Lista de lagomorfos
Contenido keyboard_arrow_down


Convenciones
Clasificación
Family Leporidae
- Genus Brachylagus Una especie
- Genus Bunolagus (conejo rígido): una especie
- Genus Caprolagus Una especie
- Genus Lepus (hares): 32 especies
- Genus Nesolagus (conejos tirados): dos especies
- Genus Oryctolagus (Conejo europeo): una especie
- Genus Pentalagus (Conejo amami): una especie
- Genus Poelagus (Conejo Bunyoro): una especie
- Genus Pronolagus (hermanos de roca roja): cuatro especies
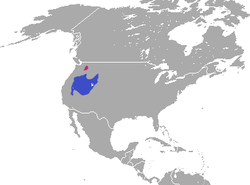
- Genus Romerolagus (conejo volcano): una especie
- Genus Sylvilagus (conejos de cóctel): 19 especies
Familia Ochotonidae
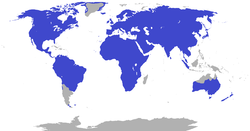
- Genus Ochotona (pikas): 29 especies
|
Lagomorfos
Family Leporidae
Familia Ochotonidae
| Nombre | Autoridad y especie | Rango | Tamaño y ecología |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ochotona (pika) | Enlace, 1795
29 especies
| Asia y América del Norte occidental | Rango de tamaño: 11 cm (4 in) de largo (Gansu pika) a 29 cm (11 in) de largo (Pika norte) Hábitats: Desierto, bosque, arbustos, zonas rocosas y pastizales Dietas: Amplia variedad de plantas |
Referencias
- ^ a b Matthee, C. A.; Van Vuuren, B. J.; Bell, D.; Robinson, T. J. (2004). "A Molecular Supermatrix of the Rabbits and Hares (Leporidae) Allows for the Identification of Five Intercontinental Exchanges During the Miocene". Systematic Biology. 53 (3): 433–477. doi:10.1080/10635150490445715. PMID 15503672.
- ^ Wilson, Reeder, pp. 185–211
- ^ a b Rohde, Ashley (2006). "Brachylagus idahoensis". Animal Diversity Web. University of Michigan. Retrieved October 22, 2021.
- ^ Rachlow, J.; Becker, P. A.; Shipley, L. (2016). "Brachylagus idahoensis". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T2963A45176206. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T2963A45176206.en.
- ^ Smith, Johnston, Alves, Hackländer, p. 91
- ^ a b Collins, K.; Bragg, C.; Birss, C. (2019). "Bunolagus monticularis". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2019: e.T3326A45176532. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-1.RLTS.T3326A45176532.en.
- ^ Smith, Johnston, Alves, Hackländer, p. 94
- ^ a b Aryal, A.; Yadav, B. (2019). "Caprolagus hispidus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2019: e.T3833A45176688. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-1.RLTS.T3833A45176688.en.
- ^ Lepus sizes:
- Antelope jackrabbit: Smith, Johnston, Alves, Hackländer, p. 160
- Snowshoe hare: Smith, Johnston, Alves, Hackländer, p. 163
- Arctic hare: Smith, Johnston, Alves, Hackländer, p. 166
- Japanese hare: Smith, Johnston, Alves, Hackländer, p. 169
- Black-tailed jackrabbit: Ballenger, Liz (1999). "Lepus californicus". Animal Diversity Web. University of Michigan. Retrieved October 22, 2021.
- White-sided jackrabbit: Dharmani, Aarti (2000). "Lepus callotis". Animal Diversity Web. University of Michigan. Retrieved October 22, 2021.
- Cape hare: Begnoche, Dana (2002). "Lepus capensis". Animal Diversity Web. University of Michigan. Retrieved November 5, 2021.
- Broom hare: Smith, Johnston, Alves, Hackländer, p. 179
- Yunnan hare: Smith, Johnston, Alves, Hackländer, p. 222
- Korean hare: Faigle, Stacy (2014). "Lepus coreanus". Animal Diversity Web. University of Michigan. Retrieved October 22, 2021.
- Corsican hare: Cooper, Thomas (2015). "Lepus corsicanus". Animal Diversity Web. University of Michigan. Retrieved October 22, 2021.
- European hare: Vu, Alan (2001). "Lepus europaeus". Animal Diversity Web. University of Michigan. Retrieved October 22, 2021.
- Ethiopian hare: Smith, Johnston, Alves, Hackländer, p. 190
- Tehuantepec jackrabbit: Warlin, Sierra (2013). "Lepus flavigularis". Animal Diversity Web. University of Michigan. Retrieved October 22, 2021.
- Granada hare: Smith, Johnston, Alves, Hackländer, p. 193
- Abyssinian hare: Nickolai, Ashley (2014). "Lepus habessinicus". Animal Diversity Web. University of Michigan. Retrieved October 22, 2021.
