Catálogos médicos humanos comunes para los resultados de análisis de sangre
Los rangos de referencia (intervalos de referencia) para análisis de sangre son conjuntos de valores utilizados por un profesional de la salud para interpretar un conjunto de resultados de pruebas médicas a partir de muestras de sangre. Los rangos de referencia para los análisis de sangre se estudian en el campo de la química clínica (también conocida como "bioquímica clínica", "patología química" o "química sanguínea pura"), la área de la patología que generalmente se ocupa del análisis de fluidos corporales.
Los resultados de las pruebas de sangre siempre deben interpretarse utilizando el rango de referencia proporcionado por el laboratorio que realizó la prueba.
Interpretación
Un rango de referencia generalmente se define como el conjunto de valores dentro del cual se encuentra el 95 % de la población normal (es decir, el intervalo de predicción del 95 %). Se determina mediante la recopilación de datos de un gran número de pruebas de laboratorio.
Plasma o sangre completa
En este artículo, todos los valores (excepto los que se enumeran a continuación) indican una concentración en plasma sanguíneo, que es aproximadamente entre un 60 y un 100 % mayor que la concentración real en sangre si la cantidad dentro de los glóbulos rojos (GR) es insignificante. El factor exacto depende del hematocrito y de la cantidad dentro de los glóbulos rojos. Las excepciones son principalmente aquellos valores que denotan concentración total en sangre, y en este artículo son:
- Todos los valores en Hematología – glóbulos rojos (excepto hemoglobina en plasma)
- Todos los valores en Hematología – glóbulos blancos
- Conteo de plaquetas (Plt)
Algunos valores son solo para el interior de los glóbulos rojos:
- Vitamina B9 (ácido fólico/folato) en glóbulos rojos
- Concentración media de hemoglobina corpuscular (MCHC)
Unidades
- La concentración masiva (g/dL o g/L) es la unidad de medición más común en los Estados Unidos. Se administra generalmente con dL (decilitres) como el denominador en los Estados Unidos, y generalmente con L (litros) en, por ejemplo, Suecia.
- La concentración de molares (mol/L) se utiliza en mayor grado en la mayoría del resto del mundo, incluido el Reino Unido y otras partes de Europa y Australia y Nueva Zelandia.
- Las unidades internacionales (UI) se basan en actividades o efectos biológicos medidos, o para algunas sustancias, una masa equivalente específica.
- La actividad enzimática (kat) se utiliza comúnmente para pruebas de función hepática como AST, ALT, LD y γ-GT en Suecia.
- Los porcentajes y unidades dependientes del tiempo (mol/s) se utilizan para parámetros derivados calculados, por ejemplo para función de células beta en la evaluación del modelo de homeostasis o la capacidad secreta de tiroides.
Arterial o venosa
(feminine)
Si no se especifica lo contrario, un rango de referencia para un análisis de sangre es generalmente el rango venoso, ya que el proceso estándar para obtener una muestra es por venopunción. Una excepción es para el ácido-base y los gases sanguíneos, que generalmente se administran para la sangre arterial.
Aún así, los valores en sangre son aproximadamente iguales entre los lados arterial y venoso para la mayoría de las sustancias, con la excepción de ácido-base, gases en sangre y fármacos (utilizados en ensayos de monitorización terapéutica de fármacos (TDM)). Los niveles arteriales de los fármacos son generalmente más altos que los niveles venosos debido a la extracción al atravesar los tejidos.
Usual u óptimo
Los rangos de referencia generalmente se dan como los valores habituales (o normales) encontrados en la población, más específicamente el intervalo de predicción en el que se encuentra el 95% de la población. Esto también puede llamarse rango estándar. Por el contrario, el rango (salud) óptimo o objetivo terapéutico es un rango o límite de referencia que se basa en concentraciones o niveles asociados con una salud óptima o un riesgo mínimo de complicaciones relacionadas. y enfermedades Para la mayoría de las sustancias presentadas, los niveles óptimos son también los que normalmente se encuentran en la población. Más específicamente, los niveles óptimos generalmente están cerca de una tendencia central de los valores encontrados en la población. Sin embargo, los niveles habituales y óptimos pueden diferir sustancialmente, sobre todo entre las vitaminas y los lípidos en la sangre, por lo que estas tablas dan límites en los rangos tanto estándar como óptimos (u objetivo). Además, algunos valores, incluidos la troponina I y el péptido natriurético cerebral, se dan como puntos de corte apropiados estimados para distinguir a las personas sanas de las personas con afecciones específicas, que aquí son infarto de miocardio e insuficiencia cardíaca congestiva, respectivamente, para las sustancias antes mencionadas.
Variabilidad
El rango de referencias puede variar según la edad, el sexo, la raza, el embarazo, la dieta, el uso de medicamentos recetados o a base de hierbas y el estrés. Los intervalos de referencia a menudo dependen del método analítico utilizado, por motivos como la inexactitud, la falta de estandarización, la falta de material de referencia certificado y la diferente reactividad de los anticuerpos. Además, los rangos de referencia pueden ser inexactos cuando los grupos de referencia usados para establecer los rangos son pequeños.
Ordenada por concentración
(feminine)
By mass and molarity
Smaller, narrower boxes indicate a more tight homeostatic regulation when measured as standard "usual" reference range.
Reference ranges for blood tests, sorted logarithmically by mass above the scale and by molarity below. (
A separate printable image is available for mass and molarity)
Hormones predominate at the left part of the scale, shown with a red at ng/L or pmol/L, being in very low concentration. There appears to be the greatest cluster of substances in the yellow part (μg/L or nmol/L), becoming sparser in the green part (mg/L or μmol/L). However, there is another cluster containing many metabolic substances like cholesterol and glucose at the limit with the blue part (g/L or mmol/L).
