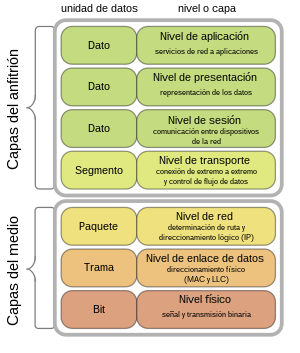
Application layer
The application layer or application layer is the seventh layer of the OSI model and the fourth layer of the TCP/IP stack.
It offers applications (user or not) the possibility of accessing the services of the other layers and defines the protocols used by applications to exchange data, such as email (POP and SMTP), database managers and file transfer protocols (FTP).
It should be noted that the user does not normally interact directly with the application layer. It usually interacts with programs that in turn interact with the application layer but hide the underlying complexity. Thus, for example, a user does not send a "GET /index.html HTTP/1.0" request to get an html page, nor does it directly read the html/xml code. Or when we chat with Instant Messenger, we don't need to encode the recipient information and data to deliver to the Presentation layer (layer 6) to send the packet.
Different protocols and services appear in this layer:
Protocols:
- FTP (File Transfer Protocol - File transfer protocol) for file transfer.
- DNS (Domain Name System - Domain name system).
- DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol - Host dynamic configuration protocol).
- HTTP (HyperText Transfer Protocol) for access to web pages.
- HTTPS (Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure) Safe hypertext transfer protocol.
- POP (Post Office Protocol) for recovery of [email].
- SMTP (Simple Mail Transport Protocol) for sending email.
- SSH (Secure SHell)
- TELNET to access remote equipment.
- TFTP (Trivial File Transfer Protocol).
- LDAP (Lightweight Directory Access Protocol).
- XMPP, (Extensible Messaging and Presence Protocol) - Standard protocol for instant messaging.
Services:
- Network applications
- www.World Wide Web).
- Link to lower layers
This layer contains the applications visible to the user. Some considerations are: security and encryption, DNS (Domain Name Service) One of the most used applications on the Internet today is the WWW (World Wide Web).
Contenido relacionado
Shellcode
IRIX
Software Engineering