Bones of the face
The splanchnocranium, or viscerocranium, refers to the part of the skull that contains the anterior part of the digestive and respiratory systems. The splanchnocranium was formed in the same way as the muscles that surround the internal part of the digestive system, that is, they were visceral musculature. Currently, it has been possible to follow the development of these muscles, which come from the dorsal part of the skull and are skeletal musculature. The mouth is also formed from the primitive mouth or stomodeus, for which its tissues are of ectodermal origin.
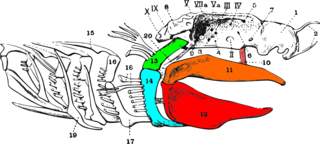
In fish, the splanchnocranium is composed of the mandibular arch (the mouth), the hyoid arch (where the spiracle is located and which usually participates in supporting the mouth) and a variable number of brachial arches, which support the gills, and the dermal bones associated with them, including the operculum bones. In tetrapods, these arches contribute variably in embryonic development to the development of the mouth, hyoid apparatus, middle ear, and larynx.
Bones that make up the splanchnocranium
In medicine, in humans, the bones of the face are considered:
- Palatine (2)
- Vomer (1)
- Lower bracket (2)
- Cygomatic or malar bones (2)
- Maxilar superior, maxila or maxilar (2)
- Maxilar inferior or jaw (1)
- Nasal (2)
- Lagrimal (2)

The nasal and lacrimal bones, being above the nasal capsules that are part of the embryonic neurocranium, are not considered part of the splanchnocranium in the comparative anatomy of vertebrates.
| Condrictios | Osteictios | Amphibians | Reptiles and Birds | Mammals | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mandibular Arc | Pavilion* (2) | Square** (2)
Premaxilar*** (2) Maxilar (2) Ectopalatin (2) Endopterigoides (2) Ectopterigoides (2) Metapterigoids (2) Prevómer (1) Yugal (2) Cuadradoyugal (2) Simple. | Square Premaxil Maxilar Palatin Pterigoides Prevómer Yugal Cuadradogal | Square Premaxil Maxilar palatino Transverse Pterigoides Prevómer Yugal Cuadradogal Septo Maxilar | And one that PremaxilMaxilar Palatine Vomer Cygomatic bones (homologist to yugal) |
| Meckel Cartilage (2) | Mentomeckeliano (2)
Dental (2) Esplenial (2) Coronoids (2) Angular (2) Supraangular (2) Articular (2) | Mentomeckeliano Dental Spolenial Coronoids Angular Supraangular Prearticular Articular | Mentomeckeliano Dental Spolenial Coronoids Angular Supraangular Prearticular Articular | Mandible (2 or 1)
(is a counterpart to the offender) Hammer (2) | |
| Hioid Arc | Hiomandibular (2) Ceratohial (2) Hipohial (2) Basihial (1) | Hiomandibular (2) Ceratohial(2) Interhial(2) Hipohial(2) Basihial(1) Urohial(2) Opercular bones | Columela
Hioid or Hioid | Columela
| Estribo (2)
|
| Arcos branquiales (bones of a bow) | Faringobranchial (2) Ceratobraquial(2) Epibranquial(2) Hipobranquial(2) Basibranquial(2) | Faringobranchial (2) Ceratobraquial Epibranquial Hipobranquial Basibranquial | laryngeal cartilage | laryngeal cartilage | laryngeal cartilage |
| *in italics: cartilage; ** in bold, endocondral osification bones; ***bones of the dermatocraneous. | |||||
Contenido relacionado
Nerve
Vegetable
Deoxyribose