- Hainan hare: Smith, Johnston, Alves, Hackländer, p. 197
- Black jackrabbit: Smith, Johnston, Alves, Hackländer, p. 198
- Manchurian hare: Smith, Johnston, Alves, Hackländer, p. 200
- Indian hare: Lundrigan, Barbara; Foote, Sarah (2003). "Lepus nigricollis". Animal Diversity Web. University of Michigan. Retrieved October 22, 2021.
- Woolly hare: Ng, Jarita (2011). "Lepus oiostolus". Animal Diversity Web. University of Michigan. Retrieved October 22, 2021.
- Alaskan hare: Smith, Johnston, Alves, Hackländer, p. 204
- Burmese hare: Smith, Johnston, Alves, Hackländer, p. 205
- Scrub hare: Kushnereit, Aimee (2004). "Lepus saxatilis". Animal Diversity Web. University of Michigan. Retrieved November 5, 2021.
- Chinese hare: Smith, Johnston, Alves, Hackländer, p. 96
- Ethiopian highland hare: Kingdon, p. 310
- Desert hare: Sullivan, Shaunna (2013). "Lepus tibetanus". Animal Diversity Web. University of Michigan. Retrieved October 22, 2021.
- Mountain hare: Smith, Johnston, Alves, Hackländer, pp. 212–213
- Tolai hare: Smith, Xie, et al., p. 291
- White-tailed jackrabbit: Verts, Carraway, p. 142
- African savanna hare: Riegler, Donald (2013). "Lepus microtis". Animal Diversity Web. University of Michigan. Retrieved November 5, 2021.
- Yarkand hare: Smith, Xie, et al., p. 292
- ^ a b Lepus habitats and diets:
- Antelope jackrabbit: Lorenzo, C.; Brown, D. E. (2019). "Lepus alleni". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2019: e.T41272A45185265. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-1.RLTS.T41272A45185265.en.
- Snowshoe hare: Mills, L.; Smith, A. T. (2019). "Lepus americanus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2019: e.T41273A45185466. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-1.RLTS.T41273A45185466.en.
- Arctic hare: Smith, A. T.; Johnston, C. H. (2019). "Lepus arcticus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2019: e.T41274A45185887. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-1.RLTS.T41274A45185887.en.
- Japanese hare: Yamada, F.; Smith, A. T. (2019). "Lepus brachyurus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2019: e.T41275A45186064. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-1.RLTS.T41275A45186064.en.; Holmberg, Jennifer (2014). "Lepus brachyurus". Animal Diversity Web. University of Michigan. Retrieved November 5, 2021.
- Black-tailed jackrabbit: Brown, D. E.; Lorenzo, C.; Álvarez-Castañeda, S. T. (2019). "Lepus californicus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2019: e.T41276A45186309. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-1.RLTS.T41276A45186309.en.; Ballenger, Liz (1999). "Lepus californicus". Animal Diversity Web. University of Michigan. Retrieved October 22, 2021.
- White-sided jackrabbit: Brown, D. E.; Smith, A. T. (2019). "Lepus callotis". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2019: e.T11792A45177499. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-2.RLTS.T11792A45177499.en.; Dharmani, Aarti (2000). "Lepus callotis". Animal Diversity Web. University of Michigan. Retrieved October 22, 2021.
- Cape hare: Johnston, C. H.; Robinson, T. J.; Child, M. F.; Relton, C. (2019). "Lepus capensis". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2019: e.T41277A45186750. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-1.RLTS.T41277A45186750.en.
- Broom hare: Ballesteros, F.; Smith, A. T. (2019). "Lepus castroviejoi". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2019: e.T11797A503908. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-2.RLTS.T11797A503908.en.
- Yunnan hare: Smith, A. T.; Johnston, C. H. (2019). "Lepus comus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2019: e.T41278A45187160. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-1.RLTS.T41278A45187160.en.; Smith, Xie, et al., p. 287
- Korean hare: Jo, Y.-S.; Smith, A. T. (2019) [errata version of 2019 assessment]. "Lepus coreanus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2019: e.T41279A161750768. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-1.RLTS.T41279A161750768.en.; Faigle, Stacy (2014). "Lepus coreanus". Animal Diversity Web. University of Michigan. Retrieved October 22, 2021.
- Corsican hare: Randi, E.; Riga, F. (2019). "Lepus corsicanus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2019: e.T41305A2952954. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-2.RLTS.T41305A2952954.en.; Cooper, Thomas (2015). "Lepus corsicanus". Animal Diversity Web. University of Michigan. Retrieved October 22, 2021.