The unit conversions of substance concentrations from the molar to the mass concentration scale above are made as follows:
-
molar concentration
×
molar mass
=
mass concentration
{displaystyle {text{molar concentration}}times {text{molar mass}}={text{mass concentration}}}

- Measured directly in distance on the scales:
-
log
10
molar mass
1000
=
distance to right (decades)
{displaystyle log _{10}{frac {text{molar mass}}{1000}}={text{distance to right (decades)}}}
 ,
,
where distance is the direct (not logarithmic) distance in number of decades or "octaves" to the right the mass concentration is found. To translate from mass to molar concentration, the dividend (molar mass and the divisor (1000) in the division change places, or, alternatively, distance to right is changed to distance to left. Substances with a molar mass around 1000g/mol (e.g. thyroxine) are almost vertically aligned in the mass and molar images. Adrenocorticotropic hormone, on the other hand, with a molar mass of 4540, is 0.7 decades to the right in the mass image. Substances with molar mass below 1000g/mol (e.g. electrolytes and metabolites) would have "negative" distance, that is, masses deviating to the left.
Many substances given in mass concentration are not given in molar amount because they haven't been added to the article.
The diagram above can also be used as an alternative way to convert any substance concentration (not only the normal or optimal ones) from molar to mass units and vice versa for those substances appearing in both scales, by measuring how much they are horizontally displaced from one another (representing the molar mass for that substance), and using the same distance from the concentration to be converted to determine the equivalent concentration in terms of the other unit. For example, on a certain monitor, the horizontal distance between the upper limits for parathyroid hormone in pmol/L and pg/mL may be 7 cm, with the mass concentration to the right. A molar concentration of, for example, 5 pmol/L would therefore correspond to a mass concentration located 7 cm to the right in the mass diagram, that is, approximately 45 pg/mL.
By units
Units do not necessarily imply anything about molarity or mass.
A few substances are below this main interval, e.g. thyroid stimulating hormone, being measured in mU/L, or above, like rheumatoid factor and CA19-9, being measured in U/mL.
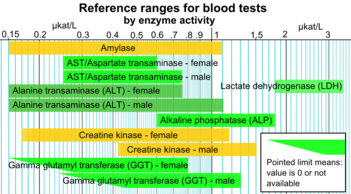
By enzyme activity
White blood cells
Sorted by category
Ions and trace metals
Included here are also related binding proteins, like ferritin and transferrin for iron, and ceruloplasmin for copper.
| Test
|
Lower limit
|
Upper limit
|
Unit*
|
Comments
|
| Sodium (Na) |
135, 137 |
145, 147 |
mmol/L or mEq/L |
See hyponatremia or hypernatremia
|
| 310, 320 |
330, 340 |
mg/dL |
|
| Potassium (K) |
3.5, 3.6 |
5.0, 5.1 |
mmol/L or mEq/L |
See hypokalemia or hyperkalemia
|
| 14 |
20 |
mg/dL |
|
| Chloride (Cl) |
95, 98, 100 |
105, 106, 110 |
mmol/L or mEq/L |
See hypochloremia or hyperchloremia
|
| 340 |
370 |
mg/dL |
|
| Ionized calcium (Ca) |
1.03, 1.10 |
1.23, 1.30 |
mmol/L |
See hypocalcaemia or hypercalcaemia
|
| 4.1, 4.4 |
4.9, 5.2 |
mg/dL |
|
| Total calcium (Ca) |
2.1, 2.2 |
2.5, 2.6, 2.8 |
mmol/L |
|
| 8.4, 8.5 |
10.2, 10.5 |
mg/dL |
|
| Total serum iron (TSI) – male |
65, 76 |
176, 198 |
µg/dL |
See hypoferremia or the following: iron overload (hemochromatosis), iron poisoning, siderosis, hemosiderosis, hyperferremia
|
| 11.6, 13.6 |
30, 32, 35 |
μmol/L |
|
| Total serum iron (TSI) – female |
26, 50 |
170 |
µg/dL |
|
| 4.6, 8.9 |
30.4 |
μmol/L |
|
| Total serum iron (TSI) – newborns |
100 |
250 |
µg/dL |
|
| 18 |
45 |
µmol/L |
|
| Total serum iron (TSI) – children |
50 |
120 |
µg/dL |
|
| 9 |
21 |
µmol/L |
|
| Total iron-binding capacity (TIBC) |
240, 262 |
450, 474 |
μg/dL |
|
| 43, 47 |
81, 85 |
µmol/L |
|
| Transferrin |
190, 194, 204 |
326, 330, 360 |
mg/dL |
|
| 25 |
45 |
μmol/L |
|
| Transferrin saturation |
20 |
50 |
% |
|
| Ferritin – Males and postmenopausal females |
12 |
300 |
ng/mL or µg/L |
|
| 27 |
670 |
pmol/L |
|
| Ferritin – premenopausal females |
12 |
150 – 200 |
ng/mL or µg/L |
|
| 27 |
330 – 440 |
pmol/L |
|
| Ammonia |
10, 20 |
35, 65 |
μmol/L |
See hypoammonemia and hyperammonemia
|
| 17, 34 |
60, 110 |
μg/dL |
|
| Copper (Cu) |
70 |
150 |
µg/dL |
See hypocupremia or hypercupremia
|
| 11 |
24 |
μmol/L |
|
| Ceruloplasmin |
15 |
60 |
mg/dL |
|
| 1 |
4 |
μmol/L |
|
| Phosphate (HPO42−) |
0.8 |
1.5 |
mmol/L |
See hypophosphatemia or hyperphosphatemia
|
| Inorganic phosphorus (serum) |
1.0 |
1.5 |
mmol/L |
|
| 3.0 |
4.5 |
mg/dL |
|
| Zinc (Zn) |
60, 72 |
110, 130 |
μg/dL |
See zinc deficiency or zinc poisoning
|
| 9.2, 11 |
17, 20 |
µmol/L |
|
| Magnesium |
1.5, 1.7 |
2.0, 2.3 |
mEq/L or mg/dL |
See hypomagnesemia or hypermagnesemia
|
| 0.6, 0.7 |
0.82, 0.95 |
mmol/L |
|
- Note: Although 'mEq' for mass and 'mEq/L' are sometimes used in the United States and elsewhere, they are not part of SI and are now considered redundant.
