GNOME Web
GNOME Web is a free web browser that uses the WebKit rendering engine for the GNOME desktop environment. It is a descendant of the Galeon browser and is also available for macOS. Until 2012 it received the name of Epiphany.
Development
Epiphany was developed by Marco Pesenti Gritti based on the Galeon browser (developed by himself) with the aim of creating a browser that fully complied with GNOME's human interface guidelines while offering a user experience Very simple. It is for this reason that Epiphany does not have its own themes, but uses the settings specified in GNOME from its control center.
It belongs to the family of web browsers that uses the WebKit rendering engine to display web pages. Until version 2.26.3 the browser used the Gecko rendering engine, but the Epiphany development team decided to drop it and go ahead with only the WebKit engine.
Epiphany supports tabbed browsing, cookie management, popup blocking, and a system of plugins.
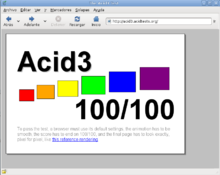
Epiphany 2.28 in September 2009 scored 100/100 on the Acid3 test.
With the GNOME version 3.4 (2012), Epiphany was renamed Web. However, the Epiphany name is still used internally for development, in bug tracking, and in source code. The package remains epiphany -browser on distributions like Debian or Ubuntu.
Web reuses GNOME frameworks and settings. Thus, your UI theme is the default GNOME theme, network settings with GNOME NetworkManager settings, printing with GNOME printing system, settings with GSettings, and GNOME default application settings.
The built-in preferences manager for Web is designed to present the user with only basic browser-specific settings. All advanced configuration is done with the GSettings configurator tools, such as the default GNOME dconf (command line) and dconf (graphical) editor. Web follows the GNOME Human Interface Guidelines and platform-wide design changes. For example, in Web 3.4, the menu for application-wide actions was moved to the top panel of GNOME Shell and the toolbar Replaced the "super menu" button, which activates the display of window-specific menu entries.
Features
Bookmarks
While most browsers offer a hierarchical bookmarking system based on folders (directories), Epiphany uses categorized bookmarks, where a single bookmark (for example "Epiphany") can be contained in multiple categories (such as "web browsers", "GNOME" and "computer programs"). Special categories include bookmarks that have been used frequently ("Most visited") and bookmarks that have not been categorized yet. This is similar to the "places" from Firefox 3.0, a feature that integrates bookmarks and history into an SQLite database. Another innovative concept from Epiphany (although originally included in Galeon) is 'Smart Bookmarks', accessed by typing a word in the address bar.
Extensions
Until version 3.6, the Web was extensible with a plugin system called epiphany-extensions. This package was distributed by web developers and contained the official extensions. Since version 3.8, this system has been removed due to stability and maintenance issues, and some popular extensions have been moved to the main app instead. A new plugin system is planned for the future.
Web Applications Mode
Since GNOME 3.2, Web allows you to create application launchers for web applications. The subsequent invocation of a launcher is rendered as a single, simple Web instance bound to a domain, with external links that open in a normal browser. The launcher created in this way is accessible from the desktop and is not limited to GNOME Shell.
Firefox Sync
Since GNOME 3.26, Web has support for Firefox Sync, which allows users to synchronize their bookmarks, history, passwords, and open tabs with Firefox Sync. They can then be shared between any copy of Firefox or Web that the user launches in Firefox Sync.
Contenido relacionado
Console
Firebird
GNU TeXmacs