- European hare: Hacklander, K.; Schai-Braun, S. (2019). "Lepus europaeus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2019: e.T41280A45187424. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-1.RLTS.T41280A45187424.en.; Vu, Alan (2001). "Lepus europaeus". Animal Diversity Web. University of Michigan. Retrieved October 22, 2021.
- Ethiopian hare: Johnston, C. H.; Tolesa, Z. (2019). "Lepus fagani". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2019: e.T11798A45178437. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-1.RLTS.T11798A45178437.en.
- Tehuantepec jackrabbit: Lorenzo, C.; Smith, A. T. (2019). "Lepus flavigularis". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2019: e.T11790A45176906. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-3.RLTS.T11790A45176906.en.; Warlin, Sierra (2013). "Lepus flavigularis". Animal Diversity Web. University of Michigan. Retrieved October 22, 2021.
- Granada hare: Soriguer, R.; Carro, F. (2019). "Lepus granatensis". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2019: e.T41306A2953195. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-1.RLTS.T41306A2953195.en.; Weaver, Derek (2013). "Lepus granatensis". Animal Diversity Web. University of Michigan. Retrieved November 5, 2021.
- Abyssinian hare: Johnston, C. H.; Tolesa, Z. (2019). "Lepus habessinicus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2019: e.T41289A45189637. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-1.RLTS.T41289A45189637.en.; Nickolai, Ashley (2014). "Lepus habessinicus". Animal Diversity Web. University of Michigan. Retrieved October 22, 2021.
- Hainan hare: Smith, A. T.; Johnston, C. (2016). "Lepus hainanus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T11793A45177783. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T11793A45177783.en.; Lundberg, Annette (2013). "Lepus hainanus". Animal Diversity Web. University of Michigan. Retrieved November 5, 2021.
- Black jackrabbit: Lorenzo, C.; Johnston, C. H. (2019). "Lepus insularis". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2019: e.T11794A45177986. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-3.RLTS.T11794A45177986.en.; Mejia, Joseph R. (1999). "Lepus insularis". Animal Diversity Web. University of Michigan. Retrieved October 22, 2021.
- Manchurian hare: Smith, A. T.; Johnston, C. H. (2019). "Lepus mandshuricus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2019: e.T41281A45187882. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-1.RLTS.T41281A45187882.en.; Smith, Xie, et al., p. 289
- Indian hare: Nameer, P. O.; Smith, A. T. (2019). "Lepus nigricollis". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2019: e.T41282A45188041. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-1.RLTS.T41282A45188041.en.; Lundrigan, Barbara; Foote, Sarah (2003). "Lepus nigricollis". Animal Diversity Web. University of Michigan. Retrieved October 22, 2021.
- Woolly hare: Smith, A. T.; Johnston, C. H. (2019). "Lepus oiostolus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2019: e.T41283A45188432. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-1.RLTS.T41283A45188432.en.; Ng, Jarita (2011). "Lepus oiostolus". Animal Diversity Web. University of Michigan. Retrieved October 22, 2021.
- Alaskan hare: Smith, A. T.; Johnston, C. H. (2019). "Lepus othus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2019: e.T11795A45178124. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-1.RLTS.T11795A45178124.en.
- Burmese hare: Johnston, C. H.; Smith, A. T. (2019). "Lepus peguensis". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2019: e.T41284A45188632. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-1.RLTS.T41284A45188632.en.
- Scrub hare: Robinson, T. J.; Child, M. F.; Relton, C.; Johnston, C. H. (2019). "Lepus saxatilis". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2019: e.T41285A45188827. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-1.RLTS.T41285A45188827.en.
- Chinese hare: Smith, A. T.; Johnston, C. H. (2019). "Lepus sinensis". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2019: e.T41286A45189035. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-1.RLTS.T41286A45189035.en.
- Ethiopian highland hare: Johnston, C. H.; Tolesa, Z. (2019). "Lepus starcki". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2019: e.T41287A45189235. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-1.RLTS.T41287A45189235.en.
- Desert hare: Smith, A. T.; Johnston, C. H. (2019). "Lepus tibetanus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2019: e.T41307A45193298. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-1.RLTS.T41307A45193298.en.; Sullivan, Shaunna (2013). "Lepus tibetanus". Animal Diversity Web. University of Michigan. Retrieved October 22, 2021.
- Mountain hare: Smith, A. T.; Johnston, C. H. (2019). "Lepus timidus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2019: e.T11791A45177198. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-1.RLTS.T11791A45177198.en.; Smith, Johnston, Alves, Hackländer, pp. 212–213
- Tolai hare: Smith, A. T.; Johnston, C. H. (2019). "Lepus tolai". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2019: e.T41308A45193447. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-1.RLTS.T41308A45193447.en.
- White-tailed jackrabbit: Brown, D. E.; Smith, A. T. (2019). "Lepus townsendii". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2019: e.T41288A45189364. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-1.RLTS.T41288A45189364.en.