Acid–base and blood gases
If arterial/venous is not specified for an acid–base or blood gas value, then it generally refers to arterial, and not venous which otherwise is standard for other blood tests.
Acid–base and blood gases are among the few blood constituents that exhibit substantial difference between arterial and venous values. Still, pH, bicarbonate and base excess show a high level of inter-method reliability between arterial and venous tests, so arterial and venous values are roughly equivalent for these.
| Test
|
Arterial/Venous
|
Lower limit
|
Upper limit
|
Unit
|
| pH |
Arterial |
7.34, 7.35 |
7.44, 7.45 |
|
| Venous |
7.31 |
7.41 |
|
| [H+] |
Arterial |
36 |
44 |
nmol/L
|
| 3.6 |
4.4 |
ng/dL
|
| Base excess |
Arterial & venous |
−3 |
+3 |
mEq/L
|
| Oxygen partial pressure (pO2) |
Arterial pO2 |
10, 11 |
13, 14 |
kPa
|
| 75, 83 |
100, 105 |
mmHg or torr
|
| Venous |
4.0 |
5.3 |
kPa
|
| 30 |
40 |
mmHg or torr
|
| Oxygen saturation |
Arterial |
94, 95, 96 |
100 |
%
|
| Venous |
Approximately 75
|
| Carbon dioxide partial pressure (pCO2) |
Arterial PaCO2 |
4.4, 4.7 |
5.9, 6.0 |
kPa
|
| 33, 35 |
44, 45 |
mmHg or torr
|
| Venous |
5.5, |
6.8 |
kPa
|
| 41 |
51 |
mmHg or torr
|
| Absolute content of carbon dioxide (CO2) |
Arterial |
23 |
30 |
mmol/L
|
| 100 |
132 |
mg/dL
|
| Bicarbonate (HCO3−) |
Arterial & venous |
18 |
23 |
mmol/L
|
| 110 |
140 |
mg/dL
|
| Standard bicarbonate (SBCe) |
Arterial & venous |
21, 22 |
27, 28 |
mmol/L or mEq/L
|
| 134 |
170 |
mg/dL
|
Liver function
| Test
|
Patient type
|
Lower limit
|
Upper limit
|
Unit
|
Comments
|
| Total protein (TotPro) |
|
60, 63 |
78, 82, 84 |
g/L |
See serum total protein Interpretation
|
| Albumin |
|
35 |
48, 55 |
g/L |
See hypoalbuminemia
|
| 3.5 |
4.8, 5.5 |
U/L
|
| 540 |
740 |
μmol/L
|
| Globulins |
|
23 |
35 |
g/L |
|
| Total bilirubin |
|
1.7, 2, 3.4, 5 |
17, 22, 25 |
μmol/L |
|
| 0.1, 0.2, 0.29 |
1.0, 1.3, 1.4 |
mg/dL |
|
| Direct/conjugated bilirubin |
|
0.0 or N/A |
5, 7 |
μmol/L |
|
| 0 |
0.3, 0.4 |
mg/dL |
|
| Alanine transaminase (ALT/ALAT) |
|
5, 7, 8 |
20, 21, 56 |
U/L |
Also called serum glutamic pyruvic transaminase (SGPT)
|
| Female |
0.15 |
0.75 |
µkat/L
|
| Male |
0.15 |
1.1
|
| Aspartate transaminase (AST/ASAT) |
Female |
6 |
34 |
IU/L |
Also called
serum glutamic oxaloacetic transaminase (SGOT)
|
| 0.25 |
0.60 |
µkat/L
|
| Male |
8 |
40 |
IU/L
|
| 0.25 |
0.75 |
µkat/L
|
| Alkaline phosphatase (ALP) |
|
0.6 |
1.8 |
µkat/L |
|
| Female |
42 |
98 |
U/L |
|
| Male |
53 |
128 |
|
| Gamma glutamyl transferase (GGT) |
|
5, 8 |
40, 78 |
U/L |
|
| Female |
|
0.63 |
µkat/L |
|
| Male |
|
0.92 |
µkat/L |
|
Cardiac tests
| Test
|
Patient type
|
Lower limit
|
Upper limit
|
Unit
|
Comments
|
| Creatine kinase (CK) |
Male |
24, 38, 60 |
174, 320 |
U/L or ng/mL |
|
| 0.42 |
1.5 |
µkat/L |
|
| Female |
24, 38, 96 |
140, 200 |
U/L or ng/mL |
|
| 0.17 |
1.17 |
µkat/L |
|
| CK-MB |
|
0 |
3, 3.8, 5 |
ng/mL or μg/L |
|
| Myoglobin |
Female |
1 |
66 |
ng/mL or µg/L |
|
| Male |
17 |
106 |
|
| Cardiac troponin T (low sensitive)
|
|
|
0.1 |
ng/mL |
99th percentile cutoff
|
| Cardiac troponin I
(high sensitive)
|
|
|
0.03
|
ng/mL
|
99th percentile cutoff
|
| Cardiac troponin T (high sensitive)
|
Male
|
|
0.022
|
ng/mL
|
99th percentile cutoff
|
| Female
|
|
0.014
|
