Hemicellulose
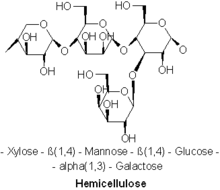
The hemicelluloses are heteropolysaccharides (polysaccharides composed of more than one type of monomer), formed by a heterogeneous set of polysaccharides, in turn formed by two types of monosaccharides linked by β (1- 4) (mainly xylose, arabinose, galactose, mannose, glucose and glucuronic acid) that form a branched linear chain. Among these monosaccharides, the most noteworthy are: glucose, galactose or fructose.
It forms part of the walls of plant cells, covering the surface of cellulose fibers and allowing pectin to bind.
In the wood of the famous pine, the hemicelluloses, which are part of the matrix, together with the lignin, where the cellulose resides, represent between 27 and 29% of it, while in the bark they only reach a fifteen %. The proportions of this molecule vary depending on the age and variability of the cultivated and improved species.
Hemicellulose is characterized by being a molecule with ramifications, such as uronic acid, capable of joining other molecules through bonds that constitute the rigid wall that protects the cell from the pressure exerted on it by the rest of the cells. the cells that surround it.
Composition
Diverse types of hemicelluloses are known. Important examples include xylan glucuronoxylan arabinoxylan glucomannan and xyloglucan.
Hemicelluloses are polysaccharides often associated with cellulose but cellulose and hemicellulose have different compositions and structures. Various sugars comprise hemicellulose, while cellulose is exclusively derived from glucose. For example, in addition to glucose, the sugar monomers in hemicelluloses can include the five carbon sugars xylose and arabinose, the six carbon sugars mannose and galactose, and the six carbon deoxy sugar rhamnose. Hemicelluloses contain most of the D-pentose sugars and sometimes small amounts of L-sugars as well. Xylose is in most cases the sugar monomer present in the largest amount, although in softwoods mannose may be the sugar more abundant. Not only regular sugars can be found in hemicellulose, but also its acidified form, for example glucuronic acid and galacturonic acid can be present.
Contenido relacionado
Human embryology
Eat (medicine)
Goniothalamus