Choanoflagellatea
The choanoflagellates (Choanoflagellatea or Choanomonada) are a small group of unicellular eukaryotes, sometimes colonial, to which a great phylogenetic importance, since they are supposed to be the closest relatives of the animals proper (Metazoans), that is, those that form the Animalia kingdom. They are also related to the true fungi (Fungi kingdom), although they are not considered their closest relatives.
The comparison of genes and proteins and the study of the ultrastructure have confirmed that the choanoflagellates are, evolutionarily speaking, the sister group of the true animals, leading some specialists to include them in the Animalia kingdom, as the most important phylum. basal, with the name of Choanomonada or Choanozoa instead of including them in the kingdom Protista.
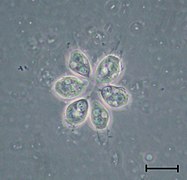
The main characteristic of these organisms is the presence of a collar or crown formed by microvilli covered with mucus around a flagellum; this makes them virtually identical to the choanocytes of porifera (sponges).
Features
The choanoflagellates are a not very diverse group, consisting of about 150 species distributed among about 50 genera in two orders. They inhabit all aquatic environments, although their presence is most notable in cold and polar seas. They filter the water to separate mainly bacteria, which is their staple food.
Structure

In its morphology there are several peculiar features. They show marked cell polarity. They have a fixation pole or peduncle, by which they can be attached to the substrate. The other pole of mobility, or kinetic, is typically enveloped by a lorica, of microtubules with the appearance of a loosely braided cage. At this same kinetic pole, the opening of the cell appears surrounded by a collar of cup-shaped microvilli, from whose center a single flagellum emerges, which shakes with a helical.
Electron microscopic examination shows that the collar, which appears continuous at lower magnification, is actually made up of a crown of microvilli (microvilli), slender, finger-like appendages.
Choanoflagellates can be found as free swimmers in the water column or sessile, adhering to the substratum directly or through the periplast.
Its life cycle has not yet been clarified. At the moment, it is not known if there is a sexual phase in your cycle. Some choanoflagellates can form cysts.
Phylogenetic relationships
From the beginning, the similarity between the anatomy of choanoflagellates and that of the filtering cells of sponges, the choanocytes, attracted attention. Some choanoflagellates form colonies, which in the case of the genera Spongomonas or Proterospongia form a fairly organized group, with a certain specialization of the cells that makes one think of a small, extremely simple sponge.. Choanoflagellates allow us to get an idea of how the evolution of some multicellular organisms (Kingdoms Animalia and Fungi) began from protists.
Like animal spermatozoa, choanoflagellates are opisthokonts, that is, the flagellum drives the cell forward, advancing with the flagellum behind, unlike most protists, which are acrokonts (the flagellum drags the cell, which advances with him ahead). It is one of the details that allow animals (and choanoflagellates) to be united with fungi in a larger group called Opisthokonta (opisthocontos), as can be seen in the following cladogram:
| Opisthokonta |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||