Chemical formula
A chemical formula is the representation of the chemical elements that make up a chemical compound and the proportion in which they are found, or the number of atoms that make up a molecule. It can also give us additional information such as how these atoms are joined by chemical bonds and even their distribution in space. To name them, the rules of chemical nomenclature are used. Example: The formula of silanes Sometimes members of a chemical family differ from each other by a constant unit, usually an additional carbon atom in a carbon chain.
There are several types of chemical formulas:
Molecular formula
The molecular formula of a chemical compound is a graphical representation of the molecular structure, showing how the atoms are arranged or spatially distributed. Chemical bonds within the molecule are shown, either explicitly or implicitly
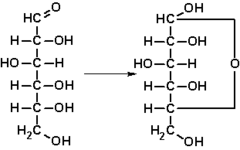
Semi-developed formula
The semi-expanded formula shows all the atoms that make up a covalent molecule, and the bonds between carbon atoms (in organic compounds) or other types of atoms. Carbon-hydrogen bonds not indicated
- CH2OH− − CHOH− − CHOH− − CHOH− − CHOH− − CHO{displaystyle CH_{2}OH-CHOH-CHOH-CHOH-CHOH-CHOH-CHOH)
Developed formula
The developed formula is the next step in complexity of the semi-developed one, indicating the bond and the location of each atom of the compound within their respective molecules, in a Cartesian plane, representing the entire structure of the compound
Structural formula
The structural formula is similar to the previous ones, but indicating the spatial geometry of the molecule by indicating distances, angles or the use of perspectives in two or three-dimensional diagrams.
Lewis Formula
Structure of Lew s, also called a dot diagram, Lewis model, or Lewis representation, is a graphical representation that shows the bonds between atoms in a molecule and pairs of lone electrons that can exist.
Diagrams
In a 2D diagram, you can see the orientation of the links using special symbols. A solid line represents a link in the plane; if the link is behind, it is represented by a dotted line; if the link is ahead, it is indicated by a triangular wedge-shaped symbol. Sometimes other types of conventions or projections are used for groups of specific compounds (Newman projection, Tollens Reagent, etc).
General formula
The general formula of a group of compounds can be represented in different ways:
Expressing the number of atoms of each kind for example
In inorganic chemistry, a family of compounds can be represented by a general formula whose subscripts (number of atoms of each class) are variables (x, y, z).
Including mathematical expressions in the subscripts
In organic chemistry, subscripts are often mathematical expressions that include the variable n (number of carbon atoms). The set of compounds that share the same general formula is called a homologous series. For example, the general formula for alcohols is: CnH(2n + 1)OH (where n ≥ 1)
| Homologous series | General formula | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Alcanos | CnH2n+2 | CH4C2H6C3H8C4H10 |
| Unsaturated monkeys | CnH2n | C2H4C3H6C4H8 |
| Monounsaturated | CnH2n-2 | C2H2C3H4C4H6 |
| Cycloalcans | CnH2n | C4H8C6H12 |
| Alcohol | CnH(2n + 1)OH | CH3OH, C2H5OH |
Including radicals and functional group
In the expression of the general formula, in organic chemistry, the structure of the compounds of a homologous series usually appears, including the part of the substituent (represented by R, R', etc) and the functional group. Example: The general formula of primary alcohols is R-OH.
| Homologous series | General formula | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Alcohol | R-OH | CH3OH, C2H5OH |
| Ethers | R-O-R | CH3-O-CH3 |
| Aldehyde | R-CHO | CH3-CHO, CH3-CH2- Right. |
| Cetonas | R-CO-R | CH3-CO-CH3 |
| Carboxylic acids | R-COO-H | CH3- COOH |
| _ | R-COO-R | CH3-CH2-COO-CH3 |
| Amnes | R-NH2 | CH3-CH2-NH2 |
| Beloved | R-CONH2 | CH3-CH2-CONH2 |
| Nitrilos | R-CN | CH3-CH2-CN |
Hill's system
The Hill system (or Hill notation) is a writing system of empirical chemical formulas, molecular chemical formulas, and components of a condensed formula such that the number of carbon atoms in a molecule listed first, the number of hydrogen atoms next, and then the number of all other chemical elements afterward, in alphabetical order of chemical symbols. When the formula does not contain carbon, all elements, including hydrogen, are listed alphabetically.
Classifying formulas according to the number of atoms of each element present in the formula according to these rules, and differences in earlier elements or numbers are treated as more significant than differences in any later elements or numbers, as sort text strings in lexicographical order: it is possible to collate chemical formulas in what is known as Hill system order.
Hill's system was first published by Edwin A. Hill of the United States Patent and Trademark Office in 1900. It is the most widely used system in chemical databases and print indexes for classifying lists of compounds.
A list of formulas in Hill system order is arranged alphabetically, as shown above, with single-letter elements preceding double-letter symbols when the symbols begin with the same letter (so "B" comes before "Be", which comes before "Br ").
The following example formulas are written using Hill's system and are listed in Hill's order:
- BrI
- BrClH2Yeah.
- CCl4
- CH3I
- C2H5Br
- H2O4S
Contenido relacionado
Fermium
Semi-metal
Dmitri Mendeleyev