Functional group
In chemistry, a functional group is a chain or group attached to a carbon chain, represented in the general formula by R for aliphatic compounds and as Ar for aromatic compounds, and which are responsible for the reactivity and chemical properties of organic compounds. They are always associated with covalent bonds to the rest of the molecule.
The chemical nomenclature of organic compounds is based on the combination of the prefixes (secondary function) and suffixes (main function) associated with the functional groups together with the names of the alkanes from which they are derived by accessing the atoms.
Homologous series and most common functional groups
A homologous series is a set of compounds that share the same functional group and therefore have similar properties and reactions. For example: the homologous series of primary alcohols possess an OH (hydroxyl) group on a terminal or primary carbon.
The homologous series and functional groups listed below are the most common. In the tables, the symbols R, R', or the like, can refer to a hydrocarbon chain, a hydrogen atom, or even any set of atoms.
Saturated
- Alkanes
Unsaturated
- Alkenes (methine functional group)
- Alkynes (alkynyl functional group)
Oxygen functions
Presence of some carbon-oxygen bond: single (CO) or double (C=O)
| Functional group | Homologous series | Formula | Structure | Prefix | Suffix | Example |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| hydroxyl group | Alcohol | R-OH | hydroxy- | -ol | ||
| Alkoxy (or aryloxy) group | Ether | ROR' | -oxy- | R -yl R' -yl ether | ||
| carbonyl group | Aldehyde | RC(=O)H |  | formil- | -to the-carbaldehyde | 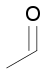 Ethanal Ethanal |
| Ketone | RC(=O)-R' | 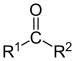 | oxo- | -one |  propanone propanone | |
| carboxyl group | Carboxylic acid | R-COOH |  | carboxy- | -ic acid |  Acetic acid Acetic acid |
| acyl group | Ester | R-COO-R' |  | -yloxycarbonyl- | R' - yl R - ate |
For the nomenclature of these functional groups, see Nomenclature of organic functions with oxygen.
Nitrogenous functions
Amides, amines, nitro compounds, Nitriles. Presence of carbon-nitrogen bonds: CN, C=N or C≡N
| Functional group | compound type | Formula | Structure | Prefix | Suffix | Example |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| amino group | Amine | R-NH 2 |  | Not me- | -Not me | |
| imine | RNCH 2 | 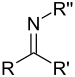 | _ | _ | ![1,5-Diazabicyclo[4.3.0]non-5-ene (BDN)](https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/a/a6/DBN.png/75px-DBN.png) | |
| aminoand carbonyl groups | Amide | R-CO-NR 2 |  | _ | -amide |  acetamide acetamide |
| imide | RC(=O)N(-R')-R" |  | _ | _ | 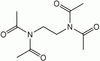 Tetramethylethyldiimide Tetramethylethyldiimide | |
| nitro group | nitro compound | R-NO 2 |  | nitro- | _ |  nitropropane nitropropane |
| nitrile group | nitrile or cyanide | R-CN | cyano- | -nitrile |  | |
| isocyanide | R-NC | alkyl isocyanide | _ |  Tert-butyl isocyanide Tert-butyl isocyanide | ||
| isocyanate | R-NCO | 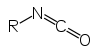 | alkyl isocyanate | _ | ||
| isothiocyanate | R-NCS |  | alkyl isothiocyanate | |||
| azo group | azo derivative | RN=NR' | azo- | -diazene |  | |
| Diazo derivative | R=N=N |  | diazo- | _ | 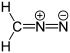 Diazomethane Diazomethane | |
| azide | RN 3 | azido- | -azide | |||
| diazonium salt | XRN ≡N _ | _ | ...ide of...-diazonium |  | ||
| _ | hydrazine | R 1 R 2 N-NR 3 R 4 |  | _ | -hydrazine | 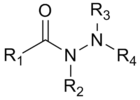 |
| _ | hydroxylamine | -NOH | 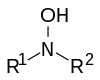 | _ | -hydroxylamine |  |
Halogenated functions
Composed of carbon, hydrogen and halogens.
| Functional group | compound type | compound formula | Prefix | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| halide group | halide | RX | halo- | _ |
| acyl group | acid halide | R-COX | Haloformil- | -oil halide |
Sulfur-containing groups
| Functional group | compound type | compound formula | Prefix | Suffix |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| sulfide group | thioether or sulfide | RSR' | alkylthio- | |
| R-SH | thiol | mercapto- | -thiol | |
| R-SO-R' | Sulfoxide | _ | _ | _ |
| R-SO 2 -R' | Sulfone | _ | _ | _ |
| _ | sulfonic acid | RSO 3H _ | sulfo- | -sulfonic acid |
Organophosphates
| Functional group | compound type | Formula | Structure | Prefix | Suffix | Example |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| sodium phosphinate | PR 3 | _ | _ | |||
| P(=O) R3 | 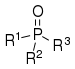 | _ | _ |  | ||
| phosphinite | P(OR)R 2 |  | _ | _ | ||
| phosphinate | P(=O)(OR)R 2 | _ | _ | |||
| phosphonite | P (OR) 2R | 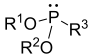 | _ | _ | ||
| Phosphonate | P(=O)(OR) 2 R | 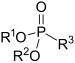 | _ | _ | ||
| Phosphite | Q(OR) 3 | _ | phosphite |  | ||
| Phosphate group | Phosphate | P(=O)(OH) 2R |  | _ | _ |  |
| phosphorane | PR 5 | 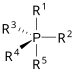 | _ | _ | 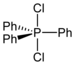 |
Contenido relacionado
Aspartic acid
Adenine
Covalent bond