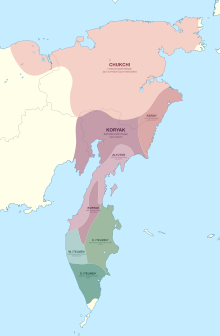
Chukoto-Kamchatka languages
The chukotko-kamchatka languages or luorawetlanas are a family of languages spoken in Siberia. Sometimes these languages are grouped together with other unrelated languages in the Palaeosiberian language group.
Classification
The family consists of 5 languages:
- Chukoto, also known as chukchi or chukot
- Coriaco or koryak
- Alutor who until recently was regarded as a choriaco dialect, but which is now recognized as an independent language.
- Kerek who until recently was regarded as a dialect of the pacifier, but which is now recognized as an independent language. In 1997 there were only two elderly speakers, so the language may be extinct, with the ethnic group assimilated by the Chucoto.
- Itelmeno, also called kamchadal, who had in 1991 about 100 speakers, almost all of them of advanced age.
On the basis of lexical comparison the ASJP project tentatively provides the following classistic tree:
| proto-Ch‐K |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Linguistic description
Phonology
According to Fortescue, Proto-Chukotko-Kamchatka has the following consonantal inventory (all signs used come from AFI):
| Labial | Alveolar | Palatal | Velar | Uvular | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Occlusive | ♪ | ♪ | *c | ♪ | ♪ |
| Fridge | ♪ | ♪ | * | * | |
| Nasal | ♪ | ♪ | * | ||
| Approximately | ♪ | ♪ | ♪ | ||
| Vibrante | ♪ |
/*c/ is properly voiceless palatal stop (not the affricate č). Note that Proto–Chukotko-Kamchatka has only voiceless stops. Although it does have voiced fricatives /*v, *ð, *ɣ, *ʁ/, which have no counterpart voiceless (such as /f, θ, x/).
/*v/ is a labiodental fricative (like the v of English or French). /*ɣ/ is a voiced velar fricative (similar to German g in sagen in some dialects, Modern Greek gamma, Persian qāf, etc.). */ʁ/ is a uvular fricative, like French r (see guttural R).
The entire series /*t, *ð, *n, *l, *r/ en alveolar, not dental.
The vowel inventory is given by:
Previous Central Poster Closed ♪ ♪ Media ♪ ♪ ♪ Open ♪ ♪
Lexical comparison
The numerals in different Chukotko-Kamchatka languages are:
GLOSA Chukchi Koryak-Alyutor Itelmen PROTO-CHUKOTKO-KAMCHATKA Altutor Kerek Koryak '1' Русский ^ ^ Русский qniGUE ♪ '2' Русский
РусскийĐitaq Русский Русский kasχ * '3' Русский Русский Русский tríq * inforMARE-roq '4' ♥ Đijaq ". * inforMARE-raq '5' mětl· møl ¬. měl apostolate měl covenant (pjat) *møtlg(a) '6' و ك و م و م م ا م ا ا ا ا ا م ا م ا م ا
(1 + 5)♫ ♫ ♫ ♫ ♫ ♫ ♫ ♫
(1 + 5)و ان ان من
(1 + 5)و ك و من من
(1 + 5)(shest.) *1+5 '7' Ростарики стани стани стани стани стани сани стани с си си си сананананана с станананани с с с с с с с с с с с с с и с с с с с с с с с с с с с с с с с с с с с с с с с с с с с с с с с с с с с с с с с с с с с с с с с с с с с с с с с с с с с с с с с с с с с
(2 + 5)Русскийaqměl морики
(2 + 5)أعربية
(2 + 5)Русский
(2 + 5)(send) *2+5 '8' Русский
(3 + 5)أعربية
(3 + 5)Русский
Amnesty InternationalРусский
(3 + 5)(vosemı) *3+5 '9' Русский
(4+5)Русский linkraqměl
(4+5)Русский
quiniajtiiŭiأعربية
qonj urgeajtə국kên(devyat) * inforMARE-raq-
mětlěgén/
qon urgeajcθkin'10' měn urgekên měn urgekin mnambitiitii měn urgekên (desyatı) *mθn urgetken(a)
The numerals in parentheses from the itelmen are simply lexical borrowings from Russian.
Contenido relacionado
Asturian Language Academy
Joan Coromines
Moroccan Arabic