- African savanna hare: Johnston, C. H.; Robinson, T. J.; Relton, C.; Child, M. F.; Smith, A. T. (2019). "Lepus victoriae". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2019: e.T41879A45194215. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-1.RLTS.T41879A45194215.en.
- Yarkand hare: Smith, A. T.; Johnston, C. H. (2017) [errata version of 2016 assessment]. "Lepus yarkandensis". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T11796A115103994. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T11796A45178274.en.
- ^ Nesolagus sizes:
- Sumatran striped rabbit: Smith, Johnston, Alves, Hackländer, p. 96
- Annamite striped rabbit: Hoedl, Amanda (2012). "Nesolagus timminsi". Animal Diversity Web. University of Michigan. Retrieved October 22, 2021.
- ^ a b Nesolagus habitats and diets:
- Sumatran striped rabbit: McCarthy, J.; Holden, J.; Martyr, D.; McCarthy, K. (2019). "Nesolagus netscheri". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2019: e.T14662A45178557. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-2.RLTS.T14662A45178557.en.
- Annamite striped rabbit: Tilker, A.; Timmins, R. J.; Nguyen The Truong, A.; Coudrat, C. N. Z.; Gray, T.; Le Trong Trai, Willcox; D. H. A., Abramov; A. V., Wilkinson; N., Steinmetz; R. (2019). "Nesolagus timminsi". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2019: e.T41209A45181925. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-1.RLTS.T41209A45181925.en.; Hoedl, Amanda (2012). "Nesolagus timminsi". Animal Diversity Web. University of Michigan. Retrieved October 22, 2021.
- ^ a b Tislerics, Ati (2000). "Oryctolagus cuniculus". Animal Diversity Web. University of Michigan. Retrieved October 22, 2021.
- ^ Villafuerte, R.; Delibes-Mateos, M. (2020) [errata version of 2019 assessment]. "Oryctolagus cuniculus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2019: e.T41291A170619657. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-3.RLTS.T41291A170619657.en.
- ^ Smith, Johnston, Alves, Hackländer, p. 105
- ^ a b Yamada, F. and Smith; A. T. (2016). "Pentalagus furnessi". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T16559A45180151. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T16559A45180151.en.
- ^ a b Portman, Charles (2004). "Poelagus marjorita". Animal Diversity Web. University of Michigan. Retrieved October 22, 2021.
- ^ Johnston, C. H.; Smith, A. T. (2019). "Poelagus marjorita". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2019: e.T41292A45189965. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-1.RLTS.T41292A45189965.en.
- ^ Pronolagus sizes:
- Natal red rock hare: Smith, Johnston, Alves, Hackländer, p. 109
- Jameson's red rock hare: Bartel, Riley (2015). "Pronolagus randensis". Animal Diversity Web. University of Michigan. Retrieved October 22, 2021.
- Smith's red rock hare: Smith, Johnston, Alves, Hackländer, p. 112
- Hewitt's red rock hare: Smith, Johnston, Alves, Hackländer, p. 113
- ^ a b Pronolagus habitats and diets:
- Natal red rock hare: Child, M. F.; Matthee, C. M.; Robinson, T. J. (2019). "Pronolagus crassicaudatus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2019: e.T41293A45190100. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-1.RLTS.T41293A45190100.en.; Smith, Johnston, Alves, Hackländer, p. 109
- Jameson's red rock hare: Child, M. F.; Matthee, C. M.; Robinson, T. J. (2019). "Pronolagus randensis". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2019: e.T41294A45190258. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-1.RLTS.T41294A45190258.en.; Bartel, Riley (2015). "Pronolagus randensis". Animal Diversity Web. University of Michigan. Retrieved October 22, 2021.
- Smith's red rock hare: Child, M. F.; Matthee, C. M.; Robinson, T. J. (2019). "Pronolagus rupestris". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2019: e.T41295A45190415. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-1.RLTS.T41295A45190415.en.; Sekine, Ryo (2000). "Pronolagus rupestris". Animal Diversity Web. University of Michigan. Retrieved November 8, 2021.
- Hewitt's red rock hare: Robinson, T. J.; Child, M. F.; Matthee, C. M. (2019). "Pronolagus saundersiae". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2019: e.T136713A45194657. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-1.RLTS.T136713A45194657.en.; Smith, Johnston, Alves, Hackländer, p. 113
- ^ a b Smith, Johnston, Alves, Hackländer, pp. 114–115
- ^ Velázquez, A.; Guerrero, J. A. (2019). "Romerolagus diazi". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2019: e.T19742A45180356. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-2.RLTS.T19742A45180356.en.