ng/mL
|
99th percentile cutoff
|
| newborn/infants
|
|
not established
|
|
more than adults
|
Brain natriuretic peptide (BNP)
|
| Interpretation |
Range / Cutoff
|
| Congestive heart failure unlikely |
< 100 pg/mL
|
| "Gray zone" |
100–500 pg/mL
|
| Congestive heart failure likely |
> 500 pg/mL
|
NT-proBNP
|
| Interpretation |
Age |
Cutoff
|
| Congestive heart failure likely |
< 75 years |
> 125 pg/mL
|
| > 75 years |
> 450pg/mL
|
Lipids
| Test
|
Patient type
|
Lower limit
|
Upper limit
|
Unit
|
Therapeutic target
|
| Triglycerides |
10–39 years |
54 |
110 |
mg/dL |
< 100 mg/dL
or 1.1 mmol/L
|
| 0.61 |
1.2 |
mmol/L
|
| 40–59 years |
70 |
150 |
mg/dL
|
| 0.77 |
1.7 |
mmol/L
|
| > 60 years |
80 |
150 |
mg/dL
|
| 0.9 |
1.7 |
mmol/L
|
| Total cholesterol |
|
3.0, 3.6 |
5.0, 6.5 |
mmol/L |
< 3.9 mmol/L
|
| 120, 140 |
200, 250 |
mg/dL |
< 150 mg/dL
|
| HDL cholesterol |
Female |
1.0, 1.2, 1.3 |
2.2 |
mmol/L |
> 1.0 or 1.6 mmol/L
40 or 60 mg/dL
|
| 40, 50 |
86 |
mg/dL
|
| HDL cholesterol |
Male |
0.9 |
2.0 |
mmol/L
|
| 35 |
80 |
mg/dL
|
LDL cholesterol
(Not valid when
triglycerides >5.0 mmol/L) |
|
2.0, 2.4 |
3.0, 3.4 |
mmol/L |
< 2.5 mmol/L
|
| 80, 94 |
120, 130 |
mg/dL |
< 100 mg/dL
|
| LDL/HDL quotient |
|
n/a |
5 |
(unitless) |
|
Tumour markers
| Test
|
Patient type
|
Cutoff
|
Unit
|
Comments
|
| Alpha fetoprotein (AFP) |
|
44 |
ng/mL or µg/L |
Hepatocellular carcinoma or testicular cancer
|
| Beta human chorionic gonadotrophin (β-hCG) |
In males and non-pregnant females |
5 |
IU/L or mU/mL |
choriocarcinoma
|
| CA19-9 |
|
40 |
U/mL |
Pancreatic cancer
|
| CA-125 |
|
30, 35 |
kU/L or U/mL |
|
| Carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) |
Non-smokers, 50 years |
3.4, 3.6 |
μg/L |
|
| Non-smokers, 70 years |
4.1 |
|
| Smokers |
5 |
|
| Prostate specific antigen (PSA) |
40–49 years |
1.2–2.9 |
μg/L or ng/mL |
More detailed cutoffs in PSA – Serum levels
|
| 70–79 years, non-African-American |
4.0–9.0
|
| 70–79 years, African-American |
7.7–13
|
| PAP |
|
3 |
units/dL (Bodansky units) |
|
| Calcitonin |
|
5, 15 |
ng/L or pg/mL |
Cutoff against medullary thyroid cancer
More detailed cutoffs in Calcitonin article
|
Endocrinology
Thyroid hormones
| Test
|
Patient type
|
Lower limit
|
Upper limit
|
Unit
|
Thyroid stimulating hormone
(TSH or thyrotropin) |
Adults –
standard range |
0.3, 0.4, 0.5, 0.6 |
4.0, 4.5, 6.0 |
mIU/L or μIU/mL
|
Adults –
optimal range |
0.3, 0.5 |
2.0, 3.0
|
| Infants |
1.3 |
19
|
Free thyroxine (FT4)
|
Normal adult |
0.7, 0.8 |
1.4, 1.5, 1.8 |
ng/dL
|
| 9, 10, 12 |
18, 23 |
pmol/L
|
Child/Adolescent
31 d – 18 y |
0.8 |
2.0 |
ng/dL
|
| 10 |
26 |
pmol/L
|
| Pregnant |
0.5 |
1.0 |
ng/dL
|
| 6.5 |
13 |
pmol/L
|
| Total thyroxine |
|
4, 5.5 |
11, 12.3 |
μg/dL
|
| 60 |
140, 160 |
nmol/L
|
| Free triiodothyronine (FT3) |
Normal adult |
0.2 |
0.5 |
ng/dL
|
| 3.1 |
7.7 |
pmol/L
|
| Children 2-16 y |
0.1 |
0.6 |
ng/dL
|
| 1.5 |
9.2 |
pmol/L
|
| Total triiodothyronine |
|
60, 75 |
175, 181 |
ng/dL
|
| 0.9, 1.1 |
2.5, 2.7 |
nmol/L
|
| Thyroxine-binding globulin (TBG) |
|
12 |
30 |
mg/L
|
| Thyroglobulin (Tg) |
|
1.5 |
30 |
pmol/L
|
| 1 |
20 |
μg/L
|
Sex hormones
The diagrams below take inter-cycle and inter-woman variability into account in displaying reference ranges for estradiol, progesterone, FSH and LH.

