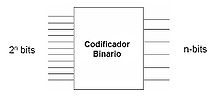
Encoder
An encoder is a combinational circuit with 2N inputs and N outputs, whose mission is to present the binary code corresponding to the activated input at the output.
There are two fundamental types of encoders: non-priority encoders and priority encoders. In the case of non-priority encoders, there may be outputs whose input cannot be known: for example, output 0 could indicate that no input is activated or that input number 0 has been activated. In addition, certain inputs can make the output present the logical sum of these inputs, causing further confusion. For this reason, this type of encoder is only used when the input data range is correctly delimited and its operation is guaranteed.
To avoid the previously mentioned problems, the encoders are designed with priority. In these systems, when there is more than one active signal, the output encodes the one with the highest priority (generally corresponding to the highest decimal value). Additionally, two more outputs are coded: one indicates that no input is active, and the other that any input is active. This measure allows discerning between the assumptions that the circuit was disabled due to the non-activation of the enable signal, that the circuit did not have any active input, or that input number 0 was activated.
We also understand as encoder (codec), a scheme that regulates a series of transformations on a signal or information. These can either transform a signal into an encoded form used for transmission or encryption or obtain the signal suitable for display or editing (not necessarily the original form) from the encoded form.
In this case, encoders are used in multimedia files to compress audio, image or video, since the original form of this type of file is too large to be processed and transmitted by currently available communication systems. They are also used in data compression to obtain a smaller file size.
Based on this new definition, we can divide encoders into lossless codecs and lossy codecs, depending on whether the information being retrieved exactly matches the original or is an approximation.
Contenido relacionado
Charles H. Moore
Convertiplane
Mail server