- ^ Sylvilagus sizes:
- Andean tapeti: Smith, Johnston, Alves, Hackländer, p. 127
- Common tapeti, Central American tapeti, Santa Marta tapeti: Ruedas, L. A.; Marques, S. S.; French, J. H.; Platt II, R. N.; Salazar-Bravo, J.; Mora, J. M.; Thompson, C. W. (October 22, 2019). "Taxonomy of the Sylvilagus brasiliensis complex in Central and South America (Lagomorpha: Leporidae)". Journal of Mammalogy. 100 (5): 1599–1630. doi:10.1093/jmammal/gyz126.
- Swamp rabbit: Smith, Johnston, Alves, Hackländer, p. 118
- Desert cottontail: Smith, Johnston, Alves, Hackländer, p. 120
- Brush rabbit: Smith, Johnston, Alves, Hackländer, p. 123
- Mexican cottontail: Smith, Johnston, Alves, Hackländer, p. 132
- Dice's cottontail: Smith, Johnston, Alves, Hackländer, p. 136
- Eastern cottontail: Smith, Johnston, Alves, Hackländer, p. 138
- Tres Marias cottontail: Viswanathan, Lata (2000). "Sylvilagus graysoni". Animal Diversity Web. University of Michigan. Retrieved October 22, 2021.
- Davis Mountains cottontail: Diersing, V. E.; Wilson, D. E. (June 17, 2021). "Systematics of the mountain-inhabiting cottontails (Sylvilagus) from southwestern United States and northern Mexico (Mammalia: Lagomorpha: Leporidae)". Proceedings of the Biological Society of Washington. 134 (1): 42–79. doi:10.2988/006-324X-134.1.42. S2CID 236295647.
- Omilteme cottontail: Lorenzo, C.; Brown, D. E.; Lanier, H. C. (2019). "Sylvilagus insonus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2019: e.T21207A45180771. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-2.RLTS.T21207A45180771.en.
- Mountain cottontail: Feldhamer, Carlyle, Chapman, p. 104
- Appalachian cottontail: Kurta, p. 96
- Marsh rabbit: Thompson, Leah (2008). "Sylvilagus palustris". Animal Diversity Web. University of Michigan. Retrieved October 22, 2021.
- Coastal tapeti: Ruedas, L. A.; Marques, S. S.; French, J. H.; Platt II, R. N.; Salazar-Bravo, J.; Mora, J. M.; Thompson, C. W. (February 9, 2017). "A Prolegomenon to the Systematics of South American Cottontail Rabbits (Mammalia, Lagomorpha Leporidae: Sylvilagus)". Miscellaneous Publications of the Museum of Zoology, University of Michigan. 205. ISSN 0076-8405.
- New England cottontail: Berenson, Tessa (2012). "Sylvilagus transitionalis". Animal Diversity Web. University of Michigan. Retrieved October 22, 2021.
- Venezuelan lowland rabbit: Durant, P.; Guevara, M. A. (March 2001). "A new rabbit species (Sylvilagus, Mammalia: Leporidae) from the lowlands of Venezuela". Revista de Biología Tropical. 49 (1).
- ^ a b Sylvilagus habitats and diets:
- Andean tapeti: Ruedas, L. A.; Smith, A. T. (2020) [errata version of 2019 assessment]. "Sylvilagus andinus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2019: e.T142541491A165117323. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-2.RLTS.T142541491A165117323.en.
- Santa Marta tapeti: Ruedas, L. A.; Marques, S. S.; French, J. H.; Platt II, R. N.; Salazar-Bravo, J.; Mora, J. M.; Thompson, C. W. (October 22, 2019). "Taxonomy of the Sylvilagus brasiliensis complex in Central and South America (Lagomorpha: Leporidae)". Journal of Mammalogy. 100 (5): 1599–1630. doi:10.1093/jmammal/gyz126.
- Swamp rabbit: Lanier, H. C.; Nielsen, C. (2019). "Sylvilagus aquaticus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2019: e.T41296A45190578. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-1.RLTS.T41296A45190578.en.; Roszko, Annamarie (2007). "Sylvilagus aquaticus". Animal Diversity Web. University of Michigan. Retrieved October 22, 2021.
- Desert cottontail: Smith, A. T.; Brown, D. E. (2019). "Sylvilagus audubonii". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2019: e.T41297A45190821. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-1.RLTS.T41297A45190821.en.
- Brush rabbit: Kelly, P. A.; Lorenzo, C.; Alvarez-Castaneda, S. T. (2019). "Sylvilagus bachmani". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2019: e.T41302A45192710. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-1.RLTS.T41302A45192710.en.
