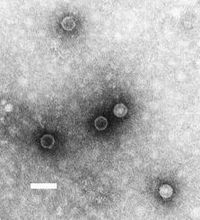
Enteroviruses
Enterovirus is a genus of positive-sense, single-stranded RNA viruses associated with various diseases in humans and other mammals. In serological studies, 71 human enterovirus serotypes have been identified, based on the results of antibody neutralization tests. Additional antigenic variants have been defined in several of the serotypes based on reduced or non-reciprocal cross-neutralization between different strains of the same variant. Based on their pathogenesis in humans and animals, enteroviruses were originally classified into four groups: Poliovirus, Coxsackie A, Coxsackie B, and Echovirus, but the existence of overlaps in the biological properties of the different groups was quickly observed. Recently isolated Enteroviruses have been named with a consecutive number system: EV68, EV69, EV70, etc.
Enteroviruses affect millions of people worldwide every year, frequently being found in respiratory secretions (saliva, sputum, or nasal mucus) and stools of infected people, as well as in contaminated food and water. Historically, polio was the most significant disease caused by an enterovirus. Today we know of 62 enteroviruses, in addition to Polioviruses, that cause disease in humans: 23 Coxsackie A viruses, 6 Coxsackie B viruses, 28 Echoviruses, and 5 other Enteroviruses. Polioviruses, as well as coxsackie and echoviruses, are transmitted by the fecal route. -oral. Infections produce very diverse symptoms, being able to cause from a slight respiratory illness (common cold), hand-foot-mouth disease, human foot-and-mouth disease, acute hemorrhagic conjunctivitis, aseptic meningitis, myocarditis, a disease similar to severe neonatal sepsis, and flaccid paralysis. sharp.
Enteroviruses generally have a relatively narrow host range. Most of the most studied are human viruses, although enteroviruses from primates, pigs, cattle, and insects are known. The best known and studied of this group are the polioviruses.
- Acute Bee Paralysis Virus
- Enterovirus Bovino
- Cricket Paralysis Virus (Drosophila C)
- Virus Gonometa
- Virus Coxsackie Human A1-22
- Human Coxsackie Virus A24
- Virus Coxsackie Human B1-6
- Human Echovirus 1-9
- Human Echovirus 11-27
- Human Echovirus 29-34
- Enterovirus Human 68-71
- Human Poliovirus 1
- Human Poliovirus 2
- Poliovirus Humano3
- Poliovirus Murino
- Enterovirus Porcino
- Enterovirus Simiesco
Differential diagnosis
A differential diagnosis can be given between enterovirus and Zika fever.
Contenido relacionado
Papaver somniferum
Manuel Elkin Patarroyo
Sturnus vulgaris