Levels of estradiol (the main estrogen), progesterone, luteinizing hormone and follicle-stimulating hormone during the menstrual cycle.
| Test
|
Patient type
|
Lower limit
|
Upper limit
|
Unit
|
| Dihydrotestosterone |
adult male |
30
|
85 |
ng/dL
|
| Testosterone |
Male, overall |
8, 10 |
27, 35 |
nmol/L
|
| 230, 300 |
780–1000 |
ng/dL
|
| Male < 50 years |
10 |
45 |
nmol/L
|
| 290 |
1300 |
ng/dL
|
| Male > 50 years |
6.2 |
26 |
nmol/L
|
| 180 |
740 |
ng/dL
|
| Female |
0.7 |
2.8–3.0 |
nmol/L
|
| 20 |
80–85 |
ng/dL
|
| 17α-Hydroxyprogesterone |
male |
0.06 |
3.0 |
mg/L
|
| 0.18 |
9.1 |
µmol/L
|
| Female (Follicular phase) |
0.2 |
1.0 |
mg/L
|
| 0.6 |
3.0 |
µmol/L
|
Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH)
|
Prepubertal |
<1 |
3 |
IU/L
|
| Adult male |
1 |
8
|
Adult female (follicular
and luteal phase) |
1 |
11
|
| Adult female (Ovulation) |
6
95% PI (standard) |
26
95% PI)
|
5
90% PI (used in diagram) |
15
(90% PI)
|
| Post-menopausal female |
30 |
118
|
Luteinizing hormone (LH)
|
Female, peak |
20
90% PI (used in diagram) |
75
(90% PI) |
IU/L
|
| Female, post-menopausal |
15 |
60
|
| Male aged 18+ |
2 |
9
|
Estradiol
(an estrogen)
|
Adult male |
50 |
200 |
pmol/L
|
| 14 |
55 |
pg/mL
|
Adult female (day 5 of follicular phase,
and luteal phase) |
70 |
500, 600 |
pmol/L
|
| 19 |
140, 160 |
pg/mL
|
| Adult female – free (not protein bound) |
0.5 |
9 |
pg/mL
|
| 1.7 |
33 |
pmol/L
|
| Post-menopausal female |
N/A |
< 130 |
pmol/L
|
| N/A |
< 35 |
pg/mL
|
Progesterone
|
Female in mid-luteal phase (day 21–23) |
17, 35 |
92 |
nmol/L
|
| 6, 11 |
29 |
ng/mL
|
| Androstenedione |
Adult male and female |
60 |
270 |
ng/dL
|
| Post-menopausal female |
|
< 180
|
| Prepubertal |
|
< 60
|
| Dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate |
Adult male and female |
30 |
400 |
µg/dL
|
SHBG
|
Adult female |
40 |
120 |
nmol/L
|
| Adult male |
20 |
60
|
Anti-Müllerian hormone (AMH)
|
13–45 years |
0.7 |
20 |
ng/mL
|
| 5 |
140 |
pmol/L
|
Other hormones
| Test
|
Patient type
|
Lower limit
|
Upper limit
|
Unit
|
| Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) |
|
2.2 |
13.3 |
pmol/L
|
| 20 |
100 |
pg/mL
|
| Cortisol |
09:00 am |
140 |
700 |
nmol/L
|
| 5 |
25 |
μg/dL
|
| Midnight |
80 |
350 |
nmol/L
|
| 2.9 |
13 |
μg/dL
|
| Growth hormone (fasting) |
|
0 |
5 |
ng/mL
|
| Growth hormone (arginine stimulation) |
|
7 |
n/a |
ng/mL
|
IGF-1
|
Female, 20 yrs |
110 |
420 |
ng/mL
|
| Female, 75 yrs |
55 |
220
|
| Male, 20 yrs |
160 |
390
|
| Male, 75 yrs |
48 |
200
|
Prolactin
|
Female |
71, 105 |
348, 548 |
mIU/L
|
| 3.4, 3.9 |
16.4, 20.3 |
µg/L
|
| Male |
58, 89 |
277, 365 |
mIU/L
|
| 2.7, 3.3 |
13.0, 13.5 |
µg/L
|
| Parathyroid hormone (PTH) |
|
10, 17 |
65, 70 |
pg/mL
|
|
1.1, 1.8 |
6.9, 7.5 |
pmol/L
|
25-hydroxycholecalciferol (a vitamin D)
– Standard reference range |
|
8, 9 |
40, 80 |
ng/mL
|
| 20, 23 |
95, 150 |
nmol/L
|
25-hydroxycholecalciferol
– Therapeutic target range |
|
30, 40 |
65, 100 |
ng/mL
|
| 85, 100 |
120, 160 |
nmol/L
|
| Plasma renin activity |
|
0.29, 1.9 |
3.7 |
ng/(mL·h)
|
|
3.3, 21 |
41 |
mcU/mL
|
Aldosterone
|
Adult |
|
19, 34.0 |
ng/dL
|
|
530, 940 |
pmol/L
|
Aldosterone-to-renin ratio
|
Adult |
|
13.1, 35.0 |
ng/dL per ng/(mL·h)
|
|
360, 970 |
pmol/liter per µg/(L·h)
|
Vitamins
Also including the vitamin B12)-related amino acid homocysteine.