- Common tapeti: Ruedas, L. A.; Marques, S. S.; French, J. H.; Platt II, R. N.; Salazar-Bravo, J.; Mora, J. M.; Thompson, C. W. (October 22, 2019). "Taxonomy of the Sylvilagus brasiliensis complex in Central and South America (Lagomorpha: Leporidae)". Journal of Mammalogy. 100 (5): 1599–1630. doi:10.1093/jmammal/gyz126.; Ruedas, L.; Smith, A. T. (2019). "Sylvilagus brasiliensis". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2019: e.T87491102A45191186. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-2.RLTS.T87491102A45191186.en.
- Mexican cottontail: Lorenzo, C.; Lanier, H. C. (2019). "Sylvilagus cunicularius". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2019: e.T21211A45181292. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-1.RLTS.T21211A45181292.en.; Smith, Johnston, Alves, Hackländer, p. 132
- Dice's cottontail: Mora, J. M.; Ruedas, L. and Smith; A. T. (2016). "Sylvilagus dicei". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T21209A45180947. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T21209A45180947.en.; Smith, Johnston, Alves, Hackländer, p. 136
- Eastern cottontail: Nielsen, C.; Lanier, H. C. (2019). "Sylvilagus floridanus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2019: e.T41299A45191626. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-1.RLTS.T41299A45191626.en.
- Central American tapeti: Ruedas, L. A.; Marques, S. S.; French, J. H.; Platt II, R. N.; Salazar-Bravo, J.; Mora, J. M.; Thompson, C. W. (October 22, 2019). "Taxonomy of the Sylvilagus brasiliensis complex in Central and South America (Lagomorpha: Leporidae)". Journal of Mammalogy. 100 (5): 1599–1630. doi:10.1093/jmammal/gyz126.; Ruedas, L.; Smith, A. T. (2019). "Sylvilagus gabbi". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2019: e.T87491157A87491160. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-1.RLTS.T87491157A87491160.en.
- Tres Marias cottontail: Lorenzo, C.; Lanier, H. C. (2019). "Sylvilagus graysoni". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2019: e.T21206A45180643. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-3.RLTS.T21206A45180643.en.; Viswanathan, Lata (2000). "Sylvilagus graysoni". Animal Diversity Web. University of Michigan. Retrieved October 22, 2021.
- Davis Mountains cottontail: Ruedas, L. A.; Smith, A. T. (2020) [errata version of 2019 assessment]. "Sylvilagus robustus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2019: e.T41310A165116781. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-3.RLTS.T41310A165116781.en.
- Omilteme cottontail: Lorenzo, C.; Brown, D. E.; Lanier, H. C. (2019). "Sylvilagus insonus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2019: e.T21207A45180771. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-2.RLTS.T21207A45180771.en.
- Mountain cottontail: Smith, A. T.; Brown, D. E. (2019). "Sylvilagus nuttallii". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2019: e.T41300A45192243. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-1.RLTS.T41300A45192243.en.; "Mountain Cottontail — Sylvilagus nuttallii". Montana Field Guide. Montana Department of Fish, Wildlife and Parks. Retrieved November 8, 2021.
- Appalachian cottontail: Barry, R.; Lanier, H. C. (2019). "Sylvilagus obscurus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2019: e.T41301A45192437. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-2.RLTS.T41301A45192437.en.
- Marsh rabbit: McCleery, R.; Lanier, H. C. (2019). "Sylvilagus palustris". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2019: e.T41303A45192995. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-1.RLTS.T41303A45192995.en.; Thompson, Leah (2008). "Sylvilagus palustris". Animal Diversity Web. University of Michigan. Retrieved October 22, 2021.
- Coastal tapeti: Ruedas, L. A.; Marques, S. S.; French, J. H.; Platt II, R. N.; Salazar-Bravo, J.; Mora, J. M.; Thompson, C. W. (February 9, 2017). "A Prolegomenon to the Systematics of South American Cottontail Rabbits (Mammalia, Lagomorpha Leporidae: Sylvilagus)". Miscellaneous Publications of the Museum of Zoology, University of Michigan. 205. ISSN 0076-8405.
- New England cottontail: Litvaitis, J.; Lanier, H. C. (2019). "Sylvilagus transitionalis". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2019: e.T21212A45181534. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-2.RLTS.T21212A45181534.en.; Berenson, Tessa (2012). "Sylvilagus transitionalis". Animal Diversity Web. University of Michigan. Retrieved October 22, 2021.
- Venezuelan lowland rabbit: Johnston, C. H.; Smith, A. T. (2019). "Sylvilagus varynaensis". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2019: e.T41311A45193972. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-1.RLTS.T41311A45193972.en.
- ^ Ochotona sizes:
- Alpine pika: Smith, Johnston, Alves, Hackländer, p. 31
- Helan Shan pika: Smith, Johnston, Alves, Hackländer, p. 33
- Gansu pika: Smith, Johnston, Alves, Hackländer, p. 35
- Collared pika: Smith, Johnston, Alves, Hackländer, p. 36
- Korean pika: Smith, Johnston, Alves, Hackländer, p. 40
- Plateau pika: Smith, Johnston, Alves, Hackländer, p. 40
- Daurian pika: Ciwko, Erin (2014). "Ochotona dauurica". Animal Diversity Web. University of Michigan. Retrieved October 17, 2021.
