Aten
Aten (whose name means 'whole' or 'complete' in Egyptian) is believed to have been an Ancient Egyptian solar deity who represented the sun's disk in the sky. He was considered, in Egyptian mythology, the spirit that encouraged life on Earth. King Akhenaten, in the course of his reign, venerated Aten, claiming him as the sole and exclusive divinity.
In early Egyptian creation myths it is claimed that he is the ultimate creator.
Egyptian name: Aten. Greek name: Aten.
Iconography
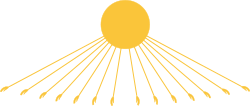
In the early days it was represented as a man with the head of a falcon (same as the representation of the Heliopolitan Ra-Harajti), later as a solar disk from which rays emerged with hands extended towards the believers, or holding signs of life. Thus, later it was considered that Aten, by nature, was everywhere and was intangible because it was the light of the sun and the energy of the world. Therefore, he did not have the physical representations that other Egyptian gods had; he was represented by the sun disk and hands as rays of light.The explanation why the Aten could not be fully represented was because the Aten was beyond creation. Thus the scenes of the gods carved in stone, which formerly represented animal and human forms, now showed the Aten as an orb aloft with life-giving rays extending towards the actual figure. This power transcended human or animal form.
Later, iconoclasm took hold, and even depictions of Aten's sun disks were banned in an edict issued by Akhenaten. In the edict, he stipulated that Aten's name must be spelled phonetically.
Mythology
In ancient times it was the solar disk of the sky, the life force that animated everything on Earth.
In the time of Amarna, Aten was a god of infinite goodness, the one who vivified Justice and cosmic Order, Maat, favoring all men equally. The sovereign was his envoy, and his prophet on earth, the only one worthy of immortality.
Syncretism
He was identified with Toth, in his nocturnal form, calling him the "Silver Aten".
In the first nine years of the Amarnian period, the Aten is identified with Ra-Horajti and Shu as a symbol of light, being "Ra, Ruler of Ajti, active in Ajet". Ra could be the essence of the Solar Disc, to which the king, who is called Ua-en-Ra, "One in Ra" or & # 34; His body is Aton & # 34;.
The cult of Aten
The cult of the Aten dates from the New Kingdom of Egypt. Thutmosis IV and Amenhotep III had paid him veneration, becoming a monotheistic cult, or preferably henotheistic, during the religious reform of Pharaoh Amenhotep IV "Amun is satisfied", who changed his name to Akhenaten " Aten's Radiance" or "Useful to Aten", in the 14th century BC. c.
His main temple was in the city of Akhetaten "The Horizon of the Aten", in present-day Amarna. The Hymn to Aten, engraved on a wall of the tomb of Ay, and written by Akhenaten, is one of the most beautiful literary exponents of Egyptian culture.
When you study Akhenaten's new religion in depth, the first thing you notice is a stubborn struggle not to leave it exclusively in the hands of the priests. There is only one maximum representative of it: the pharaoh calling himself the high priest of Ra-harajti, "He who rejoices on the horizon."
A large part of the clergy, upon losing their privileges, opposed the preferential worship of the Aten and the Egyptians continued to venerate their ancient gods to ask them for protection from illnesses or the resolution of their most pressing needs. They tried to create a new, simpler cult of the Aten, but it did not stop being more abstract and intellectual.
After the death of Akhenaten, the previous situation gradually returned and, later, Akhetaten (Amarna) was abandoned and, at the rise of the 19th Dynasty, it was intended to erase all vestiges of Amarna's theocratic adventure.
| Aten (Aton) in hieroglyphic |
|
Contenido relacionado
Song of the Nibelungs
Hunt
Gulf war