Council of Baltic Sea States
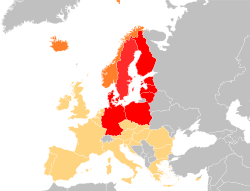
The Council of the Baltic Sea States (in English: Council of the Baltic Sea States, CBSS) is a regional forum composed of eleven countries, established with the Copenhagen Declaration of 1992 to intensify relations of cooperation and coordination between the states of the Baltic Sea. It is based in Stockholm, Sweden.
The main goal of the Council of the Baltic Sea States is to unite the Baltic Sea region in ever-closer cooperation between all Baltic Sea countries through three long-term priority areas term: "Regional identity", "Safe and protected region" and "Sustainable and Prosperous Region". These three priority areas aim to address the issues of the environment, economic development, education, culture, citizen security, children's rights and human trafficking. The Organization's Presidency rotates annually between Member States and the former, the Danish Presidency will run until June 30, 2020 and will largely focus on the reforms of the Baltic Sea Council, so that the organization can maintain its role as the central forum for dialogue in the region.
History
The CBSS was established by the region's foreign ministers in Copenhagen in 1992 as a response to the geopolitical changes that took place in the Baltic Sea region at the end of the Cold War. Since its founding, the CBSS has contributed to ensuring positive development within the Baltic Sea region and has served as a driving force for multilateral cooperation.
Since 1998 the CBSS has been served by a permanent international secretariat based in Stockholm, Sweden, financed by the Member States. The highest institution of the CBSS is the conference of foreign ministers, which meets every two years.
Members
The CBSS has 12 Member States:
 Germany
Germany Denmark
Denmark Estonia
Estonia Finland
Finland Iceland
Iceland Latvia
Latvia Lithuania
Lithuania Norway
Norway Poland
Poland Russia (submitted in March 2022 and withdrawn in May of the same year)
Russia (submitted in March 2022 and withdrawn in May of the same year) Sweden
Sweden European Union
European Union United Kingdom
United Kingdom
Structure
Senior Officials Committee
The Committee of Senior Officials (CSO) is made up of high-ranking representatives of the Ministries of Foreign Affairs of the 11 CEMB Member States, as well as a high-level representative of the European Union. The CSO serves as the main discussion forum and decision-making body for matters related to the Council's work between ministerial sessions. The CSO supervises, facilitates and aims to coordinate the work of all CEMB structures.
The term chaired by each country rotates annually and follows the Presidency of the Council. The CSO Chair is a representative, normally at ambassadorial level, appointed by the Ministry of Foreign Affairs of the country holding the Council Presidency.
Various CBSS structures function under the auspices of the CSO.
The CSO oversees the work of the Expert Groups and coordinates the work carried out on the three agreed long-term priorities: "Regional identity", "Sustainable and prosperous region" and "Safe Region".
Expert groups
- CEMB Group of Experts on Sustainable Maritime Economy
- CEMB Group of Experts on Sustainable Development - manages the Baltic Action Plan 2030
- The CBSS Group of Experts on Children at Risk
- The Working Group against Trafficking in Human Beings
Secretariat
A CEMB Permanent International Secretariat was established following a decision taken at the 7th CEMB Ministerial Session in 1998 in Nyborg, Denmark. The Secretariat was officially opened at its premises on the island of Strömsborg in Stockholm on October 20, 1998. From November 2010 to July 2020, the Secretariat was located in Räntmästarhuset, at Slussplan 9, Stockholm, Sweden. Since July 2020, the Momma Reenstiernas Palace at Wollmar Yxkullsgatan 23 is the new headquarters of the CEMB Secretariat.
The mandate of the Secretariat is as follows
- provide technical and organizational support to the President of the CEMB and the structures and working bodies of the Council;
- Ensure continuity and improved coordination of CEMB activities;
- Implement the CEMB information and communication strategy;
- Maintain CEMB files and database;
- Maintain contacts with other organizations operating in and around the Baltic Sea region, with the national authorities of member States and the media.
Strategic partners
Since the 10th CEMB Ministerial Session in 2001, the Council has intensified efforts to coordinate CEMB activities with other organizations actively working to advance regional cooperation in the Baltic Sea region. The CEMB has taken the initiative to organize annual coordination meetings, (organized and chaired by the CEMB President), with the participation of the Baltic Sea regional organisations, thus providing a more structured channel for strategic partners to express their concerns and coordinate your efforts with CEMB and other organizations such as:
- B7 Baltic Seven Islands
- BASTUN
- BCCA
- Baltic Sea Forum
- BSPC
- BSRUN
- BSSSC
- BUP
- Business Advisory Council
- CPMR
- HELCOM
- IOM
- NGO Forum
- OECD
- ScanBalt
- UBC
Long-term priorities
In June 2014, the Council decided, after an evaluation and review of the five long-term priorities of the CBSS, to incorporate three renewed long-term priorities for the Council of the Baltic Sea States: "Identity regional, sustainable and prosperous region and security". and safe region.
- Regional identity
- Target: Promote an identity of the Baltic Sea Region and intensify contacts that support its future development;
Objective: To develop the concept of identity of the Baltic Sea Region and a sense of membership of the Baltic Sea Region through commitment, participation and multilevel governance, in a community spirit and to create a notion of regional unity across borders by developing person-to-person contacts through dialogue, networks and macroregional institutions;
- Sustainable and Prospera Region
- Target: Develop the Baltic Sea Region as a model region of sustainable societies capable of managing and using resources efficiently, to leverage the potential for economic, technological, ecological and social innovation in the region to ensure its prosperity, environmental protection and social cohesion; contribute to the eradication of obstacles to the integral and sustainable development of the region;
Objectives: To improve the overall competitiveness of the Baltic Sea region through sustainable economic growth and labour markets, research and development, innovative infrastructure, integrated maritime policy, transport and communications; to support the transition from the Baltic Sea region to a competitive, ecological low-carbon economy and thus ensure sustainable development and inclusive growth; to support additional actions to achieve a good environmental state and a healthy ecosystem that supports a prosperous region
- Safe region
- Target: Improve the security of society in the Baltic Sea region and ensure that the inhabitants of the region are protected and resistant to violence, accidents and emergencies through preparedness, and are protected against damage caused by criminal exploitation and trafficking in persons;
- Objectives: To counteract all forms of trafficking in human beings in the Baltic Sea region through prevention and protection projects based on a coherent and multidisciplinary approach; to promote comprehensive and sustainable protection of children in order to prevent and respond to all forms of violence against children through a multisectoral approach and enhanced cooperation between relevant authorities and other stakeholders in the Baltic Sea region; to strengthen the resilience of society to disasters
Contenido relacionado
Saeima
Cotangent bundle
Federal Electoral Institute