| Test
|
Patient type
|
Standard range
|
Optimal range
|
Unit
|
| Lower limit
|
Upper limit
|
Lower limit
|
Upper limit
|
| Vitamin A |
|
30 |
65 |
|
|
µg/dL
|
Vitamin B9
(Folic acid/Folate) – Serum |
Age > 1 year |
3.0 |
16 |
5 |
|
ng/mL or μg/L
|
| 6.8 |
36 |
11 |
|
nmol/L
|
Vitamin B9
(Folic acid/Folate) – Red blood cells |
|
200 |
600 |
|
|
ng/mL or μg/L
|
|
450 |
1400 |
|
|
nmol/L
|
| Pregnant |
|
|
400 |
|
ng/mL or μg/L
|
|
|
900 |
|
nmol/L
|
| Vitamin B12 (Cobalamin) |
|
130, 160 |
700, 950 |
|
|
ng/L
|
|
100, 120 |
520, 700 |
|
|
pmol/L
|
Homocysteine
|
|
3.3, 5.9 |
7.2, 15.3 |
|
6.3 |
μmol/L
|
|
45, 80 |
100, 210 |
|
85 |
μg/dL
|
| Vitamin C (Ascorbic acid) |
|
0.4 |
1.5 |
0.9 |
|
mg/dL
|
| 23 |
85 |
50 |
|
μmol/L
|
| 25-hydroxycholecalciferol (a vitamin D) |
|
8, 9 |
40, 80 |
30, 40 |
65, 100 |
ng/mL
|
| 20, 23 |
95, 150 |
85, 100 |
120, 160 |
nmol/L
|
| Vitamin E |
|
|
|
28 |
|
μmol/L
|
|
|
1.2 |
|
mg/dL
|
Toxins
| Test
|
Limit type
|
Limit
|
Unit
|
| Lead |
Optimal health range |
< 20 or 40 |
µg/dL
|
| Blood ethanol content |
Limit for drunk driving |
0, 0.2, 0.8 |
‰ or g/L
|
| 17.4 |
mmol/L
|
Hematology
Red blood cells
These values (except Hemoglobin in plasma) are for total blood and not only blood plasma.
| Test
|
Patient
|
Lower limit
|
Upper limit
|
Unit
|
Comments
|
| Hemoglobin (Hb) |
Male |
2.0, 2.1 |
2.5, 2.7 |
mmol/L |
Higher in neonates, lower in children.
|
| 130, 132, 135 |
162, 170, 175 |
g/L
|
| Female |
1.8, 1.9 |
2.3, 2.5 |
mmol/L |
Sex difference negligible until adulthood.
|
| 120 |
150, 152, 160 |
g/L
|
| Hemoglobin subunits (sometimes displayed simply as "Hemoglobin") |
Male |
8.0, 8.4 |
10.0, 10.8 |
mmol/L |
4 per hemoglobin molecule
|
| Female |
7.2, 7.6 |
9.2, 10.0
|
| Hemoglobin in plasma |
|
0.16 |
0.62 |
μmol/L |
Normally diminutive compared with inside red blood cells
|
|
1 |
4 |
mg/dL
|
| Glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c) |
< 50 years |
3.6 |
5.0 |
% of Hb |
|
| > 50 years |
3.9 |
5.3
|
| Haptoglobin |
< 50 years |
0.35 |
1.9 |
g/L |
|
| > 50 years |
0.47 |
2.1
|
| Hematocrit (Hct) |
Male |
0.39, 0.4, 0.41, 0.45 |
0.50, 0.52, 0.53, 0.62 |
L/L |
|
| Female |
0.35, 0.36, 0.37 |
0.46, 0.48 |
L/L |
|
| Child |
0.31 |
0.43 |
L/L |
|
| Mean corpuscular volume (MCV) |
Male |
76, 82 |
100, 102 |
fL |
Cells are larger in neonates, though smaller in other children.
|
| Female |
78 |
101 |
fL
|
| Red blood cell distribution width (RDW) |
|
11.5 |
14.5 |
% |
|
| Mean cell hemoglobin (MCH) |
|
0.39 |
0.54 |
fmol/cell |
|
| 25, 27 |
32, 33, 35 |
pg/cell
|
| Mean corpuscular hemoglobin concentration (MCHC) |
|
4.8, 5.0 |
5.4, 5.6 |
mmol/L |
|
|
31, 32 |
35, 36 |
g/dL or %
|
| Erythrocytes/Red blood cells (RBC) |
Male |
4.2, 4.3 |
5.7, 5.9, 6.2, 6.9 |
x1012/L
or
million/mm3 |
|
| Female |
3.5, 3.8, 3.9 |
5.1, 5.5 |
|
| Infant/Child |
3.8 |
5.5 |
|
| Reticulocytes |
Adult |
26 |
130 |
x109/L |
|
| 0.5 |
1.5 |
% of RBC |
|
| Newborn |
1.1 |
4.5 |
% of RBC |
|
| Infant |
0.5 |
3.1 |
% of RBC |
|
| Immature reticulocyte fraction (IRF) |
Adult |
1.6 |
12.1 |
% of reticulocytes |
|
| Reticulocyte hemoglobin equivalent |
Adult |
30.0 |
37.6 |
% |
|
| 24.1 |
35.8 |
pg
|
| Immature platelet fraction (IPF) |
Adult |
0.8 |
5.6 |
% |
|
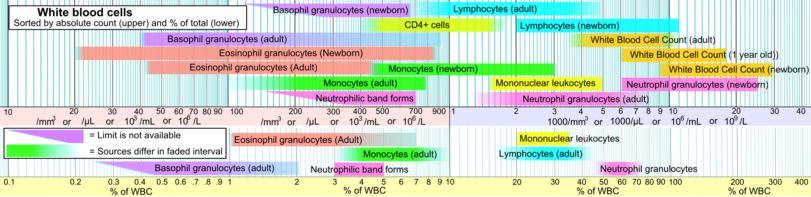
White blood cells
These values are for total blood and not only blood plasma.
