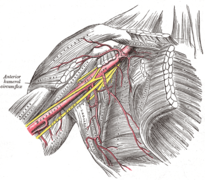
Brachial artery
The brachial artery, also known as the brachial artery, is the artery of the arm. axillary artery which changes its name to the brachial or humeral artery from the lower border of the pectoralis major muscle after crossing the teres major muscle. It courses downward and inward and is positioned medial to the biceps brachii muscle, reaching the internal biceps canal (Cruveilhier's canal), to reach the cubital fossa and divide into its two terminal branches: the radial artery and the ulnar artery. or ulnar.
Branches
Collateral branches:
- 1) Deep artery of the arm, external collateral, deep brachial or deep.
- Arteries of the humerus.
- Rama deltoidea. This branch is distinguished from many other small muscle branches because it is more constant and with origin, path and territory less variable.
- Average collateral artery.
- Radial collateral artery.
- (2) Lower or collateral artery lower internal collateral.
- (3) Upper or collateral artery upper internal collateral.
Terminal branches:
- 1) Arteria ulnar o cubital.
- 2) Radial artery.
Arterial Tree in Anatomical Terminology
Anatomical Terminology includes the following tree for the brachial artery (See discussion):
- A12.2.09.019 Surface brachial artery (A12.2.09.019)artery brachialis superficialis)
- A12.2.09.020 Deep arm artery (artery deep brachii)
- A12.2.09.021 Numeral arteries (arteriae nutriciae humeri; arteriae nutrients humeri)
- A12.2.09.022 Branch deltoid of the deep artery of the arm (ramus deltoideus arteriae profundae brachii)
- A12.2.09.023 Average collateral artery (A12.2.09.023)artery collateralis media)
- A12.2.09.024 Radial collateral artery (A12.2.09.024)artery collateralis radialis)
- A12.2.09.025 Upper Qualitative Collateral Arteryartery collateralis ulnaris superior)
- A12.2.09.026 Lower cubital collateral artery (artery collateralis ulnaris inferior)
Tour
Start at the lower border of the teres major muscle to finish two finger spans over the cubital fossa (cubital fossa) in front of the neck of the radius. It is situated medially of the brachial and brachial biceps muscles; in its inferolateral course it accompanies the median nerve.
Deep artery of the arm or profunda brachialis
This artery enters above the medial intermuscular septum of the upper arm into the humerotricipital triangle (inferior axillary space) with the radial nerve, and together they cross the posterior aspect of the humeral shaft from medial to lateral by the torsion canal (groove for the radial nerve), traversing the medial region, where it supplies the triceps brachii muscle. Shortly before the lateral epicondyle (epicondyle), it divides into two terminal branches:
- Radial collateral artery.
- Average collateral artery.
Supply artery of the humerus
Arises in the middle third of the arm and enters through the nutrition canal of the anteromedial aspect of the humerus, heading distally towards the elbow.
Inferior ulnar collateral artery or inferior ulnar collateral artery
5 cm from the crease of the elbow, it passes medially under the medial epicondyle (epitrochlea ) of the humerus and anastomoses (joins) with the anterior branch of the recurrent artery ulnar, forming part of the periarticular complex of the elbow.
Superior ulnar collateral artery or superior ulnar collateral artery
It originates in the upper arm. Oblique downward and medially, pierces the medial intermuscular septum, meets the ulnar nerve posteriorly, follows the medial head of the triceps brachii muscle, supplying branches to it, and on the posterior aspect of the elbow anastomoses with the posterior ramus of the ulnar recurrent artery.
Additional images
|
Contenido relacionado
Similarly, the meeting of medical specialists in Buenos Aires, ―in conjunction with the World Federation of Hemophilia― agree on the use of the equation for the replacement of factor VIII (with results in UI) that corresponds to:
Pleural effusion
Tuberculosis