Carrier wave
A carrier wave is a wave, generally sinusoidal, that will be used to modify some of its parameters (amplitude, frequency or phase) to a signal called modulating with the purpose of in order to transmit information. This carrier wave is of a much higher frequency than that of the modulating signal.
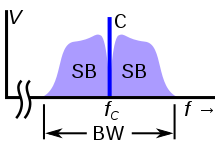
By modulating a signal, its spectral content is shifted in frequency, occupying a certain bandwidth around the frequency of the carrier wave. This allows multiple signals to be frequency multiplexed simply by using different carrier waves, thus making more efficient use of the frequency spectrum.
In telecommunications, the wavelength of the carrier wave (λ), expressed in meters (m), of the signal is related to the speed of light (c), expressed in meters per second (m/s), divided by the frequency (f), in hertz (Hz), according to the expression:
λ λ =cf{displaystyle lambda ={frac {c}{f}}}}
So, for example, to transmit a 30 MHz signal (which would have a wavelength of 10 m) you would need an antenna whose length is a multiple or submultiple of 10 m. By modulating said signal, it is possible to reduce the size of the necessary antenna.
Carrier waves are used to transmit radio signals to a radio receiver. Both amplitude modulation (AM) and frequency modulation (FM) signals are transmitted with the help of carrier frequencies. The frequency for a given radio station is actually the frequency of its carrier wave.
Carrierless modulation systems
Modern forms of radio communication (such as spread spectrum and ultra-longband) do not use a conventional sine carrier wave, nor OFDM (used in DSL and the European standard for HDTV).
- OFDM can be thought as a set of symmetrical bearer waves. The rules governing the spread of carrier waves affect OFDM differently than 8VSB.
- Some forms of widened spectrum transmission (and most ultra-long band forms) are mathematically defined as lacking bearer waves. The transmitter's implementations typically produce residual carriers that may, or may not, be detectable or transmitted.
Carrier leak
Carrier leakage is interference caused by crosshead or DC offset. It is present as an unmodulated sine wave within the signal bandwidth, the amplitude of which is independent of the signal amplitude. See frequency mixers, to read more about carrier runaway or local oscillator passthrough.
Contenido relacionado
Space shuttle program
Prey
Help:Images