| Test
|
Patient type
|
Lower limit
|
Upper limit
|
Unit
|
| White Blood Cell Count (WBC) |
Adult |
3.5, 3.9, 4.1, 4.5 |
9.0, 10.0, 10.9, 11 |
- x109/L
- x103/mm3 or
- x103/μL
|
| Newborn |
9 |
30
|
| 1 year old |
6 |
18
|
Neutrophil granulocytes
(A.K.A. grans, polys, PMNs, or segs) |
Adult |
1.3, 1.8, 2 |
5.4, 7, 8 |
x109/L
|
| 45–54 |
62, 74 |
% of WBC
|
| Newborn |
6 |
26 |
x109/L
|
| Neutrophilic band forms |
Adult |
|
0.7 |
x109/L
|
| 3 |
5 |
% of WBC
|
| Lymphocytes |
Adult |
0.7, 1.0 |
3.5, 3.9, 4.8 |
x109/L
|
| 16–25 |
33, 45 |
% of WBC
|
| Newborn |
2 |
11 |
x109/L
|
| Monocytes |
Adult |
0.1, 0.2 |
0.8 |
x109/L
|
| 3, 4.0 |
7, 10 |
% of WBC
|
| Newborn |
0.4 |
3.1 |
x109/L
|
Mononuclear leukocytes
(Lymphocytes + monocytes) |
Adult |
1.5 |
5 |
x109/L
|
| 20 |
35 |
% of WBC
|
| CD4+ T cells |
Adult |
0.4, 0.5 |
1.5, 1.8 |
x109/L
|
| Eosinophil granulocytes |
Adult |
0.0, 0.04 |
0.44, 0.45, 0.5 |
x109/L
|
| 1 |
3, 7 |
% of WBC
|
| Newborn |
0.02 |
0.85 |
x109/L
|
| Basophil granulocytes |
Adult |
40 |
100, 200, 900 |
x106/L
|
| 0.0 |
0.75, 2 |
% of WBC
|
| Newborn |
|
0.64 |
x109/L
|
Coagulation
| Test
|
Lower limit
|
Upper limit
|
Unit
|
Comments
|
| Thrombocyte/Platelet count (Plt) |
140, 150 |
350, 400, 450 |
x109/L or
x1000/µL |
|
| Mean platelet volume (MPV) |
7.2, 7.4, 7.5 |
10.4, 11.5, 11.7 |
fL |
|
| Prothrombin time (PT) |
10, 11, 12 |
13, 13.5, 14, 15 |
s |
PT reference varies between laboratory kits – INR is standardised
|
| INR |
0.9 |
1.2 |
|
The INR is a corrected ratio of a patient's PT to normal
|
| Activated partial thromboplastin time (APTT) |
18, 30 |
28, 42, 45 |
s |
|
| Thrombin clotting time (TCT) |
11 |
18 |
s |
|
| Fibrinogen |
1.7, 2.0 |
3.6, 4.2 |
g/L |
|
| Antithrombin |
0.80 |
1.2 |
kIU/L |
|
| 0.15, 0.17 |
0.2, 0.39 |
mg/mL
|
| Bleeding time |
2 |
9 |
minutes |
|
| Viscosity |
1.5 |
1.72 |
cP |
|
Immunology
Acute phase proteins
Acute phase proteins are markers of inflammation.
| Test
|
Patient
|
Lower limit
|
Upper limit
|
Unit
|
Comments
|
Erythrocyte sedimentation rate
(ESR) |
Male |
0 |
Age÷2 |
mm/h |
ESR increases with age and tends to be higher in females.
|
| Female |
(Age+10)÷2
|
| C-reactive protein (CRP) |
|
|
5, 6 |
mg/L |
|
|
200, 240 |
nmol/L
|
| Alpha 1-antitrypsin (AAT) |
|
20, 22 |
38, 53 |
μmol/L |
|
|
89, 97 |
170, 230 |
mg/dL |
|
| Procalcitonin |
|
|
0.15 |
ng/mL or μg/L |
|
Isotypes of antibodies
| Test
|
Patient
|
Lower limit
|
Upper limit
|
Unit
|
| IgA |
Adult |
70, 110 |
360, 560 |
mg/dL
|
| IgD |
0.5 |
3.0
|
| IgE |
0.01 |
0.04
|
| IgG |
800 |
1800
|
| IgM |
54 |
220
|
Autoantibodies
Autoantibodies are usually absent or very low, so instead of being given in standard reference ranges, the values usually denote where they are said to be present, or whether the test is a positive test. There may also be an equivocal interval, where it is uncertain whether there is a significantly increased level.
