except for the islands of Tumaco and El Morro, which are home to four of the five communes of the city of San Andrés de Tumaco.
Economy
The main source of income for the Colombian insular region is tourism.
San Andrés has the most beautiful beaches and one of the main hotel complexes in the country, which is visited annually by nationals and foreigners. The archipelago is also famous for the movement of its trade.
Gorgona is an ideal natural park for biological research. Eco-tourism is practiced in the region on a large scale.
Culture
San Andres and Providencia
Festivities
The Green Moon Festival is a celebration that makes visible a way of being and celebrating that is typical of Afro-Caribbean people. Despite having a recent origin, the festival presents characteristics that tell the history of these islands. The absolute disappearance of the indigenous presence, as well as the colonization by the English who introduced Africans to work on large plantations, are manifested today in the culture of San Andres.
The festival begins with a march that runs through the main streets of San Andrés to the rhythm of martial drums that mark the beat, used by the hosts, of the numerous percussion band to develop original choreographies. The military rhythms are accompanied by marching steps suggested by drum keys, which vary depending on the leader who leads the youth military band. These leaders establish a kind of competition among themselves when, being in front of the band, they indicate the rhythmic markings, which the group must interpret and transfer without losing contact with the immediately preceding rhythm.
The Crab Festival is a typical celebration of San Andrés, where the islanders prepare various dishes based on crab, such as (carambolas, rice with crab, cakes, cakes, snacks) to the taste of the islanders themselves and tourists who participate in this festival, it is accompanied by music and dance to liven up the celebrations in which the gastronomic samples prepared with this dish are the delight of all.
Gastronomy
The typical dishes of San Andrés are made with fish, lobsters, snails and crabs accompanied with plantains, coconut, coconut milk and cassava. The best known typical dish is the rondón, which is a kind of fish casserole with snails slowly cooked in coconut milk, with cassava, plantains and fish.
Typical costumes
The quintessential San Andrés dress for women is a long-sleeved white blouse with a high neck, combined with a long skirt that usually reaches the ankles. In addition, accessories such as a headscarf of some bright color are usually added to this suit.
As for the men's suit, this too consists mainly of a white shirt. The pants are usually gray, although they can also be seen in cream, or even black, always combined with black shoes.
National Natural Parks
- Natural National Park Old Providence McBean Lagoon
- Natural National Park Coral Islands of the Rosary and San Bernardo
- Natural National Park Gorgona
- Natural National Park Malpelo
- National Natural Park Sanquianga
Contenido relacionado
Santiago de Chile
Alvaro Obregon (Mexico City)
Hasuda (Saitama)