- Chinese red pika: Smith, Johnston, Alves, Hackländer, p. 46
- Forrest's pika: Smith, Johnston, Alves, Hackländer, p. 47
- Glover's pika: Smith, Johnston, Alves, Hackländer, pp. 48–49
- Hoffmann's pika: Smith, Johnston, Alves, Hackländer, p. 50
- Northern pika: Smith, Johnston, Alves, Hackländer, pp. 51–52
- Ili pika: Smith, Johnston, Alves, Hackländer, p. 54
- Koslov's pika: Smith, Johnston, Alves, Hackländer, p. 56
- Ladak pika: Smith, Johnston, Alves, Hackländer, pp. 57–58
- Large-eared pika: Jordan, Dana (2005). "Ochotona macrotis". Animal Diversity Web. University of Michigan. Retrieved October 17, 2021.
- Manchurian pika: Smith, Johnston, Alves, Hackländer, pp. 60–61
- Nubra pika: Smith, Johnston, Alves, Hackländer, p. 62
- Kazakh pika: Smith, Johnston, Alves, Hackländer, pp. 63–64
- Pallas's pika: Smith, Johnston, Alves, Hackländer, p. 66
- American pika: Smith, Johnston, Alves, Hackländer, pp. 68–70
- Steppe pika: Smith, Johnston, Alves, Hackländer, p. 73
- Royle's pika: Smith, Johnston, Alves, Hackländer, pp. 75–76
- Afghan pika: Smith, Johnston, Alves, Hackländer, p. 77
- Turkestan red pika: Smith, Johnston, Alves, Hackländer, p. 80
- Tsing-ling pika: Smith, Johnston, Alves, Hackländer, p. 82
- Moupin pika: Smith, Johnston, Alves, Hackländer, p. 83
- Thomas's pika: Smith, Johnston, Alves, Hackländer, p. 84
- Turuchan pika: Smith, Johnston, Alves, Hackländer, p. 86
- ^ a b Ochotona habitats and diets:
- Alpine pika: Smith, A. T.; Cook, J. (2016). "Ochotona alpina". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T41255A45182115. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T41255A45182115.en.
- Helan Shan pika: Smith, A. T.; Li, W. (2016). "Ochotona argentata". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T41986A45194521. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T41986A45194521.en.
- Gansu pika: Smith, A. T.; Liu, S. (2016). "Ochotona cansus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T41256A45182335. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T41256A45182335.en.
- Collared pika: Lanier, H. and Hik; D. (2016). "Ochotona collaris". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T41257A45182533. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T41257A45182533.en.
- Korean pika: Smith, A. T.; Jo, Y.-S. (2019) [errata version of 2016 assessment]. "Ochotona coreana". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T87948071A161750319. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T87948071A161750319.en.
- Plateau pika: Smith, A. T. and Liu; S. (2019) [amended version of 2016 assessment]. "Ochotona curzoniae". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2019: e.T41258A160699229. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-3.RLTS.T41258A160699229.en.
- Daurian pika: Smith, A. T.; Cook, J. (2016). "Ochotona dauurica". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T41259A45182905. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T41259A45182905.en.; Ciwko, Erin (2014). "Ochotona dauurica". Animal Diversity Web. University of Michigan. Retrieved October 17, 2021.
- Chinese red pika: Smith, A. T.; Lissovsky, A. (2016). "Ochotona erythrotis". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T41260A45183115. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T41260A45183115.en.
- Forrest's pika: Smith, A. T.; Liu, S. (2016). "Ochotona forresti". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T15048A45178927. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T15048A45178927.en.
- Glover's pika: Smith, A. T.; Liu, S. (2016). "Ochotona gloveri". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T41261A45183256. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T41261A45183256.en.; Smith, Johnston, Alves, Hackländer, pp. 48–49
- Hoffmann's pika: Smith, A. T. and Lissovsky; A. (2016). "Ochotona hoffmanni". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T40800A45181807. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T40800A45181807.en.; Smith, Johnston, Alves, Hackländer, p. 50
- Northern pika: Smith, A. T.; Lissovsky, A. (2016). "Ochotona hyperborea". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T87948061A45183490. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T87948061A45183490.en.; Smith, Johnston, Alves, Hackländer, pp. 51–52
- Ili pika: Li, W.; Smith, A. T. (2019). "Ochotona iliensis". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2019: e.T15050A45179204. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-1.RLTS.T15050A45179204.en.; Smith, Johnston, Alves, Hackländer, p. 54
- Koslov's pika: Li, W.; Smith, A. T. (2019). "Ochotona koslowi". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2019: e.T15046A45178669. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-1.RLTS.T15046A45178669.en.
