Friedrich Wöhler
Friedrich Wöhler (Eschersheim, Frankfurt am Main, July 31, 1800 - Göttingen, September 23, 1882) was a German educator and chemist, best known for his synthesis of urea, although also for being the first to isolate several chemical elements, such as beryllium or metallic aluminum.
Biography
Wöhler was born in Eschersheim, which belonged to Hanau at the time, but is now a suburb of Frankfurt am Main.
His father, August Anton Wöhler, a stableman in Eschersheim, was a veterinarian, agronomist, educator and philanthropist. The house where he was born is located at 71 Alt-Eschersheim Street and is preserved as a national historic monument. Wöhler married Franziska Wöhler in 1830 in Kassel, who died in 1832 while she was giving birth to her second child. After being widowed, he married Julie Pfeiffer for the second time. He had a total of six children, two from his first marriage and four from his second.
In 1823 Wöhler finished his medical studies in Heidelberg in the laboratory of Leopold Gmelin. Through him and On his recommendation, he obtained an internship in Stockholm between 1823 and 1824, under the supervision of Jöns Jacob Berzelius, then already a renowned chemist (in 1828 he synthesized urea).
He taught chemistry from 1826 to 1831 at the Polytechnic School in Berlin. In 1839 he was elected a foreign member of the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences. Subsequently, he became Ordinary Professor of Chemistry at the University of Göttingen, where he remained until his death in 1882.
Contributions to Chemistry
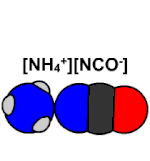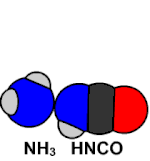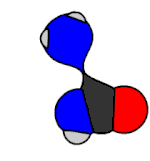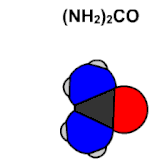
He is considered a pioneer in organic chemistry (also called carbon chemistry today) as a result of the synthesis of urea by the Wöhler synthesis in 1828. This discovery became a refutation of vitalism, the hypothesis that what maintains the activity of living beings is a "vital force" special.
Main works, discoveries and research
Wöhler was also known for being the co-discoverer of beryllium, silicon and silicon nitride, as well as the synthesis of calcium carbide, among others. In 1834 Wöhler and Justus Liebig published research on bitter almond oil. They showed by their experiments that a group of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms can behave like an element, take the place of an element, and can be exchanged for other elements in chemical compounds. Thus the foundations of the doctrine of compound radicals were laid, a doctrine that had a profound influence on the development of chemistry.
The isolation of elemental bodies and the investigation of their properties was one of his favorite activities. In 1827 he obtained metallic aluminum as a fine powder, and in 1845 improved methods enabled him to obtain it in wholly metallic globules. Nine years later Henri Étienne Sainte-Claire Deville, unaware of Wöhler's work, adopted the same methods in his efforts to prepare the metal on an industrial scale; the result of Wöhler's claim of priority was that the two scientists became good friends and joined in an investigation, published in 1856-1857, which yielded "adamantine boron". By the same method that he had succeeded with aluminum (reduction of chloride by potassium) Wöhler in 1828 obtained metallic beryllium and yttrium.
Legacy
Wöhler's discoveries had a great influence on the theory of chemistry. The journals for each year between 1820 and 1881 contain the genesis of his contributions to the field of chemistry. In the magazine "Scientific American" of 1882, it was remarked that for two or three of his investigations he deserves the highest honor a scientist can obtain, but the sum of his work is absolutely overwhelming. If he had never lived, the chemistry would look very different than it does now".
Eponymy
- The lunar crater Wöhler carries this name in his memory.
Contenido relacionado
Oliver Cromwell
Dolores González Catarain
Carlos Nunez Munoz