| Test
|
Negative
|
Equivocal
|
Positive
|
Unit
|
| anti-SS-A (Ro) |
< 1.0 |
n/a |
≥ 1.0 |
Units (U)
|
| anti-SS-B (La) |
< 1.0 |
n/a |
≥ 1.0
|
| Anti ds-DNA |
< 30.0 |
30.0–75.0 |
> 75.0 |
International Units per millilitre (IU/mL)
|
| Anti ss-DNA |
< 8 |
8–10 |
> 10 |
Units per millilitre (U/mL)
|
| Anti-histone antibodies |
< 25 |
n/a |
> 25
|
Cytoplasmic anti-neutrophil
cytoplasmic antibodies (c-ANCA) |
< 20 |
21–30 |
> 30
|
Perinuclear anti-neutrophil
cytoplasmic antibodies (p-ANCA) |
< 5 |
n/a |
> 5
|
| Anti-mitochondrial antibodies (AMA) |
< 0.1 |
0.1-0.9 |
≥ 1.0 |
Units (U)
|
| Rheumatoid factor (RF) |
< 20 |
20–30 |
> 30 |
Units per millilitre (U/mL)
|
Antistreptolysin O titre (ASOT) in
preschoolers |
|
|
> 100
|
| ASOT at school age |
> 250
|
| ASOT in adults |
> 125
|
| Test
|
Negative
|
Low/weak positive
|
Moderate positive
|
High/strong positive
|
Unit
|
| Anti-phospholipid IgG |
< 20 |
20–30 |
31–50 |
> 51 |
GPLU/mL
|
| Anti-phospholipid IgM |
< 1.5 |
1.5–2.5 |
2–9.9 |
> 10 |
MPL /mL
|
| Anti-phospholipid IgA |
< 10 |
10–20 |
21–30 |
> 31 |
arb U/mL
|
| Anti-citrullinated protein antibodies |
< 20 |
20–39 |
40–59 |
> 60 |
EU
|
Other immunology
| Test
|
Lower limit
|
Upper limit
|
Unit
|
| Serum free light chains (FLC): kappa/lambda ratio |
0.26 |
1.65 |
(unitless)
|
Other enzymes and proteins
| Test
|
Lower limit
|
Upper limit
|
Unit
|
Comments
|
| Serum total protein |
60, 63 |
78, 82, 84 |
g/L |
|
| Lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) |
50 |
150 |
U/L |
|
| 0.4 |
1.7 |
μmol/L |
|
| 1.8 |
3.4 |
µkat/L |
< 70 years old
|
| Amylase |
25, 30, 53 |
110, 120, 123, 125, 190 |
U/L |
|
| 0.15 |
1.1 |
µkat/L |
|
| 200 |
240 |
nmol/L |
|
D-dimer
|
n/a |
500 |
ng/mL |
Higher in pregnant women
|
| 0.5 |
mg/L
|
| Lipase |
7, 10, 23 |
60, 150, 208 |
U/L |
|
| Angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) |
23 |
57 |
U/L |
|
| Acid phosphatase |
|
3.0 |
ng/mL |
|
| Eosinophil cationic protein (ECP) |
2.3 |
16 |
µg/L |
|
Other electrolytes and metabolites
Electrolytes and metabolites:
For iron and copper, some related proteins are also included.
| Test
|
Patient type
|
Lower limit
|
Upper limit
|
Unit
|
Comments
|
| Osmolality |
|
275, 280, 281 |
295, 296, 297 |
mOsm/kg |
Plasma weight excludes solutes
|
| Osmolarity |
|
Slightly less than osmolality |
mOsm/L |
Plasma volume includes solutes
|
| Urea |
|
3.0 |
7.0 |
mmol/L |
BUN – blood urea nitrogen
|
| 7 |
18, 21 |
mg/dL
|
| * Uric acid |
|
0.18 |
0.48 |
mmol/L |
|
| Female |
2.0 |
7.0 |
mg/dL |
|
| Male |
2.1 |
8.5 |
mg/dL |
|
| Creatinine |
Male |
60, 68 |
90, 118 |
μmol/L |
May be complemented with creatinine clearance
|
| 0.7, 0.8 |
1.0, 1.3 |
mg/dL
|
| Female |
50, 68 |
90, 98 |
μmol/L
|
| 0.6, 0.8 |
1.0, 1.1 |
mg/dL
|
| BUN/Creatinine Ratio |
|
5 |
35 |
– |
|
| Plasma glucose (fasting) |
|
3.8, 4.0 |
6.0, 6.1 |
mmol/L |
See also glycated hemoglobin (in hematology)
|
| 65, 70, 72 |
100, 110 |
mg/dL
|
| Full blood glucose (fasting) |
|
3.3 |
5.6 |
mmol/L
|
| 60 |
100 |
mg/dL
|
| Random glucose |
|
3.9 |
7.8 |
mmol/L
|
| 70 |
140 |
mg/dL
|
| Lactate (Venous) |
|
4.5 |
19.8 |
mg/dL |
|
| 0.5 |
2.2 |
mmol/L |
|
| Lactate (Arterial) |
|
4.5 |
14.4 |
mg/dL |
|
| 0.5 |
1.6 |
mmol/L |
|
| Pyruvate |
|
300 |
900 |
μg/dL |
|
| 34 |
102 |
μmol/L |
|
| Ketones |
|
|
1 |
mg/dL |
|
|
0.1 |
mmol/L |
|
Medication
| Test
|
Lower limit
|
Upper limit
|
Unit
|
Comments
|
| Digoxin |
0.5 |
2.0 |
ng/mL |
Narrow therapeutic window
|
| 0.6 |
2.6 |
nmol/L
|
| Lithium |
0.4, 0.5, 0.8 |
1.3 |
mmol/L |
Narrow therapeutic window
|
| Paracetamol |
|
30 |
mg/L |
Risk of paracetamol toxicity at higher levels
|
|
200 |
µmol/L
|
Más resultados...