- Ladak pika: Smith, A. T.; Li, W. (2016). "Ochotona ladacensis". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T41264A45183725. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T41264A45183725.en.; Smith, Johnston, Alves, Hackländer, pp. 57–58
- Large-eared pika: Smith, A. T.; Lissovsky, A. (2016). "Ochotona macrotis". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T41265A45183918. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T41265A45183918.en.; Smith, Johnston, Alves, Hackländer, p. 59
- Manchurian pika: Smith, A. T.; Lissovsky, A. (2016). "Ochotona mantchurica". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T87948094A87948100. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T87948094A87948100.en.; Smith, Johnston, Alves, Hackländer, pp. 60–61
- Nubra pika: Smith, A. T.; Li, W. (2016). "Ochotona nubrica". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T15051A45179343. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T15051A45179343.en.; Smith, Johnston, Alves, Hackländer, p. 62
- Kazakh pika: Smith, A. T.; Lissovsky, A. (2016). "Ochotona opaca". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T99892252A99892261. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T99892252A99892261.en.; Smith, Johnston, Alves, Hackländer, pp. 63–64
- Pallas's pika: Lissovsky, A.; Smith, A. T. (2016). "Ochotona pallasii". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T99890206A45184094. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T99890206A45184094.en.; DeMers, Anna (2007). "Ochotona pallasi". Animal Diversity Web. University of Michigan. Retrieved October 17, 2021.
- American pika: Smith, A. T. and Beever; E. (2016). "Ochotona princeps". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T41267A45184315. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T41267A45184315.en.; Smith, Johnston, Alves, Hackländer, pp. 68–70
- Steppe pika: Smith, A. T.; Lissovsky, A. (2016). "Ochotona pusilla". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T15052A45179445. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T15052A45179445.en.; Smith, Johnston, Alves, Hackländer, p. 73
- Royle's pika: Smith, A. T. and Bhattacharyya; S. (2016). "Ochotona roylei". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T41268A45184591. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T41268A45184591.en.; Smith, Johnston, Alves, Hackländer, pp. 75–76
- Afghan pika: Smith, A. T.; Johnston, C. (2016). "Ochotona rufescens". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T41269A45184750. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T41269A45184750.en.
- Turkestan red pika: Smith, A. T.; Lissovsky, A. (2016). "Ochotona rutila". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T41270A45184897. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T41270A45184897.en.
- Tsing-ling pika: Smith, A. T. and Lissovsky; A. (2016). "Ochotona syrinx". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T87948175A87948187. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T87948175A87948187.en.
- Moupin pika: Smith, A. T.; Liu, S. (2016). "Ochotona thibetana". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T41271A45185018. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T41271A45185018.en.
- Thomas's pika: Smith, A. T.; Liu, S. (2019). "Ochotona thomasi". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2019: e.T15053A45179577. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-1.RLTS.T15053A45179577.en.
- Turuchan pika: Smith, A. T. and Lissovsky; A. (2016). "Ochotona turuchanensis". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T41503A45194115. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T41503A45194115.en.
Fuentes
- Feldhamer, George A.; Thompson, Bruce Carlyle; Chapman, Joseph A. (2003). Mamíferos Salvajes de América del Norte. Johns Hopkins University Press. ISBN 978-0-8018-7416-1.
- Kingdon, Jonathan (2015). The Kingdon Field Guide to African Mammals (Segunda edición). Bloomsbury Publishing. ISBN 978-1-4729-2531-2.
- Kurta, Allen (1995). Mamíferos de la Región de los Grandes Lagos. University of Michigan Press. ISBN 978-0-472-06497-7.
- Smith, Andrew T.; Johnston, Charlotte H.; Alves, Paolo C.; Hackländer, Klaus, eds. (2018). Lagomorphs: Pikas, Conejos y Hares del Mundo. Johns Hopkins University Press. ISBN 978-1-4214-2340-1.
- Smith, Andrew T.; Xie, Yan; Hoffmann, Robert S.; Lunde, Darrin; MacKinnon, John; Wilson, Don E.; Wozencraft, W. Chris, eds. (2010). Guía de los mamíferos de China. Princeton University Press. ISBN 978-1-4008-3411-2.
- Verts, B. J.; Carraway, Leslie N. (1998). Land Mammals of Oregon. University of California Press. ISBN 978-0-520-21199-5.
- Hoffmann, Robert S.; Smith, Andrew T. (2005). Wilson, Don E.; Reeder, DeeAnn M. (eds.). Especies Mamíferas del MundoVol. 1 (3rd ed.). Johns Hopkins University Press. ISBN 978-0-8018-8221-0.
Más resultados...